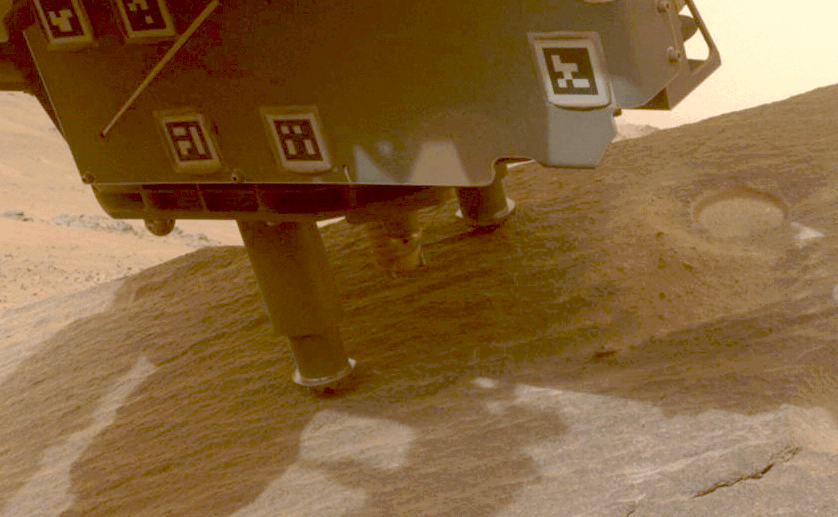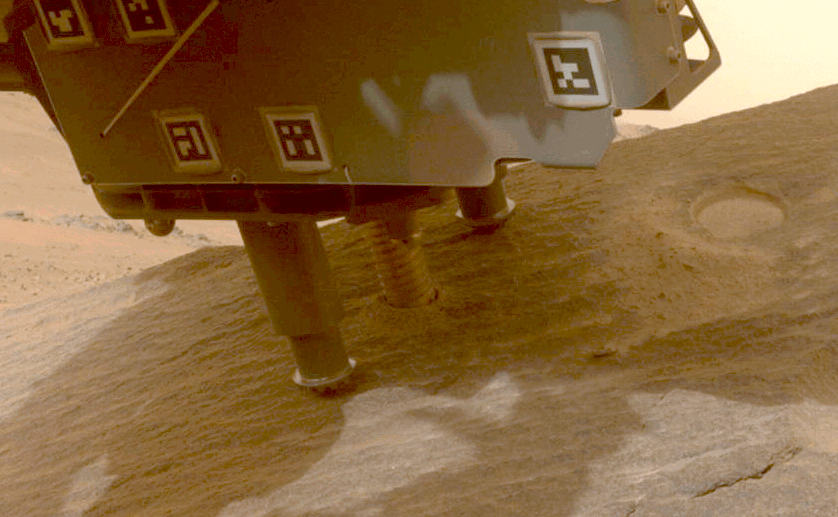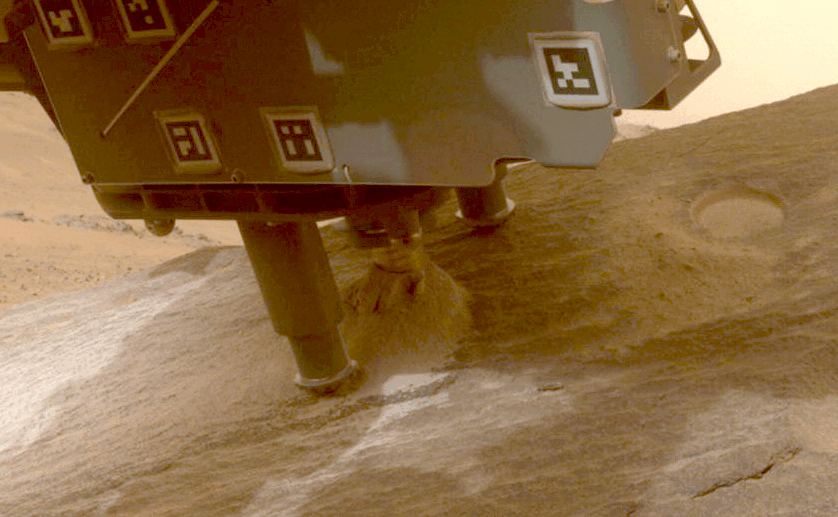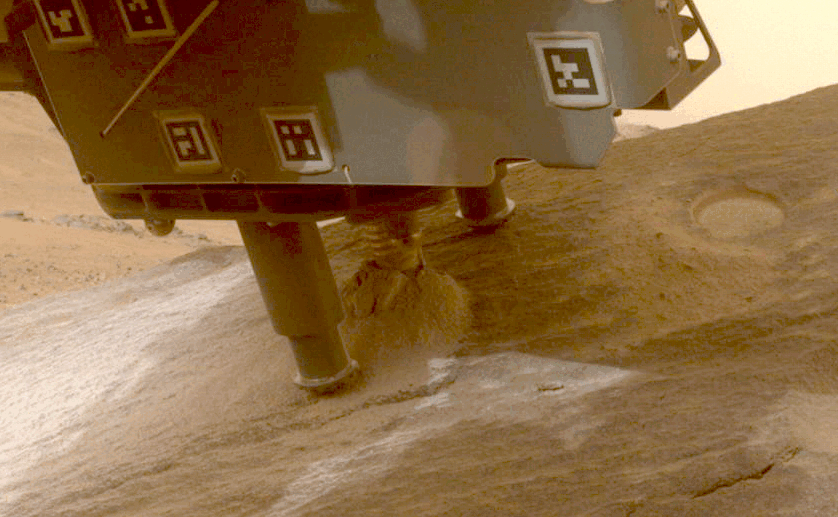
NASA’s Perseverance rover collects a sample from a Martian rock using a drill bit on the end of its robotic arm.Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA announced today that it is abandoning its long-standing plan for ferrying rock and soil samples from Mars to Earth. Instead, the agency will seek proposals for quicker and cheaper ways to deliver the samples to Earth.
An independent review board concluded last year that NASA’s Mars sample return mission could cost as much as US$11 billion, more than the cost of launching the James Webb Space Telescope. In a report released today, a separate NASA review team concluded that even if the agency spent that much money, the samples would not reach Earth until 2040. The agency had originally sought to drop the samples on Earth in the early 2030s.
The $11-billion price tag is “too expensive”, said NASA administrator Bill Nelson at a press briefing, and “not returning the samples until 2040 is unacceptable”. Nelson said the agency “is committed to bringing at least some of the samples back” and later said NASA would return “more than 30” of the 43 planned samples.
Scaling back
NASA’s Perseverance rover has already collected more than 20 rock samples from Jezero Crater, where the rover landed in 2021. Scientists think that the crater was once filled with a lake of water, and samples from the crater and its surroundings could provide a window into the planet’s history and, perhaps, evidence of past life on the red planet.
In the agency’s original vision, a NASA spacecraft would have flown to Mars carrying a two-part retrieval system: a 2.3-tonne lander — which would have been the heaviest vehicle ever to land on Mars — and a rocket to fly the lander and samples into Martian orbit. There, they were to meet a spacecraft launched by the European Space Agency that would fly the samples to Earth.
Now, NASA plans to solicit proposals — from companies as well as NASA centres — for a streamlined system, perhaps using a lighter lander, said Nicky Fox, the associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, at the briefing. The deadline for proposals is 17 May, and the revised mission will be chosen later this year. Fox did not respond directly to reporters’ questions about when the samples will reach Earth under the new scheme.
NASA recommends spending $200 million of its planetary-science budget for 2025 on assessing alternative architectures for Mars sample return, Fox said. Dedicating any more money to the mission threatened to “cannibalize” other planetary science missions, Nelson said.
Back to the drawing board
Vicky Hamilton, a planetary scientist at the Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado, expressed disappointment that almost eight months after the independent review board released its report, the agency still lacks a solid plan for “a very valuable science goal.”
Returning these samples would also demonstrate capability for a two-way trip to Mars before astronauts make the journey, says Bethany Ehlmann, a planetary scientist at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, California. “The sample-return technology is here, it exists,” she says. “It’s a matter of putting the pieces together.”
But scientists were relieved about one announcement: Fox said the revised timeline for sample return will not affect the science goals for Perseverance, including plans for it to explore terrain beyond Jezero Crater.
NASA’s Mars rover makes ‘fantastic’ find in search for past life
Among samples collected outside the crater will be “some of the ancient crust of Mars, representing rocks older than we have seen yet in Jezero Crater, some of which may have been altered by near-surface water”, says Meenakshi Wadhwa, a planetary scientist at Arizona State University in Tempe and principal scientist for the Mars sample return programme.
So far, the only Mars samples that scientists have been able to study on Earth are bits and pieces ejected from the red planet that made it to Earth as meteorites. All known Martian meteorites are igneous rocks, meaning that they solidified from lava, and all are very old. They provide valuable timestamps for parts of Mars’s geological evolution, but carry little information about how the planet’s surface was shaped by the water that once flowed across it.
To achieve the mission’s main goal of searching for signs of past life, the real treasures are layered sedimentary rocks formed by minerals and organic matter deposited over the eons by water. Perseverance’s instruments have already detected organic molecules in Martian samples, but whether those molecules are a marker of past life can be determined only by closer scrutiny in laboratories on Earth.

 Flying Mars rocks to Earth could cost an astronomical $11 billion
Flying Mars rocks to Earth could cost an astronomical $11 billion
 A year on Mars: How NASA’s Perseverance hit a geological jackpot
A year on Mars: How NASA’s Perseverance hit a geological jackpot
 What’s happened to China’s first Mars rover?
What’s happened to China’s first Mars rover?
 Is the Mars rover’s rock collection worth $11 billion?
Is the Mars rover’s rock collection worth $11 billion?