- RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT
Mice eat less and explore more after intake of certain amino acids

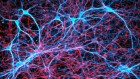
Orexin receptors (red) dot brain neurons. Scientists have now uncovered the effects of non-essential amino acids acting on these neurons. Credit: C.J.Guerin, PhD, MRC Toxicology Unit/Science Photo Library
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 603, 768 (2022)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-00830-z
References
Viskaitis, P. et al. Curr. Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2022.02.067 (2022)