Abstract
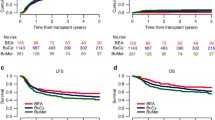
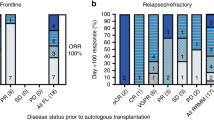
High-dose chemotherapy (HDC) was investigated in high-risk neuroblastoma (HR-NBL) to reduce the risk of relapse. We report the results of the 30-year experience of a cohort of patients with HR-NBL treated with high-dose (HD) busulfan (Bu)-containing regimens. From 1980 to 2009, 215 patients aged >1 year with stage 4 NBL were treated with HD Bu-containing regimens at Gustave Roussy. These data were prospectively recorded in the Pediatric Transplantation Database. The median age at diagnosis was 40 months (12–218 months). All patients had a stage 4 neuroblastoma. NMYC amplification was displayed in 24% of the tumors. The hematopoietic support consisted of bone marrow or PBSCs in 46% and 49% of patients, respectively. The 5-year event-free survival and overall survival rates of the whole cohort were 35.1% and 40%, respectively. Age at diagnosis, bone marrow involvement and tumor response after induction chemotherapy were significant prognostic factors. Toxicity was manageable and decreased over time, owing to both PBSC administration and better supportive care. Based on this experience, HD Bu–melphalan (Mel) has been implemented in Europe and compared with Carboplatin–Etoposide–Mel in the European SIOP Neuroblastoma (SIOPEN)/HR-NBL randomized protocol. It has now become the standard HDC in the SIOPEN HR strategy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matthay KK, Reynolds CP, Seeger RC, Shimada H, Adkins ES, Haas-Kogan D et al. Long-term results for children with high-risk neuroblastoma treated on a randomized trial of myeloablative therapy followed by 13-cis-retinoic acid: a Children's Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 1007–1013; Errata, J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 1862–1863.
Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Seeger RC, Stram DO, Harris RE, Ramsay NK et al. Treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma with intensive chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous bone marrow transplantation and 13-cis-retinoic acid. Children's Cancer Group. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 1165–1173.
Berthold F, Boos J, Burdach S, Erttmann R, Henze G, Hermann J et al. Myeloablative megatherapy with autologous stem-cell rescue versus oral maintenance chemotherapy as consolidation treatment in patients with high-risk neuroblastoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2005; 6: 649–658.
Pritchard J, Cotterill SJ, Germond SM, Imeson J, de Kraker J, Jones DR et al. High dose melphalan in the treatment of advanced neuroblastoma: results of a randomized trial (ENSG-1) by the European Neuroblastoma Study Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2005; 44: 348–357.
Vitale V, Franzone P . The role of TBI in conditioning regimens for children. Bone Marrow Transplant 1991; 7 (Suppl 3): 32–34.
Frei E 3rd, Teicher BA, Holden SA, Cathcart KN, Wang YY. Preclinical studies and clinical correlation of the effect of alkylating dose. Cancer Res 1988; 48: 6417–6423.
Ciurea SO, Andersson BS . Busulfan in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 523–536.
Flandin I, Hartmann O, Michon J, Pinkerton R, Coze C, Stephan JL et al. Impact of TBI on late effects in children treated by megatherapy for Stage IV neuroblastoma. A study of the French Society of Pediatric oncology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006; 64: 1424–1431.
Brodeur GM, Pritchard J, Berthold F, Carlsen NL, Castel V, Castelberry RP et al. Revisions of the international criteria for neuroblastoma diagnosis, staging and response to treatment. J Clin Oncol 1993; 11: 1466–1477.
Frappaz D, Michon J, Hartmann O, Bouffet E, Lejars O, Rubie H et al. Etoposide and carboplatin in neuroblastoma: a French Society of Pediatric Oncology phase II study. J Clin Oncol 1992; 10: 1592–1601.
Coze C, Hartmann O, Michon J, Frappaz D, Dusol F, Rubie H et al. NB87 induction protocol for stage 4 neuroblastoma in children over 1 year of age: a report from the French Society of Pediatric Oncology. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 3433–3440.
Valteau-Couanet D, Michon J, Boneu A, Rodary C, Perel Y, Bergeron C et al. Results of induction chemotherapy in children older than 1 year with a stage 4 neuroblastoma treated with the NB 97 French Society of Pediatric Oncology (SFOP) protocol. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 532–540.
Ladenstein R, Valteau-Couanet D, Brock P, Yaniv I, Castel V, Laureys G et al. Randomized trial of prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor during rapid COJEC induction in pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma: the European HR-NBL1/SIOPEN study. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 3516–3524.
Bostrom B, Enockson K, Johnson A, Bruns A, Blazar B . Plasma pharmacokinetics of high-dose oral busulfan in children and adults undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Transplant 2003; 7: 12–28.
Vassal G, Michel G, Espérou H, Gentet JC, Valteau-Couanet D, Doz F et al. Prospective validation of a novel IV busulfan fixed dosing for paediatric patients to improve therapeutic AUC targeting without drug monitoring. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2008; 61: 113–123.
Veal GJ, Nguyen L, Paci A, Riggi M, Amiel M, Valteau-Couanet D et al. Busulfan pharmacokinetics following intravenous and oral dosing regimens in children receiving high-dose myeloablative chemotherapy for high-risk neuroblastoma as part of the HR-NBL-1/SIOPEN trial. Eur J Cancer 2012; 48: 3063–3072.
Bouligand J, Boland I, Valteau-Couanet D, Deroussent A, Kalifa C, Hartmann O et al. In children and adolescents, the pharmacodynamics of high-dose busulfan is dependent on the second alkylating agent used in the combined regimen (melphalan or thiotepa). Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32: 979–986.
Santos GW, Tutschka PJ, Brookmeyer R, Saral R, Beschorner WE, Bias WB et al. Marrow transplantation for acute nonlymphocytic leukemia after treatment with busulfan and cyclophosphamide. N Engl J Med 1983; 309: 1347–1353.
Beaujean F, Hartmann O, Pico J, Parmentier C, Hayat M, Lemerle J et al. Incubation of autologous bone marrow graft with ASTA Z 7557: comparative studies of hematological reconstitution after purged or nonpurged bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1987; 4: 105–115.
Vassal G, Deroussent A, Hartmann O, Challine D, Benhamou E, Valteau-Couanet D et al. Dose-dependent neurotoxicity of high-dose busulfan in children: a clinical and pharmacological study. Cancer Res 1990; 50: 6203–6207.
Guerrini-Rousseau L, Goma G, Dufour C, Valteau-Couanet D. Varicella-zoster virus infections after high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation in children with malignancies. EBMT Meet Abstr Book 2012; S143(P514).
Buggia I, Zecca M, Alessandrino EP, Locatelli F, Rosti G, Bosi A et al. Itraconazole can increase systemic exposure to busulfan in patients given bone marrow transplantation. GITMO (Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo). Anticancer Res 1996; 16: 2083–2088.
Corbacioglu S, Cesaro S, Faraci M, Valteau-Couanet D, Gruhn B, Rovelli A et al. Defibrotide for prophylaxis of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in paediatric haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation: an open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012; 379: 1301–1309.
Bearman SI, Appelbaum FR, Buckner CD, Petersen FB, Fisher LD, Clift RA et al. Regimen-related toxicity in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol 1988; 6: 1562–1568.
McDonald GB, Hinds MS, Fisher LD, Schoch HG, Wolford JL, Banaji M et al. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver and multiorgan failure after bone marrow transplantation: a cohort study of 355 patients. Ann Intern Med 1993; 118: 255–267.
Ladenstein RL, Poetschger U, Luksch R, Brock P, Castel V, Yaniv I et al. Busulphan-melphalan as a myeloablative therapy (MAT) for high-risk neuroblastoma: results from the HR-NBL1/SIOPEN trial. JCO - ASCO Annu Meet Abstr Part 2 2011; 29 (Suppl 18): 2.
Hartmann O, Valteau-Couanet D, Vassal G, Lapierre V, Brugières L, Delgado R et al. Prognostic factors in metastatic neuroblastoma in patients over 1 year of age treated with high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation: a multivariate analysis in 218 patients treated in a single institution. Bone Marrow Transplant 1999; 23: 789–795.
Breslow N, McCann B . Statistical estimation of prognosis for children with neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 1971; 31: 2098–2103.
Schmidt ML, Lal A, Seeger RC, Maris JM, Shimada H, O'Leary M et al. Favorable prognosis for patients 12 to 18 months of age with stage 4 nonamplified MYCN neuroblastoma: a Children's Cancer Group Study. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 6474–6480.
George R, London WB, Maris JM, Cohn SL, Diller L, Look AT et al. Age as a continuous variable in predicting outcome for neuroblastoma patients with metastatic disease: impact of tumor biologic features. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 2003; 22: 799 (abstr 3213).
London WB, Castleberry RP, Matthay KK, Look AT, Seeger RC, Shimada H et al. Evidence for an age cutoff greater than 365 days for neuroblastoma risk group stratification in the Children's Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 6459–6465.
Monclair T, Brodeur GM, Ambros PF, Brisse HJ, Cecchetto G, Holmes K et al. The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) staging system: an INRG Task Force report. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 298–303.
Ladenstein R, Poetschger U, Luksch R, Brock P, Castel V, Yaniv I et al. Influence of age and stage on outcome in the high risk neuroblastoma HR-NBL1/SIOPEN trial. Advanced Neuroblastoma Meeting (ANR) Abstract Book 2014, p246 (POC046).
Valteau-Couanet D, Le Deley MC, Bergeron C, Ducassou S, Michon J, Rubie H et al. Long-term results of the combination of the N7 induction chemotherapy and the busulfan-melphalan high-dose chemotherapy. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2014; 61: 977–981.
Yanik G, Naranjo A, Parisi MT, Shulkin BL, Nadel H, Gelfand MJ et al. Impact of post-induction Curie scores as prognostic marker in high risk neuroblastoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015; 21: S107.
Decarolis B, Schneider C, Hero B, Simon T, Volland R, Roels F et al. Iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy scoring allows prediction of outcome in patients with stage 4 neuroblastoma: results of the Cologne interscore comparison study. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 944–951.
Garaventa A, Luksch R, Biasotti S, Severi G, Pizzitola MR, Viscardi E et al. A phase II study of topotecan with vincristine and doxorubicin in children with recurrent/refractory neuroblastoma. Cancer 2003; 98: 2488–2494.
Hartmann O, Le Corroller AG, Blaise D, Michon J, Philip I, Norol F et al. Peripheral blood stem cell and bone marrow transplantation for solid tumors and lymphomas: hematologic recovery and costs. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 1997; 126: 600–607.
Haut PR, Cohn S, Morgan E, Hubbell M, Danner-Koptik K, Olszewski M et al. Efficacy of autologous peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) harvest and engraftment after ablative chemotherapy in pediatric patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 1998; 4: 38–42.
Valteau-Couanet D, Faucher C, Auperin A, Michon J, Milpied N, Boiron JM et al. Cost effectiveness of day 5 G-CSF (Lenograstim) administration after PBSC transplantation: results of a SFGM-TC randomised trial. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 547–552.
Valteau-Couanet D, Benhamou E, Vassal G, Stambouli F, Lapierre V, Couanet D et al. Consolidation with a busulfan-containing regimen followed by stem cell transplantation in infants with poor prognosis stage 4 neuroblastoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 937–942.
Brugieres L, Hartmann O, Benhamou E, Zafrani ES, Caillaud JM, Patte C et al. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver following high-dose chemotherapy and autologous bone marrow transplantation in children with solid tumors: incidence, clinical course and outcome. Bone Marrow Transplant 1988; 3: 53–58.
Acknowledgements
We thank Lorna Saint Ange for editing and Imène Hezam for the secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Bone Marrow Transplantation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Proust-Houdemont, S., Pasqualini, C., Blanchard, P. et al. Busulfan–melphalan in high-risk neuroblastoma: the 30-year experience of a single institution. Bone Marrow Transplant 51, 1076–1081 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.75
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.75