Abstract
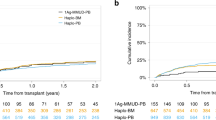
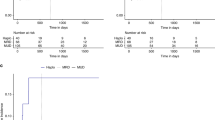
Post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PT-Cy) is the backbone of GvHD prophylaxis following haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation (haplo-HCT). PT-Cy has also been used in matched related (MRD) and unrelated (MUD) settings. It is not known whether outcomes are similar between haplo-HCT and MRD/MUD HCT when PT-Cy is used. We performed a retrospective analysis of 83 patients with AML who underwent HCT (using PT-Cy-based GvHD prophylaxis) from MRD, MUD or haploidentical donors. The groups were similar in baseline characteristics with the exception of older age in the MRD/MUD group (P=0.012). In multivariate analysis, the effect of donor type (MRD/MUD vs haploidentical) on transplant outcomes was not significant in any of the models except for faster neutrophil recovery after MRD/MUD transplants (hazard ratio: 2.21; 95% confidence interval: 1.31–3.72, P=0.002). In conclusion, we showed similar outcomes in MRD/MUD vs haploidentical HCT (except slower count recovery following haplo-HCT) when PT-Cy is used for GvHD prophylaxis. Although slower count recovery following haplo-HCT (compared with MRD/MUD transplants without PT-Cy) has been attributed to using PT-Cy, our results suggest that HLA disparity is the primary cause of this difference. Furthermore, our analysis supports PT-Cy as a viable option for GvHD prophylaxis after MRD/MUD transplants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luznik L, Jalla S, Engstrom LW, Iannone R, Fuchs EJ . Durable engraftment of major histocompatibility complex-incompatible cells after nonmyeloablative conditioning with fludarabine, low-dose total body irradiation, and posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Blood 2001; 98: 3456–3464.
O'Donnell PV, Luznik L, Jones RJ, Vogelsang GB, Leffell MS, Phelps M et al. Nonmyeloablative bone marrow transplantation from partially HLA-mismatched related donors using posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2002; 8: 377–386.
Luznik L, Bolaños-Meade J, Zahurak M, Chen AR, Smith BD, Brodsky R et al. High-dose cyclophosphamide as single-agent, short-course prophylaxis of graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2010; 115: 3224–3230.
Kanakry CG, O'Donnell PV, Furlong T, de Lima MJ, Wei W, Medeot M et al. Multi-institutional study of post-transplantation cyclophosphamide as single-agent graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation using myeloablative busulfan and fludarabine conditioning. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 3497–3505.
Rashidi A, DiPersio JF, Westervelt P, Vij R, Schroeder MA, Cashen AF et al. Comparison of outcomes after peripheral blood haploidentical versus matched unrelated donor allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloidleukemia: a retrospective single-center review. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2016; e-pub ahead of print 17 May 2016; doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2016.05.010.
Bashey A, Zhang X, Jackson K, Brown S, Ridgeway M, Solh M et al. Comparison of outcomes of hematopoietic cell transplants from T replete haploidentical donors using post-transplantation cyclophosphamide with 10 of 10 HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1, and -DQB1 allele-matched unrelated donors and HLA-identical sibling donors: a multivariable analysis including disease risk index. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2016; 22: 125–133.
Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, Walker H, Chatters S, Goldstone AH et al. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood 2010; 116: 354–365.
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1628–1633.
Martinelli G, Trabetti E, Farabegoli P, Testoni N, Bandini G, Motta MR et al. Early detection of bone marrow engraftment by amplification of hypervariable DNA regions. Haematologica 1997; 82: 156–160.
Rowlings PA, Przepiorka D, Klein JP, Gale RP, Passweg JR, Henslee-Downey PJ et al. IBMTR Severity Index for grading acute graft-versus-host disease: retrospective comparison with Glucksberg grade. Br J Haematol 1997; 97: 855–864.
Jagasia MH, Greinix HT, Arora M, Williams KM, Wolff D, Cowen EW et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: I. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015; 21: 389–401.
Fine JP, Gray RJ . A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 1999; 94: 496–509.
Ghosh N, Karmali R, Rocha V, Ahn KW, DiGilio A, Hari PN et al. Reduced-intensity transplantation for lymphomas using haploidentical related donors versus HLA-matched sibling donors: a Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research Analysis. J Clin Oncol 2016; epub ahead of print 6 June 2016; doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.66.3476.
Ciurea SO, Zhang MJ, Bacigalupo AA, Bashey A, Appelbaum FR, Aljitawi OS et al. Haploidentical transplant with posttransplant cyclophosphamide vs matched unrelated donor transplant for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2015; 126: 1033–1040.
Bashey A, Zhang X, Sizemore CA, Manion K, Brown S, Holland HK et al. T-cell-replete HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic transplantation for hematologic malignancies using post-transplantation cyclophosphamide results in outcomes equivalent to those of contemporaneous HLA-matched related and unrelated donor transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 1310–1316.
Di Stasi A, Milton DR, Poon LM, Hamdi A, Rondon G, Chen J et al. Similar transplantation outcomes for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome patients with haploidentical versus 10/10 human leukocyte antigen-matched unrelated and related donors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 1975–1981.
Ringdén O, Labopin M, Ciceri F, Velardi A, Bacigalupo A, Arcese W et al. Is there a stronger graft-versus-leukemia effect using HLA-haploidentical donors compared with HLA-identical siblings? Leukemia 2016; 30: 447–455.
Kongtim P, Cao K, Ciurea SO . Donor specific anti-HLA antibody and risk of graft failure in haploidentical stem cell transplantation. Adv Hematol 2016; 2016: 4025073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashidi, A., Slade, M., DiPersio, J. et al. Post-transplant high-dose cyclophosphamide after HLA-matched vs haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation for AML. Bone Marrow Transplant 51, 1561–1564 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.217
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.217
This article is cited by
-
Comparable outcomes among unmanipulated haploidentical, matched unrelated, and matched sibling donors in BU-based myeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for intermediate and adverse risk acute myeloid leukemia in complete remission: a single-center study
Annals of Hematology (2021)
-
Comparison of the outcomes after haploidentical and cord blood salvage transplantations for graft failure following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation for severe acquired aplastic anemia: a case-control study of post-transplant cyclophosphamide included regimen vs. anti-thymocyte globulin & colony-stimulating factor-based regimen
Science China Life Sciences (2020)
-
Impacts of post-transplantation cyclophosphamide treatment after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Comparable survival using a CMV-matched or a mismatched donor for CMV+ patients undergoing T-replete haplo-HSCT with PT-Cy for acute leukemia: a study of behalf of the infectious diseases and acute leukemia working parties of the EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2018)