Abstract
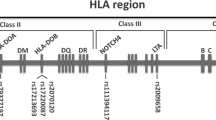
Despite HLA allele matching, significant acute GvHD remains a major barrier to successful unrelated donor BMT. We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) to identify recipient and donor genes associated with the risk of acute GvHD. A case–control design (grade III–IV versus no acute GvHD) and pooled GWA approach was used to study European-American recipients with hematological malignancies who received myeloablative conditioning non-T-cell-depleted first transplantation from HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1, -DQB1 allele level (10/10) matched unrelated donors. DNA samples were divided into three pools and tested in triplicate using the Affymetrix Genome-wide SNP Array 6.0. We identified three novel susceptibility loci in the HLA-DP region of recipient genomes that were associated with III–IV acute GvHD (rs9277378, P=1.58E−09; rs9277542, P=1.548E−06 and rs9277341, P=7.718E−05). Of these three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), rs9277378 and rs9277542 are located in non-coding regions of the HLA-DPB1 gene and the two are in strong linkage disequilibrium with two other published SNPs associated with acute GvHD, rs2281389 and rs9277535. Eighteen other recipient SNPs and 3 donor SNPs with a high level of significance (8E−07 or lower) were found. Our report contributes to emerging data showing clinical significance of the HLA-DP region genetic markers beyond structural matching of DPB1 alleles.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee SJ, Klein J, Haagenson M, Baxter-Lowe LA, Confer DL, Eapen M et al. High-resolution donor-recipient HLA matching contributes to the success of unrelated donor marrow transplantation. Blood 2007; 110: 4576–4583.
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Urbani E, Perruccio K, Shlomchik WD, Tosti A et al. Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoietic transplants. Science 2002; 295: 2097–2100.
Wallny HJ, Rammensee HG . Identification of classical minor histocompatibility antigen as cell-derived peptide. Nature 1990; 343: 275–278.
Holler E, Kolb HJ, Mittermuller J, Kaul M, Ledderose G, Duell T et al. Modulation of acute graft-versus-host-disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) release in the course of pretransplant conditioning: role of conditioning regimens and prophylactic application of a monoclonal antibody neutralizing human TNF alpha (MAK 195 F). Blood 1995; 86: 890–899.
Goyal RK, Lin Y, Schultz KR, Ferrell RE, Kim Y, Fairfull L et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphisms are associated with severity of acute graft-versus-host disease following matched unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation in children: a Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Consortium study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 927–936 e1.
Mullally A, Ritz J . Beyond HLA: the significance of genomic variation for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2007; 109: 1355–1362.
Mullighan CG, Petersdorf EW . Genomic polymorphism and allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 19–27.
International HapMap C, Altshuler DM, Gibbs RA, Peltonen L, Altshuler DM, Gibbs RA et al. Integrating common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature 2010; 467: 52–58.
Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, Duerr RH, McGovern DP, Hui KY et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2012; 491: 119–124.
Kamatani Y, Wattanapokayakit S, Ochi H, Kawaguchi T, Takahashi A, Hosono N et al. A genome-wide association study identifies variants in the HLA-DP locus associated with chronic hepatitis B in Asians. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 591–595.
Pereyra F, Jia X, McLaren PJ, Telenti A, de Bakker PI, Walker BD et al. The major genetic determinants of HIV-1 control affect HLA class I peptide presentation. Science 2010; 330: 1551–1557.
Thomas R, Thio CL, Apps R, Qi Y, Gao X, Marti D et al. A novel variant marking HLA-DP expression levels predicts recovery from hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol 2012; 86: 6979–6985.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GvHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Spencer CC, Su Z, Donnelly P, Marchini J . Designing genome-wide association studies: sample size, power, imputation, and the choice of genotyping chip. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000477.
Rye HS, Dabora JM, Quesada MA, Mathies RA, Glazer AN . Fluorometric assay using dimeric dyes for double- and single-stranded DNA and RNA with picogram sensitivity. Anal Biochem 1993; 208: 144–150.
Pearson JV, Huentelman MJ, Halperin RF, Tembe WD, Melquist S, Homer N et al. Identification of the genetic basis for complex disorders by use of pooling-based genomewide single-nucleotide-polymorphism association studies. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 80: 126–139.
Dunckley T, Huentelman MJ, Craig DW, Pearson JV, Szelinger S, Joshipura K et al. Whole-genome analysis of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 775–788.
Macgregor S, Zhao ZZ, Henders A, Nicholas MG, Montgomery GW, Visscher PM . Highly cost-efficient genome-wide association studies using DNA pools and dense SNP arrays. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: e35.
Achkar JP, Klei L, de Bakker PI, Bellone G, Rebert N, Scott R et al. Amino acid position 11 of HLA-DRbeta1 is a major determinant of chromosome 6p association with ulcerative colitis. Genes Immun 2012; 13: 245–252.
Nishida N, Sawai H, Matsuura K, Sugiyama M, Ahn SH, Park JY et al. Genome-wide association study confirming association of HLA-DP with protection against chronic hepatitis B and viral clearance in Japanese and Korean. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e39175.
Seto WK, Wong DK, Kopaniszen M, Proitsi P, Sham PC, Hung IF et al. HLA-DP and IL28B polymorphisms: influence of host genome on hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B. Clin Infect Dis 2013; 56: 1695–1703.
Wong DK, Watanabe T, Tanaka Y, Seto WK, Lee CK, Fung J et al. Role of HLA-DP polymorphisms on chronicity and disease activity of hepatitis B infection in Southern Chinese. PLoS One 2013; 8: e66920.
Xu Z, Taylor JA . SNPinfo: integrating GWAS and candidate gene information into functional SNP selection for genetic association studies. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: W600–W605.
O'Brien TR, Kohaar I, Pfeiffer RM, Maeder D, Yeager M, Schadt EE et al. Risk alleles for chronic hepatitis B are associated with decreased mRNA expression of HLA-DPA1 and HLA-DPB1 in normal human liver. Genes Immun 2011; 12: 428–433.
Petersdorf EW, Malkki M, O'HUigin C, Carrington M, Gooley T, Haagenson MD et al. High HLA-DP expression and graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med 2015; 373: 599–609.
Petersdorf EW, Malkki M, Gooley TA, Spellman SR, Haagenson MD, Horowitz MM et al. MHC-resident variation affects risks after unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation. Sci Transl Med 2012; 4: 144ra101.
Fleischhauer K, Shaw BE, Gooley T, Malkki M, Bardy P, Bignon JD et al. Effect of T-cell-epitope matching at HLA-DPB1 in recipients of unrelated-donor haemopoietic-cell transplantation: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol 2012; 13: 366–374.
Johnson AD, Handsaker RE, Pulit SL, Nizzari MM, O'Donnell CJ, de Bakker PI . SNAP: A web-based tool for identification and annotation of proxy SNPs using HapMap. Bioinformatics 2008; 24: 2938.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dan Scheller for research repository management, Deborah Hollingshead for coordinating the GWAS experiments, and Dr A Kim Ritchey for his support and guidance for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Bone Marrow Transplantation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, R., Lee, S., Wang, T. et al. Novel HLA-DP region susceptibility loci associated with severe acute GvHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 52, 95–100 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.210
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.210