Abstract
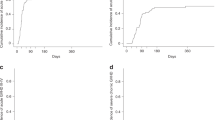
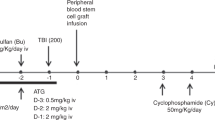
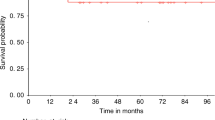
Ninety-seven patients affected by high-risk hematological malignancies underwent G-CSF primed, unmanipulated bone marrow (BM) transplantation from a related, haploidentical donor. All patients were prepared with an identical conditioning regimen including Thiotepa, Busilvex, Fludarabine (TBF) and antithymocyte globulin given at myeloablative (MAC=68) or reduced (reduced intensity conditioning (RIC)=29) dose intensity and received the same GvHD prophylaxis consisting of the combination of methotrexate, cyclosporine, mycofenolate-mofetil and basiliximab. Patients were transplanted in 1st or 2nd CR (early phase: n=60) or in >2nd CR or active disease (advanced phase: n=37). With a median time of 21 days (range 12–38 days), the cumulative incidence (CI) of neutrophil engraftment was 94±3%. The 100-day CI of III–IV grade acute GvHD and the 2-year CI of extensive chronic GvHD were 9±3% and 12±4%, respectively. Overall, at a median follow-up of 2.2 years (range 0.3–5.6), 44 out of 97 (45%) patients are alive in CR. The 5-year probability of overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) for patients in early and advanced phase was 53±7 vs 24±8% (P=0.006) and 48±7 vs 22±8% (P=0.01), respectively. By comparing MAC with RIC patient groups, the transplant-related mortality was equivalent (36±6 vs 28±9%) while the relapse risk was lower for the MAC patients (22±6 vs 45±11%), who showed higher OS (48±7 vs 29±10%) and DFS (43±7 vs 26±10%). However, all these differences did not reach a statistical significance. In multivariate analysis, diagnosis and recipient age were significant factors for OS and DFS. In conclusion, this analysis confirms, on a longer follow-up and higher number of patients, our previous encouraging results obtained by using MAC and RIC TBF regimen as conditioning for G-CSF primed, unmanipulated BM transplantation from related, haploidentical donor in patients with high-risk hematological malignancies, lacking an HLA-identical sibling or unrelated donor and in need to be urgently transplanted.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T-cell depletion for the treatment of hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 38: 291–297.
Xu LP, Liu KY, Liu DH, Han W, Chen H, Chen YH et al. A novel protocol for haploidentical hematopoietic SCT without in vitro T-cell depletion in the treatment of severe acquired aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 1507–1512.
Chang YJ, Huang XJ . Haploidentical bone marrow transplantation without T-cell depletion. Semin Oncol 2012; 39: 653–663.
Solomon SR, Sizemore CA, Sanacore M, Zhang X, Brown S, Holland HK et al. Haploidentical transplantation using T cell replete peripheral blood stem cells and myeloablative conditioning in patients with high-risk hematologic malignancies who lack conventional donors is well tolerated and produces excellent relapse-free survival: results of a prospective phase II trial. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 1859–1866.
Bashey A, Zhang X, Sizemore CA, Manion K, Brown S, Holland HK et al. T-cell-replete HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic transplantation for hematologic malignancies using post-transplantation cyclophosphamide results in outcomes equivalent to those of contemporaneous HLA-matched related and unrelated donor transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 1310–1316.
Di Bartolomeo P, Santarone S, De Angelis G, Picardi A, Cudillo L, Cerretti R et al. Haploidentical, unmanipulated, G-CSF-primed bone marrow transplantation for patients with high-risk hematologic malignancies. Blood 2013; 12: 849–857.
Raiola AM, Dominietto A, Ghiso A, Di Grazia C, Lamparelli T, Gualandi F et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical bone marrow transplantation and posttransplantation cyclophosphamide for hematologic malignancies after myeloablative conditioning. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 117–122.
Laughlin MJ, Eapen M, Rubinstein P, Wagner JE, Zhang MJ, Champlin RE et al. Outcome after transplantation of cord blood or bone marrow from unrelated donors in adults with acute leukaemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 2265–2275.
Rocha V, Labopin M, Sanz G, Arcese W, Schwerdtfeger R, Bosi A et al. Transplants of umbilical cord blood orbone marrow from unrelated donors in adults with acute leukaemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 2276–2285.
Gupta V, Tallman MS, Weisdorf DJ . Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adults with acute Myeloid leukaemia: myths, controversies and unknowns. Blood 2011; 117: 2307–2318.
Weisdorf D . Which donor or graft source should you choose for the strongest GVL? Is there really any difference. Best Practice and Research. Clin Haematol 2013; 26: 293–296.
Ballen KK, Spitzer TR . The great debate: haploidentical or cord blood transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 323–329.
Ballen KK, Koreth J, Chen YB, Dey BR, Spitzer TR . Selection of optimal alternative graft source: mismatched unrelated donor, umbilical cord blood, or haploidentical transplant. Blood 2012; 113: 1972–1980.
Brunstein CG, Fuchs EJ, Carter SL, Karanes C, Costa LJ, Wu J et al. Alternative donor transplantation after reduced intensity conditioning: results of parallel phase 2 trials using partially HLA-mismatched related bone marrow or unrelated double umbilical cord blood grafts. Blood 2011; 118: 282–288.
Aversa F, Tabilio A, Velardi A, Cunningham I, Terenzi A, Falzetti F et al. Treatment of high-risk acute leukemia with T-cell-depleted stem cells from related donors with one fully mismatched HLA haplotype. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: 1186–1193.
Aversa F, Terenzi A, Tabilio A, Falzetti F, Carotti A, Ballanti S et al. Full haplotype-mismatched hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: a phase II study in patients with acute leukemia at high risk of relapse. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 3447–3454.
Lu DP, Dong L, Wu T, Huang XJ, Zhang MJ, Han W et al. Conditioning including antithymocyte globulin followed by unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation can achieve comparable outcomes with HLA-identical sibling transplantation. Blood 2006; 107: 3065–3073.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W et al. Treatment of acute leukemia with unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 257–265.
Luznik L, O’Donnell PV, Symons HJ, Chen AR, Leffell MS, Zahurak M et al. HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies using nonmyeloablative conditioning and high-dose, post-transplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 641–650.
Ciurea SO, Mulanovich V, Saliba RM, Bayraktar UD, Jiang Y, Bassett R et al. Improved early outcomes using a T cell replete graft compared with T cell depleted haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 1835–1844.
Martelli MF, Di Ianni M, Ruggeri L, Pierini A, Falzetti F, Carotti A et al. ‘Designed’ grafts for HLA-haploidentical stem cell transplantation. Blood 2014; 123: 967–973.
Chen BJ, Cui X, Liu C, Chao NJ . Prevention of graft-versus-host disease while preserving graft-versus-leukemia effect after selective depletion of host-reactive T cells by photodynamic cell purging process. Blood 2002; 99: 3083–3088.
Federmann B, Bornhauser M, Meisner C, Kordelas L, Beelen DW, Stuhler G et al. Haploidentical allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in adults using CD3/CD19 depletion and reduced intensity conditioning: a phase II study. Haematologica 2012; 97: 1523–1531.
Schuster FR, Meisel R, Führer M, Reuther S, Hauer J, Tischer J et al. Anti-leukaemic activity of a novel haploidentical-transplantation approach employing unmanipulated bone marrow followed by CD6-depleted peripheral blood stem cells in children with refractory/relapsed acute leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2013; 162: 802–807.
Daniele N, Scerpa MC, Caniglia M, Bernardo ME, Rossi C, Ciammetti C et al. Transplantation in the onco-hematology field: focus on the manipulation of αβ and γδ T cells. Pathol Res Pract 2012; 208: 67–73.
Lu SY, Liu KY, Liu DH, Xu LP, Huang XJ . High frequencies of CD62L+ naive regulatory T cells in allografts are associated with a low risk of acute graft-versus-host disease following unmanipulated allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Exp Immunol 2011; 165: 264–277.
Bertaina A, Merli P, Rutella S, Pagliara D, Bernardo ME, Masetti R et al. HLA-haploidentical stem cell transplantation after removal of αβ+ T and B-cells in children with non-malignant disorders. Blood 2014; 124: 822–826.
Ji SQ, Chen HR, Yan HM, Wang HX, Liu J, Zhu PY et al. Anti-CD25 monoclonal antibody (basiliximab) for prevention of graft-versus-host disease after haploidentical bone marrow transplantation for hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 349–354.
Luznik L, O’Donnell PV, Fuchs EJ . Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide for tolerance induction in HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation. Semin Oncol 2012; 39: 683–693.
Sanz J, Boluda JC, Martín C, González M, Ferrá C, Serrano D et al. Single-unit umbilical cord blood transplantation from unrelated donors in patients with hematological malignancy using busulfan, thiotepa, fludarabine and ATG as myeloablative conditioning regimen. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 1287–1293.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974; 18: 295–304.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Shulman HM, Kleiner D, Lee SJ, Morton T, Pavletic SZ, Farmer E et al. Histopathologic diagnosis of chronic graft-versus-host disease: National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: II. Pathology Working Group Report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 31–47.
Gooley TA, Leisenring W, Crowley J, Storer BE . Estimation of failure probabilities in the presence of competing risks: new representations of old estimators. Stat Med 1999; 18: 695–706.
Gray RJ . A class of K-sample tests for comparing the cumulative incidence of a competing risk. Ann Stat 1988; 16: 1141–1154.
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1999; 53: 457–481.
Mantel N . Evaluation of survival data and two new rank order statistics arising in its consideration. Cancer Chemother Rep 1966; 50: 163–170.
Cox DR . Regression models and life-tables. J R Stat Soc Ser B 1972; 34: 187–220.
Maffongelli G, Tatarelli P, De Angelis G, Cerretti R, Picardi A, Cudillo L et al. A matched-pair analysis of infections and related mortality in haploidentical vs HLA identical transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2014; 49: S84.
Vago L, Perna SK, Zanussi M, Mazzi B, Barlassina C, Stanghellini MT et al. Loss of mismatched HLA in leukemia after stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 478–488.
Vago L, Toffalori C, Ciceri F, Fleischhauer K . Genomic loss of mismatched human leukocyte antigen and leukemia immune escape from haploidentical graft-versus-leukemia. Semin Oncol 2012; 39: 707–715.
Zeidan AM, Forde PM, Symons H, Chen A, Smith BD, Pratz K et al. HLA-haploidentical donor lymphocyte infusions for patients with relapsed hematologic malignancies after related HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 314–318.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Agenzia Regionale del Lazio per i Trapianti e le Patologie Connesse and from the “Matteo Fabrizio” Onlus-Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article was published as part of a supplement, supported by WIS-CSP Foundation, in collaboration with Gilead, Milteny Biotec, Gamida cell, Adienne Pharma and Biotech, Medac hematology, Kiadis Pharma and Almog Diagnostic.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arcese, W., Picardi, A., Santarone, S. et al. Haploidentical, G-CSF-primed, unmanipulated bone marrow transplantation for patients with high-risk hematological malignancies: an update. Bone Marrow Transplant 50 (Suppl 2), S24–S30 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.91
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.91
This article is cited by
-
Myeloablative conditioning with thiotepa-busulfan-fludarabine does not improve the outcome of patients transplanted with active leukemia: final results of the GITMO prospective trial GANDALF-01
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
Contemporary haploidentical stem cell transplant strategies in children with hematological malignancies
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Thiotepa and antithymocyte globulin-based conditioning prior to haploidentical transplantation with posttransplant cyclophosphamide in high-risk hematological malignancies
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Idarubicin-intensified haploidentical HSCT with GvHD prophylaxis of ATG and basiliximab provides comparable results to sibling donors in high-risk acute leukemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)
-
Impact of conditioning intensity in T-replete haplo-identical stem cell transplantation for acute leukemia: a report from the acute leukemia working party of the EBMT
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016)