Abstract
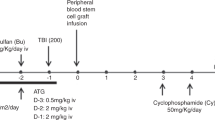
Although pretransplant alemtuzumab can reduce GVHD following allogeneic transplantation, it may also increase the risk of mixed donor T-cell chimerism and infections. We hypothesized that the early use of DLI without withdrawal of immunosuppressive drugs in patients with mixed T-cell chimerism would lower the risk of relapse without significantly increasing the risk of GVHD post DLI. Thirty-six patients (median age 59 years) were treated in this phase II trial using reduced-intensity conditioning including s.c. alemtuzumab (total dose 43 mg) and a PBSC graft from a matched unrelated donor (UD). DLI without withdrawal of immunosuppressive drugs was administered to all 25 patients with <50% donor T-cell chimerism on day +60. The cumulative risks of acute and chronic GVHD were 42% and 59%, respectively. Estimated probabilities of non-relapse mortality (NRM) at day 100 and 1 year were 3% and 14%, respectively. With a median follow up 2.4 years, estimated survivals at day 100, 1 and 2 years were 97%, 71% and 57%, respectively. In multivariate analysis, the occurrence of acute GVHD was associated with an increased risk of mortality, whereas the occurrence of chronic GVHD had a protective effect, associated with decreased relapse and improved disease-free survival. Low-dose alemtuzumab and preemptive DLI provides favorable transplant outcomes including low NRM in an older patient population with high-risk malignancies undergoing UD transplantation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weisdorf DJ, Nelson G, Lee SJ, Haagenson M, Spellman S, Antin JH et al. Sibling versus unrelated donor allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia: refined HLA matching reveals more graft-versus-host disease but not less relapse. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1475–1478.
Jagasia M, Arora M, Flowers ME, Chao NJ, McCarthy PL, Cutler CS et al. Risk factors for acute GVHD and survival after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 2012; 119: 296–307.
Chakraverty R, Peggs K, Chopra R, Milligan DW, Kottaridis PD, Verfuerth S et al. Limiting transplantation-related mortality following unrelated donor stem cell transplantation by using a nonmyeloablative conditioning regimen. Blood 2002; 99: 1071–1078.
Branson K, Chopra R, Kottaridis PD, McQuaker G, Parker A, Schey S et al. Role of nonmyeloablative allogeneic stem-cell transplantation after failure of autologous transplantation in patients with lymphoproliferative malignancies. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 4022–4403.
Morris E, Thomson K, Craddock C, Mahendra P, Milligan D, Cook G et al. Outcomes after alemtuzumab-containing reduced-intensity allogeneic transplantation regimen for relapsed and refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2004; 104: 3865–3871.
Peggs KS, Hunter A, Chopra R, Parker A, Mahendra P, Milligan D et al. Clinical evidence of a graft-versus-Hodgkin's-lymphoma effect after reduced-intensity allogeneic transplantation. Lancet 2005; 365: 1934–1941.
Tauro S, Craddock C, Peggs K, Begum G, Mahendra P, Cook G et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation using a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen has the capacity to produce durable remissions and long-term disease-free survival in patients with high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplasia. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 9387–9393.
Schnitzer TJ, Yocum DE, Michalska M, Balius R, Snider ME, Hays A et al. Subcutaneous administration of CAMPATH-1H: clinical and biological outcomes. J Rheumatol 1997; 24: 1031–1036.
Lundin J, Kimby E, Bjorkholm M, Broliden P-A, Celsing F, Hjalmar V et al. Phase II trial of subcutaneous anti-CD52 monoclonal antibody alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) as first-line treatment for patients with B- cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Blood 2002; 100: 768–773.
van Besien K, Dew A, Lin S, Joseph L, Godley LA, Larson RA et al. Patterns and kinetics of T-cell chimerism after allo transplant with alemtuzumab-based conditioning: mixed chimerism protects from GVHD, but does not portend disease recurrence. Leuk Lymphoma 2009; 50: 1809–1817.
Shaw BE, Byrne JL, Das-Gupta E, Carter GI, Russell NH . The impact of chimerism patterns and predonor leukocyte infusion lymphopenia on survival following T cell-depleted reduced intensity conditioned transplants. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 550–559.
Mackinnon S, Barnett L, Heller G, O'Reilly RJ . Minimal residual disease is more common in patients who have mixed T-cell chimerism after bone marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 1994; 83: 3409–3416.
Mohty M, Avinens O, Faucher C, Viens P, Blaise D, Eliaou JF . Predictive factors and impact of full donor T-cell chimerism after reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2007; 92: 1004–1006.
Thomson KJ, Morris EC, Milligan D, Parker AN, Hunter AE, Cook G et al. T-cell-depleted reduced-intensity transplantation followed by donor leukocyte infusions to promote graft-versus-lymphoma activity results in excellent long-term survival in patients with multiply relapsed follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 3695–3700.
Mohamedbhai SG, Edwards N, Morris EC, Mackinnon S, Thomson KJ, Peggs KS . Predominant or complete recipient T-cell chimerism following alemtuzumab-based allogeneic transplantation is reversed by donor lymphocytes and not associated with graft failure. Br J Haematol 2012; 156: 516–522.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 945–956.
Kaplan E, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 84: 360–372.
Klein JP, Rizzo JD, Zhang MJ, Keiding N . Statistical methods for the analysis and presentation of the results of bone marrow transplants. Part 1: unadjusted analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 909–915.
Pérez-Simón JA, Kottaridis PD, Martino R, Craddock C, Caballero D, Chopra R et al. Nonmyeloablative transplantation with or without alemtuzumab: comparison between 2 prospective studies in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 2002; 100: 3121–3127.
Hale G, Zhang M-J, Bunjes D, Prentice HG, Spence D, Horowitz MM et al. Improving the outcome of bone marrow transplantation by using CD52 monoclonal antibodies to prevent graft-versus-host disease and graft rejection. Blood 1998; 32: 4581–4590.
Kottaridis PD, Milligan DW, Chopra R, Chakraverty RK, Chakrabarti S, Robinson S et al. In vivo CAMPATH 1H prevents graft-versus-host disease following nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation. Blood 2000; 96: 2419–2425.
Khouri IF, Albitar M, Saliba RM, Ippoliti C, Ma YC, Keating MJ et al. Low-dose alemtuzumab (Campath) in myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation for CD52-positive malignancies: decreased incidence of acute graft-versus-host-disease with unique pharmacokinetics. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 833–837.
Myers GD, Krance RA, Weiss H, Kuehnle I, Demmler G, Heslop HE et al. Adenovirus infection rates in pediatric recipients of alternate donor allogeneic bone marrow transplants receiving either antithymocyte globulin (ATG) or alemtuzumab (Campath). Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 1001–1008.
Bertz H, Spyridonidis A, Waäsch R, Grüllich C, Egger M, Finke J . A novel GVHD-prophylaxis with low-dose alemtuzumab in allogeneic sibling or unrelated donor hematopoetic cell transplantation: the feasibility of deescalation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1563–1570.
Juliusson G, Theorin N, Karlsson K, Frödin U, Malm C . Subcutaneous alemtuzumab vs ATG in adjusted conditioning for allogeneic transplantation: influence of Campath dose on lymphoid recovery, mixed chimerism and survival. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 503–510.
Poiré X, van Besien K . Alemtuzumab in allogeneic hematopoetic stem cell transplantation. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2011; 11: 1099–1111.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Soiffer RJ, Lerademacher J, Ho V, Kan F, Artz A, Champlin RE et al. Impact of immune modulation with anti-T-cell antibodies on the outcome of reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Blood 2011; 117: 6963–6970.
Hasskarl J, Zerweck A, Wäsch R, Ihorst G, Bertz H, Finke J . Induction of graft versus malignancy effect after unrelated allogeneic PBSCT using donor lymphocyte infusions derived from frozen aliquots of the original graft. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 277–282.
Yan CH, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Liu YR, Chen H et al. Risk stratification-directed donor lymphocyte infusion could reduce relapse of standard-risk acute leukemia patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2012; 119: 3256–3262.
Guillaume T, Gaugler B, Chevallier P, Delaunay J, Ayari S, Clavert A et al. Escalated lymphodepletion followed by donor lymphocyte infusion can induce a graft-versus-host response without overwhelming toxicity. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 1112–1117.
Abbi KK, Zhu J, Ehmann WC, Epner E, Carraher M, Mierski J et al. G-CSF mobilized vs conventional donor lymphocytes for therapy of relapse or incomplete engraftment after allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 357–362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solomon, S., Sizemore, C., Zhang, X. et al. Preemptive DLI without withdrawal of immunosuppression to promote complete donor T-cell chimerism results in favorable outcomes for high-risk older recipients of alemtuzumab-containing reduced-intensity unrelated donor allogeneic transplant: a prospective phase II trial. Bone Marrow Transplant 49, 616–621 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pre-emptive and prophylactic donor lymphocyte infusion following allogeneic stem cell transplantation
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
Relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia: an overview of prevention and treatment
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Mixed T cell lineage chimerism in acute leukemia/MDS using pre-emptive donor lymphocyte infusion strategy—Is it prognostic?—a single-center retrospective study
Blood Cancer Journal (2021)
-
Optimizing peripheral blood stem cells transplantation outcome through amend relapse and graft failure: a review of current literature
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2017)
-
Low-dose alemtuzumab for GvHD prevention followed by prophylactic donor lymphocyte infusions in high-risk leukemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)