Abstract
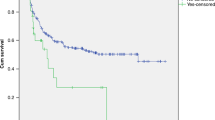
There is increasing evidence suggesting that both angiogenesis and endothelial injury are involved in GVHD. To study the dynamics of angiogenesis, we examined 26 patients with AML who had undergone allogeneic haematopoietic SCT. All were in CR and had either acute GVHD (aGVHD) or chronic GVHD (cGVHD). We performed immunohistochemical studies of BM microvessel density (MVD) using Abs against vascular-endothelial (VE)-cadherin, CD34 and CD105, and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2. At the time of diagnosis, the MVD in AML patients was higher than that in the normal controls, and the MVD decreased after induction chemotherapy. Patients with aGVHD had a significantly higher MVD than patients without aGVHD. Conversely, patients with cGVHD did not have a significantly different MVD. In previous aGVHD, we also found more VEGF+ megakaryocytes. XY FISH in sex-mismatched patients showed that the BM blood vessels consisted mainly of recipient endothelial cells. Taken together, these results suggest that new vessel formation and the VEGF/VEGFR system are involved in aGVHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gratwohl A, Baldomero H . Trends of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the third millennium. Curr Opin Hematol 2009; 16: 420–426.
Socié G, Blazar BR . Acute graft-versus-host disease: from the bench to the bedside. Blood 2009; 114: 4327–4336.
Tichelli A, Gratwohl A . Vascular endothelium as 'novel' target of graft-versus-host disease. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2008; 21: 139–148.
Biedermann BC, Sahner S, Gregor M, Tsakiris DA, Jeanneret C, Pober JS et al. Endothelial injury mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and loss of microvessels in chronic graft versus host disease. Lancet 2002; 359: 2078–2083.
Biedermann BC, Tsakiris DA, Gregor M, Pober JS, Gratwohl A . Combining altered levels of effector transcripts in circulating T cells with a marker of endothelial injury is specific for active graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32: 1077–1084.
Folkman J . Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid, and other disease. Nat Med 1995; 1: 27–31.
Gille H, Kowalski J, Li B, LeCouter J, Moffat B, Zioncheck TF et al. Analysis of biological effects and signaling properties of Flt-1 (VEGFR-1) and KDR (VEGFR-2). A reassessment using novel receptor-specific vascular endothelial growth factor mutants. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 3222–3230.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J . The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 2003; 9: 669–676.
Padró T, Bieker R, Ruiz S, Steins M, Retzlaff S, Bürger H et al. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its cellular receptor KDR (VEGFR-2) in the bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1302–1310.
Letilovic T, Vrhovac R, Verstovsek S, Jaksic B, Ferrajoli A . Role of angiogenesis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 2006; 107: 925–934.
Stifter G, Heiss S, Gastl G, Tzankov A, Stauder R . Over-expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in bone marrow biopsies from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: relationship to anemia and prognosis. Eur J Haematol 2005; 75: 485–491.
Medinger M, Skoda R, Gratwohl A, Theocharides A, Buser A, Heim D et al. Angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor-/receptor expression in myeloproliferative neoplasms: correlation with clinical parameters and JAK2-V617F mutational status. Br J Haematol 2009; 146: 150–157.
Medinger M, Tzankov A, Kern J, Pircher A, Hermann M, Ott HW et al. Increased Dkk3 protein expression in platelets and megakaryocytes of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms. Thromb Haemost 2011; 105: 72–80.
Tzankov A, Heiss S, Ebner S, Sterlacci W, Schaefer G, Augustin F et al. Angiogenesis in nodal B cell lymphomas: a high throughput study. J Clin Pathol 2007; 60: 476–482.
Kumar S, Witzig TE, Greipp PR, Rajkumar SV . Bone marrow angiogenesis and circulating plasma cells in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 2003; 122: 272–274.
Medinger M, Fischer N, Tzankov A . Vascular endothelial growth factor-related pathways in hemato-lymphoid malignancies. J Oncol 2010; 2010: 729725.
Penack O, Henke E, Suh D, King CG, Smith OM, Na IK et al. Inhibition of neovascularization to simultaneously ameliorate graft-vs-host disease and decrease tumor growth. J Natl Cancer Inst 2010; 102: 894–908.
Penack O, Socié G, van den Brink MR . The importance of neovascularization and its inhibition for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2011; 117: 4181–4189.
Fonsatti E, Del Vecchio L, Altomonte M, Sigalotti L, Nicotra MR, Coral S et al. Endoglin: an accessory component of the TGFbeta-binding receptor-complex with diagnostic, prognostic, and bioimmunotherapeutic potential in human malignancies. J Cell Physiol 2001; 18: 1–7.
Warrington K, Hillarby MC, Li C, Letarte M, Kumar S . Functional role of CD105 in TGF-beta1 signalling in murine and human endothelial cells. Anticancer Res 2005; 25: 1851–1864.
Luque A, Slevin M, Turu MM, Juan-Babot O, Badimon L, Krupinski J . CD105 positive neovessels are prevalent in early stage carotid lesions, and correlate with the grade in more advanced carotid and coronary plaques. J Angiogenes Res 2009; 1: 6.
Vestweber D . VE-cadherin: the major endothelial adhesion molecule controlling cellular junctions and blood vessel formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008; 28: 223–232.
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues.. IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2008.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, Büchner T, Willman CL, Estey EH et al. International Working Group for Diagnosis, Standardization of Response Criteria, Treatment Outcomes, and Reporting Standards for Therapeutic Trials in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for Diagnosis, Standardization of Response Criteria, Treatment Outcomes, and Reporting Standards for Therapeutic Trials in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 4642–4649.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 945–956.
Padró T, Ruiz S, Bieker R, Bürger H, Steins M, Kienast J et al. Increased angiogenesis in the bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2000; 95: 2637–2644.
Dubinski W, Gabril M, Iakovlev VV, Scorilas A, Youssef YM, Faragalla H et al. Assessment of the prognostic significance of endoglin (CD105) in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using automated image analysis. Hum Pathol 2012; 43: 1037–1043.
Yao Y, Pan Y, Chen J, Sun X, Qiu Y, Ding Y . Endoglin (CD105) expression in angiogenesis of primary hepatocellular carcinomas: analysis using tissue microarrays and comparisons with CD34 and VEGF. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2007; 37: 39–48.
Wikstrom P, Lissbrant IF, Stattin P, Egevad L, Bergh A . Endoglin (CD105) is expressed on immature blood vessels and is a marker for survival in prostate cancer. Prostate 2002; 51: 268–275.
Dallas NA, Samuel S, Xia L, Fan F, Gray MJ, Lim SJ et al. Endoglin (CD105): a marker of tumor vasculature and potential target for therapy. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 1931–1937.
Pirotte S, Lamour V, Lambert V, Alvarez Gonzalez ML, Ormenese S, Noël A et al. Dentin matrix protein 1 induces membrane expression of VE-cadherin on endothelial cells and inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis by blocking VEGFR-2 phosphorylation. Blood 2011; 117: 2515–2526.
Wallez Y, Vilgrain I, Huber P . Angiogenesis: the VE-cadherin switch. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2006; 16: 55–59.
Corada M, Zanetta L, Orsenigo F, Breviario F, Lampugnani MG, Bernasconi S et al. A monoclonal antibody to vascular endothelial-cadherin inhibits tumor angiogenesis without side effects on endothelial permeability. Blood 2002; 100: 905–911.
Liao F, Doody JF, Overholser J, Finnerty B, Bassi R, Wu Y et al. Selective targeting of angiogenic tumor vasculature by vascular endothelial-cadherin antibody inhibits tumor growth without affecting vascular permeability. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 2567–2575.
Luft T, Dietrich S, Falk C, Conzelmann M, Hess M, Benner A et al. Steroid-refractory GVHD: T-cell attack within a vulnerable endothelial system. Blood 2011; 118: 1685–1692.
Pircher A, Hilbe W, Heidegger I, Drevs J, Tichelli A, Medinger M . Biomarkers in tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic therapy. Int J Mol Sci 2011; 12: 7077–7099.
Wartiovaara U, Salven P, Mikkola H, Lassila R, Kaukonen J, Joukov V et al. Peripheral blood platelets express VEGF-C and VEGF which are released during platelet activation. Thromb Haemost 1998; 80: 171–175.
Lunn RA, Sumar N, Bansal AS, Treleaven J . Cytokine profiles in stem cell transplantation: possible use as a predictor of graft-versus-host disease. Hematology 2005; 10: 107–114.
Min CK, Kim SY, Lee MJ, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is associated with reduced severity of acute graft-versus-host disease and nonrelapse mortality after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 38: 149–156.
Nachbaur D, Schumacher P, Auberger J, Clausen J, Kircher B . Vascular endothelial growth factor and activin-a serum levels following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 942–947.
Porkholm M, Bono P, Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Kivivuori S-M . Higher angiopoietin-2 and VEGF levels predict shorter EFS and increased non-relapse mortality after pediatric hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 50–55.
Murata H, Janin A, Leboeuf C, Soulier J, Gluckman E, Meignin V et al. Donor-derived cells and human graft-versus-host disease of the skin. Blood 2007; 109: 2663–2665.
Willemze AJ, Bakker AC, von dem Borne PA, Bajema IM, Vossen JM . The effect of graft-versus-host disease on skin endothelial and epithelial cell chimerism in stem-cell transplant recipients. Transplantation 2009; 87: 1096–1101.
Mueller RJ, Stussi G, Puga Yung G, Nikolic M, Soldini D, Halter J et al. Persistence of recipient-type endothelium after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2011; 96: 119–127.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Professor Alois Gratwohl for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medinger, M., Tichelli, A., Bucher, C. et al. GVHD after allogeneic haematopoietic SCT for AML: angiogenesis, vascular endothelial growth factor and VEGF receptor expression in the BM. Bone Marrow Transplant 48, 715–721 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.200
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.200
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Endothelial cell dysfunction: a key determinant for the outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Effects of lenalidomide on the bone marrow microenvironment in acute myeloid leukemia: Translational analysis of the HOVON103 AML/SAKK30/10 Swiss trial cohort
Annals of Hematology (2021)
-
High mortality in hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy with and without concomitant acute graft-versus-host disease
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)
-
Numerical impairment of nestin+ bone marrow niches in acute GvHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for AML
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)
-
Angiogenic factors are associated with development of acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Medical Sciences] (2015)