Abstract
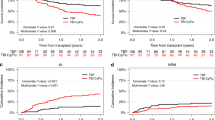
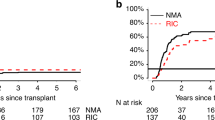
A total of 36 consecutive patients with AML in CR underwent reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic SCT (RISCT) with fludarabine and melphalan conditioning. All patients were ineligible for myeloablative transplantation because of age or comorbidity. In total, 30 patients were in first CR and six patients were in second CR. Donors were siblings in 21 (58%) patients and were unrelated in 15 (42%) patients. Hematopoietic cell transplant specific comorbidity scores ⩾3 were present in 26 (72%) patients. With a median follow-up of 52 months (range, 34–103 months), OS and PFS rates at 4 years were 71% (s.e., 8%) and 68% (s.e., 8%), respectively. At 4 years, the cumulative incidence of non-relapse mortality was 20% (s.e., 7%) and of relapse mortality was 8% (s.e., 5%). Neither OS nor PFS was affected by older age (>60 years), unrelated donor, melphalan dose, or comorbidity score. At last follow up, of the 24 surviving patients, 21 (88%) had performance status (ECOG) of 0 without any active chronic GVHD requiring steroids. Hence, RISCT with fludarabine and melphalan conditioning produces durable long-term remission in older patients with AML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lowenberg B, Downing JR, Burnett A . Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 1051–1062.
Appelbaum FR, Gundacker H, Head DR, Slovak ML, Willman CL, Godwin JE et al. Age and acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2006; 107: 3481–3485.
Juliusson G, Antunovic P, Derolf A, Lehmann S, Mollgard L, Stockelberg D et al. Age and acute myeloid leukemia: real world data on decision to treat and outcomes from the Swedish Acute Leukemia Registry. Blood 2009; 113: 4179–4187.
Hamadani M, Awan FT, Copelan EA . Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults with acute myeloid leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 556–567.
Koreth J, Schlenk R, Kopecky KJ, Honda S, Sierra J, Djulbegovic BJ et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective clinical trials. JAMA 2009; 301: 2349–2361.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005; 106: 2912–2919.
Alyea EP, Kim HT, Ho V, Cutler C, Gribben J, DeAngelo DJ et al. Comparative outcome of nonmyeloablative and myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients older than 50 years of age. Blood 2005; 105: 1810–1814.
Baron F, Storb R . Hematopoietic cell transplantation after reduced-intensity conditioning for older adults with acute myeloid leukemia in complete remission. Curr Opin Hematol 2007; 14: 145–151.
McClune BL, Weisdorf DJ, Pedersen TL, Tunes da Silva G, Tallman MS, Sierra J et al. Effect of age on outcome of reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission or with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 1878–1887.
Aoudjhane M, Labopin M, Gorin NC, Shimoni A, Ruutu T, Kolb HJ et al. Comparative outcome of reduced intensity and myeloablative conditioning regimen in HLA identical sibling allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients older than 50 years of age with acute myeloblastic leukaemia: a retrospective survey from the Acute Leukemia Working Party (ALWP) of the European group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Leukemia 2005; 19: 2304–2312.
Hegenbart U, Niederwieser D, Sandmaier BM, Maris MB, Shizuru JA, Greinix H et al. Treatment for acute myelogenous leukemia by low-dose, total-body, irradiation-based conditioning and hematopoietic cell transplantation from related and unrelated donors. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 444–453.
van Besien K, Artz A, Smith S, Cao D, Rich S, Godley L et al. Fludarabine, melphalan, and alemtuzumab conditioning in adults with standard-risk advanced acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 5728–5738.
Tauro S, Craddock C, Peggs K, Begum G, Mahendra P, Cook G et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation using a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen has the capacity to produce durable remissions and long-term disease-free survival in patients with high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplasia. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 9387–9393.
Grigg AP, Gibson J, Bardy PG, Reynolds J, Shuttleworth P, Koelmeyer RL et al. A prospective multicenter trial of peripheral blood stem cell sibling allografts for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission using fludarabine-cyclophosphamide reduced intensity conditioning. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 560–567.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, Buchner T, Willman CL, Estey EH et al. Revised recommendations of the international working group for diagnosis, standardization of response criteria, treatment outcomes, and reporting standards for therapeutic trials in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 4642–4649.
de Lima M, Anagnostopoulos A, Munsell M, Shahjahan M, Ueno N, Ippoliti C et al. Nonablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning regimens in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: dose is relevant for long-term disease control after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004; 104: 865–872.
Giralt S, Thall PF, Khouri I, Wang X, Braunschweig I, Ippolitti C et al. Melphalan and purine analog-containing preparative regimens: reduced-intensity conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies undergoing allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation. Blood 2001; 97: 631–637.
Oran B, Giralt S, Saliba R, Hosing C, Popat U, Khouri I et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for the treatment of high-risk acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome using reduced-intensity conditioning with fludarabine and melphalan. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 454–462.
Martino R, Iacobelli S, Brand R, Jansen T, van Biezen A, Finke J et al. Retrospective comparison of reduced-intensity conditioning and conventional high-dose conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using HLA-identical sibling donors in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2006; 108: 836–846.
Schetelig J, Bornhauser M, Schmid C, Hertenstein B, Schwerdtfeger R, Martin H et al. Matched unrelated or matched sibling donors result in comparable survival after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a report from the cooperative German Transplant Study Group. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 5183–5191.
Walter RB, Pagel JM, Gooley TA, Petersdorf EW, Sorror ML, Woolfrey AE et al. Comparison of matched unrelated and matched related donor myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation for adults with acute myeloid leukemia in first remission. Leukemia 2010; 24: 1276–1282.
Estey E, de Lima M, Tibes R, Pierce S, Kantarjian H, Champlin R et al. Prospective feasibility analysis of reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) regimens for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Blood 2007; 109: 1395–1400.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Richard Champlin has received consultant/advisory fees from Genzyme; and research funding from Otsuka and Genzyme. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popat, U., de Lima, M., Saliba, R. et al. Long-term outcome of reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic SCT in patients with AML in CR. Bone Marrow Transplant 47, 212–216 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2011.61
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2011.61
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pilot study using post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy), tacrolimus and mycophenolate GVHD prophylaxis for older patients receiving 10/10 HLA-matched unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)
-
Addition of melphalan to fludarabine/busulfan (FLU/BU4/MEL) provides survival benefit for patients with myeloid malignancy following allogeneic bone-marrow transplantation/peripheral blood stem-cell transplantation
International Journal of Hematology (2019)
-
Long-term survival after allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation for AML in remission: single-centre results after TBI-based myeloablative and non-myeloablative conditioning
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2013)
-
Strategies to Reduce Relapse after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2013)