Abstract
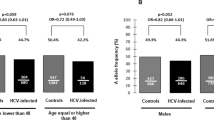
Immune response to viral infection is an important determinant of liver injury in chronic hepatitis C (CHC). Experimental and clinical data suggest a protective role of interleukin-10 (IL-10) in hepatic fibrogenesis. The significance of two SNPs of the interleukin-10 receptor 1 (IL-10R1), S138G (SNP3) and G330R (SNP4) was investigated on (i) susceptibility to CHC, (ii) progression of hepatic fibrosis and (iii) response to interferon/ribavirin therapy. DNA and liver biopsies were obtained from 212 patients with HCV (hepatitis C virus)-genotype-1 infection. The allele frequencies were 0.17 for SNP3 and 0.33 for SNP4, both of which were indifferent from healthy controls (0.17 and 0.32, respectively). Stage 1 liver fibrosis was found in 22 cases (10.4%), stage 2 in 108 (50.9%), stage 3 in 27 (12.8%), and stage 4 (cirrhosis) in 55 (25.9%). An association was found between the SNP4 allele and the presence of cirrhosis (P=0.01). Homozygous SNP4 individual variants segregated within the cirrhosis group (P=0.03). We found neither an association with SNP3 nor with the necroinflammatory disease activity (as measured by ALT levels) nor with the response to antiviral therapy. Our work implies that IL-10R1 SNP4 is a recessively inherited risk factor for hepatic cirrhosis in HCV genotype-1 infection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IL-10:
-
interleukin-10
- IL-10R1:
-
interleukin-10 receptor 1
- cSNP:
-
coding single-nucleotide polymorphism
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PBMC:
-
peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- CHC:
-
chronic hepatitis C
- HCV:
-
hepatitis C virus
References
Seeff LB, Hollinger FB, Alter HJ et al. Long-term mortality and morbidity of transfusion-associated non-A, non-B, and type C hepatitis: A National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute collaborative study. Hepatology 2001; 33: 455–463.
Kenny-Walsh E . Clinical outcomes after hepatitis C infection from contaminated anti-D immune globulin. N Engl J Med 1999; 22: 1228–1233.
Parana R, Vitvitski L, Andrade Z et al. Acute sporadic non-A, non-B hepatitis in Northeastern Brazil: etiology and natural history. Hepatology 1999; 30: 289–293.
Hofer H, Watkins-Riedel T, Janata O et al. Spontaneous viral clearance in patients with acute hepatitis C can be predicted by repeated measurements of serum viral load. Hepatology 2003; 37: 60–64.
Poynard T, Bedossa P, Opolon P, and the OBSVIRC, METAVIR, CLINIVIR, and DOSVIRC groups. Natural history of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Lancet 1997; 349: 825–832.
Wiese M, Berr F, Lafrenz M, Porst H, Oesen U . Low frequency of cirrhosis in a hepatitis C (genotype 1b) single-source outbreak in germany: a 20-year multicenter study. Hepatology 2000; 32: 91–96.
Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Koida I et al. A multivariate analysis of risk factors for hepatocellular carcinogenesis: a prospective observation of 795 patients with viral and alcoholic cirrhosis. Hepatology 1993; 18: 47–53.
Tsukuma H, Hiyama T, Tanaka S et al. Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med 1993; 328: 1797–1801.
Colombo M, de Franchis R, Del Ninno E et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Italian patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 1995; 325: 675–680.
Sanchez-Quijano A, Andreu J, Gavilan F et al. Influence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection on the natural course of chronic parenterally acquired hepatitis C. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1995; 14: 949–953.
Zarski JP, Bohn B, Bastie A et al. Characteristics of patients with dual infection by hepatitis B and C viruses. J Hepatol 1998; 28: 27–33.
Minuk GY . The influence of host factors on the natural history of chronic hepatitis C viral infections. J Viral Hepat 1999; 6: 271–276.
Edwards-Smith CJ, Jonsson JR, Purdie DM, Bansal A, Shorthouse C, Powell EE . Interleukin-10 promoter polymorphism predicts initial response of chronic hepatitis C to interferon alfa. Hepatology 1999; 30: 526–530.
Powell EE, Edwards-Smith CJ, Hay JL et al. Host genetic factors influence disease progression in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2000; 31: 828–833.
Thio CL, Thomas DL, Carrington M . Chronic viral hepatitis and the human genome. Hepatology 2000; 31: 819–827.
Manns MP, McHutchinson JG, Gordon SC et al. Peginterferon alfa-2b in combination with ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic heptitis C: results of a randomized trial. Lancet 2001; 358: 958–965.
Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 975–982.
Poynard T, McHutchison J, Manns M et al. Impact of pegylated interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin on liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2002; 122: 1303–1313.
Moore KW, De Waal MR, Coffman RL, O'Garra A . Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 2001; 19: 683–765.
Dharancy S, Canva V, Gambiez L, Paris JC, Desreumaux P . Hepatic deficiency of interleukin 10 in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: 1411–1412.
Louis H, Van Laethem JL, Wu W et al. Interleukin-10 controls neutrophilic infiltration, hepatocyte proliferation, and liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice. Hepatology 1998; 8: 1607–1615.
Reitamo S, Remitz A, Tamai K et al. Interleukin 10 modulates type 1 collagen and matrix metalloprotease gene expression in cultured human skin fibroblasts. J Clin Invest 1994; 94: 2489–2492.
Wang SC, Ohata M, Schrum L, Rippe RA, Tsukamoto H . Expression of interleukin-10 by in vitro and in vivo activated hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 302–308.
Nelson DR, Lauwers GY, Lau JY, Davis GL . Interleukin 10 treatment reduces fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a pilot trial of interferon nonresponders. Gastroenterology 2000; 118: 655–660.
Nelson DR, Tu Z, Soldevila-Pico C et al. Long-term interleukin 10 therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients has a proviral and anti-inflammatory effect. Hepatology 2003; 38: 859–868.
Wangoo A, Laban C, Cook HT, Glenville B, Shaw RJ . Interleukin-10- and corticosteroid-induced reduction in type I procollagen in a human ex vivo scar culture. Int J Exp Pathol 1997; 78: 33–41.
Tan J, Indelicato S, Narula S, Zavodny P, Chou C . Characterization of interleukin-10 receptors on human and mouse cells. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 21053–21059.
Ho A, Liu Y, Khan T, Hsu D, Bazan J, Moore K . A receptor for interleukin 10 is related to interferon receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 11267–11271.
Liu Y, Wei SH, Ho AS, de Waal M, Moore KW . Expression cloning and characterization of a human IL-10 receptor. J Immunol 1994; 152: 1821–1829.
Spencer SD, Di Marco F, Hooley J et al. The orphan receptor CRF2-4 is an essential subunit of the interleukin 10 receptor. J Exp Med 1998; 187: 571–578.
Kotenko SV, Krause CD, Izotova LS, Pollack BP, Wu W, Pestka S . Identification and functional characterization of a second chain of the interleukin-10 receptor complex. EMBO J 1997; 16: 5894–5903.
Finbloom DS, Winestock KD . IL-10 induces the tyrosine phosphorylation of tyk2 and Jak1 and the differential assembly of STAT1 alpha and STAT3 complexes in human T cells and monocytes. J Immunol 1995; 155: 1079–1090.
Stahl N, Farruggella TJ, Boulton TG, Zhong Z, Darnell JE, Yancopoulos GD . Choice of STATs and other substrates specified by modular tyrosine-based motifs in cytokine receptors. Science 1995; 267: 1349–1353.
Darnell JE . STATs and gene regulation. Science 1997; 277: 1630–1635.
Donnelly RP, Dickensheets H, Finbloom DS . The interleukin-10 signal transduction pathway and regulation of gene expression in mononuclear phagocytes. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1999; 19: 563–573.
Riley JK, Takeda K, Akira S, Schreiber RD . Interleukin-10 receptor signaling through the JAK-STAT pathway. Requirement for two distinct receptor-derived signals for anti-inflammatory action. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 16513–16521.
Gasche C, Grundtner P, Zwirn P et al. Novel variants of the IL-10 receptor 1 affect inhibition of monocyte TNF-alpha production. J Immunol 2003; 170: 5578–5582.
Reitamo S, Remitz A, Tamai K et al. Interleukin 10 modulates type 1 collagen and matrix metalloprotease gene expression in cultured human skin fibroblasts. J Clin Invest 1994; 94: 2489–2492.
Nelson DR, Lauwers GY, Lau JY, Davis GL . Interleukin 10 treatment reduces fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a pilot trial of interferon nonresponders. Gastroenterology 2000; 118: 655–660.
Nelson DR, Tu Z, Soldevila-Pico C et al. Long-term interleukin 10 therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients has a proviral and anti-inflammatory effect. Hepatology 2003; 38: 859–868.
Zwirn P, Grundtner P, Gasche C . Ethnic distribution of cSNPs in the IL-10 receptor 1 (IL-10 R1). Proceedings of the Falk Symposium, Vol 133, 2003, p 70, abstract.
Vidigal PG, Germer JJ, Zein NN . Polymorphisms in the interleukin-10, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and transforming growth factor-beta1 genes in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with interferon and ribavirin. J Hepatol 2002; 36: 271–277.
Yee LJ, Tang J, Gibson AW, Kimberly R, Van Leeuwen DJ, Kaslow RA . Interleukin 10 polymorphisms as predictors of sustained response in antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis C infection. Hepatology 2001; 33: 708–712.
Constantini PK, Wawrzynowicz-Syczewska M, Clare M et al. Interleukin-1, interleukin-10 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphisms in hepatitis C virus infection: an investigation of the relationships with spontaneous viral clearance and response to alpha-interferon therapy. Liver 2002; 22: 404–412.
Lio D, Caruso C, Di Stefano R et al. IL-10 and TNF-alpha polymorphisms and the recovery from HCV infection. Hum Immunol 2003; 64: 674–680.
Ferenci P, Brunner H, Nachbaur K et al. Combination of interferon induction therapy and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis c. Hepatology 2001; 34: 1006–1011.
Jessner W, Gschwandtler M, Steindl-Munda P et al. A pilot study on primary interferon resistance as predictor of non response to treatment in chronic hepatitis virus genotype 1 infection. Lancet 2001; 358: 1241–1242.
Jessner W, Stauber R, Hackl F et al. Early viral kinetics on treatment with pegylated interferon-alpha-2a in chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection. J Viral Hepatitis 2003; 10: 37–42.
Ludwig J . The nomenclature of chronic active hepatitis: an obituary. Gastroenterology 1993; 105: 274–278.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Austrian Science Foundation P15314 and the OeNB Anniversary Fund ONB10543 to CG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofer, H., Neufeld, J., Oesterreicher, C. et al. Bi-allelic presence of the interleukin-10 receptor 1 G330R allele is associated with cirrhosis in chronic HCV-1 infection. Genes Immun 6, 242–247 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364168
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364168
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
An intracytoplasmic IL-10 receptor variant permits rapid reduction in STAT3 activation
Genes & Immunity (2011)
-
Environmental and Genetic Factors Influence the Relationship Between Circulating IL‐10 and Obesity Phenotypes
Obesity (2010)
-
Gene polymorphisms in Toll-like receptors, interleukin-10, and interleukin-10 receptor alpha and lymphoma risk
Genes & Immunity (2006)
-
Associations of the IL2Rα, IL4Rα, IL10Rα, and IFN γ R1 cytokine receptor genes with AIDS progression in a French AIDS cohort
Immunogenetics (2006)