Abstract
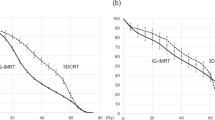
To compare late genitourinary (GU) and gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity of radiotherapy (RT) to localized fields for prostate cancer delivered using intensity-modulated RT (IMRT) versus conventional RT (ConvRT). The records of 461 patients were reviewed; 355 patients received IMRT and 106 received ConvRT. Late GU and GI toxicity were compared. Late GU toxicity rates were not significantly different (P=0.166); however, late GI toxicity rates were lower with IMRT (P=0.001). Regression analyses demonstrated that only IMRT use (P=0.006) predicted reduction in late GI toxicity but no factors correlated with late GU toxicity. IMRT did not influence late GU toxicity but was associated with a reduction of late GI toxicity over ConvRT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanks GE . Conformal radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Ann Med 2000; 32: 57–63.
Jani AB, Hellman S . Early prostate cancer: clinical decision-making. Lancet 2003; 361: 1045–1053.
Pollack A, Zagars GK, Rosen II . Prostate cancer treatment with radiotherapy: maturing methods that minimize morbidity. Semin Oncol 1999; 26: 150–161.
Goitein M . The inverse problem. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1990; 18: 489–491.
Jani AB, Roeske JC, Rash C . Intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) for prostate cancer. Clin Prostate Cancer 2003; 2: 98–105.
Zelefsky MJ, Fuks Z, Leibel SA . Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for prostate cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol 2002; 12: 229–237.
Tubiana M, Eschwege F . Conformal radiotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy – clinical data. Acta Oncol 2000; 39: 555–567.
Shu HK, Lee TT, Vigneauly E, Xia P, Pickett B, Phillips TL et al. Toxicity following high-dose three-dimensional conformal and intensity-modulated radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. Urology 2001; 57: 102–107.
Zelefsky MJ, Fuks Z, Hunt M, Yamada Y, Marion C, Ling CC et al. High-dose intensity modulated radiation therapy for prostate cancer: early toxicity and biochemical outcome in 772 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002; 53: 1111–1116.
Zelefsky MJ, Fuks Z, Happersett L, Lee HJ, Ling CC, Burman CM et al. Clinical experience with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) in prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol 2000; 55: 241–249.
Zelefsky MJ, Fuks Z, Hunt M, Lee HJ, Lombardi D, Ling CC et al. High dose radiation delivered by intensity modulated conformal radiotherapy improves the outcome of localized prostate cancer. J Urol 2001; 166: 876–881.
Teh BS, Mai WY, Uhl BM, Augspurger ME, Grant 3rd WH, Lu HH et al. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) for prostate cancer with the use of a rectal balloon for prostate immobilization: acute toxicity and dose-volume analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2001; 49: 705–712.
De Meerleer G, Vakaet L, Meersschout S, Villeirs G, Verbaeys A, Oosterlinck W et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy as primary treatment for prostate cancer: acute toxicity in 114 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2004; 60: 777–787.
Pollack A, Hanlon AL, Horwitz EM, Feigenberg SJ, Konski AA, Movsas B et al. Dosimetry and preliminary acute toxicity in the first 100 men treated for prostate cancer on a randomized hypofractionation dose escalation trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006; 64: 518–526.
Kupelian PA, Thakkar VV, Khuntia D, Reddy CA, Klein EA, Mahadevan A . Hypofractionated intensity-modulated radiotherapy (70 Gy at 2.5 Gy per fraction) for localized prostate cancer: long-term outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005; 63: 1463–1468.
Jani AB . The effectiveness of combining hormone therapy and radiotherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2004; 5: 2469–2477.
Ryu JK, Winter K, Michalski JM, Purdy JA, Markoe AM, Earle JD et al. Interim report of toxicity from 3D conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) for prostate cancer on 3DOG/RTOG 9406, level III (79.2 Gy). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002; 54: 1036–1046.
Michalski JM, Winter K, Purdy JA, Wilder RB, Perez CA, Roach M et al. Preliminary evaluation of low-grade toxicity with conformal radiation therapy for prostate cancer on RTOG 9406 dose levels I and II. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003; 56: 192–198.
Sailer SL, Chaney EL, Rosenman JG, Sherouse GW, Tepper JE . Treatment planning at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Semin Radiat Oncol 1992; 2: 267–273.
Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG). Toxicity Information. Sections 7–8: Acute and Late Radiation Morbidity Criteria) http://www.rtog.org/members/toxicity/main.html.
Dawson-Saunders B, Trapp RG . Basic and Clinical Biostatistics. Prentice Hall: East Norwalk, CT, 1990.
Agresti A . Categorical Data Analysis, 2nd edn. Wiley: New York, NY, 2002.
Zavoina W, McKelvey RD . A statistical model for the analysis of ordinal level dependent variables. J Math Sociol 1975; 4: 103–120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jani, A., Su, A., Correa, D. et al. Comparison of late gastrointestinal and genitourinary toxicity of prostate cancer patients undergoing intensity-modulated versus conventional radiotherapy using localized fields. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 10, 82–86 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500910
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500910
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Predictors of long-term survival for localized prostate cancer treated with high-dose IMRT stratified by NCCN 2015 guidelines in a community hospital setting
Journal of Radiation Oncology (2016)
-
Kontroversen der Therapie des Hochrisiko-Prostatakarzinoms
Der Onkologe (2015)
-
Outcomes of high-dose intensity-modulated radiotherapy alone with 1 cm planning target volume posterior margin for localized prostate cancer
Radiation Oncology (2013)
-
Toxicity report of once weekly radiation therapy for low-risk prostate adenocarcinoma: preliminary results of a phase I/II trial
Radiation Oncology (2011)
-
Optimal organ-sparing intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) regimen for the treatment of locally advanced anal canal carcinoma: a comparison of conventional and IMRT plans
Radiation Oncology (2007)