Abstract
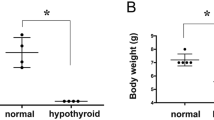
Hormonal imbalances are involved in many of the age-related pathologies, as neurodegenerative and psychiatric diseases. Specifically, thyroid state alterations in the adult are related to psychological changes and mood disorders as depression. The dentate gyrus of the hippocampal formation undergoes neurogenesis in adult mammals including humans. Recent evidence suggests that depressive disorders and their treatment are tightly related to the number of newly born neurons in the dentate gyrus. We have studied the effect of thyroid hormones (TH) on hippocampal neurogenesis in adult rats in vivo. A short period of adult-onset hypothyroidism impaired normal neurogenesis in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus with a 30% reduction in the number of proliferating cells. Hypothyroidism also reduced the number of newborn neuroblasts and immature neurons (doublecortin (DCX) immunopositive cells) which had a severely hypoplastic dendritic arborization. To correlate these changes with hippocampal function, we subjected the rats to the forced swimming and novel object recognition tests. Hypothyroid rats showed normal memory in object recognition, but displayed abnormal behavior in the forced swimming test, indicating a depressive-like disorder. Chronic treatment of hypothyroid rats with TH not only normalized the abnormal behavior but also restored the number of proliferative and DCX-positive cells, and induced growth of their dendritic trees. Therefore, hypothyroidism induced a reversible depressive-like disorder, which correlated to changes in neurogenesis. Our results indicate that TH are essential for adult hippocampal neurogenesis and suggest that mood disorders related to adult-onset hypothyroidism in humans could be due, in part, to impaired neurogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vanderpump MP, Tunbridge WM . Epidemiology and prevention of clinical and subclinical hypothyroidism. Thyroid 2002; 12: 839–847.
Joffe RT . Hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis. In: Pfaff D, Arnold A, Etgen A, Fahrbach S, Rubin R (eds). Hormones, Brain, and Behavior. Academic Press: San Diego, 2002, pp 867–881.
Bauer M, Whybrow P . Thyroid hormone, Brain, and Behavior. In: Pfaff D, Arnold A, Etgen A, Fahrbach S, Rubin R (eds) Hormones, Brain, and Behavior. Academic Press: San Diego, 2002, pp 239–264.
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S et al. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 2003; 301: 805–809.
Malberg JE, Duman RS . Cell proliferation in adult hippocampus is decreased by inescapable stress: reversal by fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003; 28: 1562–1571.
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 1998; 4: 1313–1317.
Alvarez-Buylla A, Garcia-Verdugo JM . Neurogenesis in adult subventricular zone. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 629–634.
Gage FH . Neurogenesis in the adult brain. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 612–613.
Gould E, Gross CG . Neurogenesis in adult mammals: some progress and problems. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 619–623.
Palmer TD, Willhoite AR, Gage FH . Vascular niche for adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol 2000; 425: 479–494.
Nacher J, Crespo C, McEwen BS . Doublecortin expression in the adult rat telencephalon. Eur J Neurosci 2001; 14: 629–644.
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH . Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 2002; 415: 1030–1034.
Kempermann G, Wiskott L, Gage FH . Functional significance of adult neurogenesis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2004; 14: 186–191.
Shors TJ, Townsend DA, Zhao M, Kozorovitskiy Y, Gould E . Neurogenesis may relate to some but not all types of hippocampal-dependent learning. Hippocampus 2002; 12: 578–584.
Gould E, Beylin A, Tanapat P, Reeves A, Shors TJ . Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat Neurosci 1999; 2: 260–265.
Tanapat P, Hastings NB, Rydel TA, Galea LA, Gould E . Exposure to fox odor inhibits cell proliferation in the hippocampus of adult rats via an adrenal hormone-dependent mechanism. J Comp Neurol 2001; 437: 496–504.
Keilhoff G, Becker A, Grecksch G, Bernstein HG, Wolf G . Cell proliferation is influenced by bulbectomy and normalized by imipramine treatment in a region-specific manner. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, Epub ahead of print.
Trejo JL, Carro E, Torres-Aleman I . Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates exercise-induced increases in the number of new neurons in the adult hippocampus. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 1628–1634.
Bernal J . Thyroid hormones and Brain Development. In: Pfaff D, Arnold A, Etgen A, Fahrbach S, Rubin R (eds). Hormones, Brain, and Behavior. Academic Press: San Diego, 2002, pp 543–587.
Legrand J . Effects of thyroid hormones on central nervous system. In: Yanai J (ed). Neurobehavioral Teratology. Elsevier: Amsterdam, 1984, pp 331–363.
Martinez-Galan JR, Pedraza P, Santacana M, Escobar del Ray F, Morreale de Escobar G, Ruiz-Marcos A . Early effects of iodine deficiency on radial glial cells of the hippocampus of the rat fetus. A model of neurological cretinism. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 2701–2709.
Madeira MD, Cadete-Leite A, Andrade JP, Paula-Barbosa MM . Effects of hypothyroidism upon the granular layer of the dentate gyrus in male and female adult rats: a morphometric study. J Comp Neurol 1991; 314: 171–186.
Guadano-Ferraz A, Benavides-Piccione R, Venero C, Lancha C, Vennstrom B, Sandi C et al. Lack of thyroid hormone receptor alpha1 is associated with selective alterations in behavior and hippocampal circuits. Mol Psychiatry 2003; 8: 30–38.
Venero C, Guadano-Ferraz A, Herrero AI, Nordstrom K, Manzano J, de Escobar GM et al. Anxiety, memory impairment, and locomotor dysfunction caused by a mutant thyroid hormone receptor alpha1 can be ameliorated by T3 treatment. Genes Dev 2005; 19: 2152–2163.
Fernandez M, Pirondi S, Manservigi M, Giardino L, Calza L . Thyroid hormone participates in the regulation of neural stem cells and oligodendrocyte precursor cells in the central nervous system of adult rat. Eur J Neurosci 2004; 20: 2059–2070.
Lemkine GF, Raji A, Alfama G, Turque N, Hassani Z, Alegria-Prevot O et al. Adult neural stem cell cycling in vivo requires thyroid hormone and its alpha receptor. FASEB J 2005; 19: 863–865.
Desouza LA, Ladiwala U, Daniel SM, Agashe S, Vaidya RA, Vaidya VA . Thyroid hormone regulates hippocampal neurogenesis in the adult rat brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 2005; 29: 414–426.
Ambrogini P, Cuppini R, Ferri P, Mancini C, Ciaroni S, Voci A et al. Thyroid hormones affect neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult rat. Neuroendocrinology 2005; 81: 244–253.
Iniguez MA, Rodriguez-Pena A, Ibarrola N, Morreale de Escobar G, Bernal J . Adult rat brain is sensitive to thyroid hormone. Regulation of RC3/neurogranin mRNA. J Clin Invest 1992; 90: 554–558.
Berbel P, Guadano-Ferraz A, Martinez M, Quiles JA, Balboa R, Innocenti GM . Organization of auditory callosal connections in hypothyroid adult rats. Eur J Neurosci 1993; 5: 1465–1478.
Zarrow MX, Yochim JM, McCarthy JL . Experimental Endocrinology: A Sourcebook of Basic Techniques. London: Academic Press, Inc., 1964.
Zavacki AM, Ying H, Christoffolete MA, Aerts G, So E, Harney JW et al. Type 1 iodothyronine deiodinase is a sensitive marker of peripheral thyroid status in the mouse. Endocrinology 2005; 146: 1568–1575.
Escobar-Morreale HF, del Rey FE, Obregon MJ, de Escobar GM . Only the combined treatment with thyroxine and triiodothyronine ensures euthyroidism in all tissues of the thyroidectomized rat. Endocrinology 1996; 137: 2490–2502.
Kuhn HG, Dickinson-Anson H, Gage FH . Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J Neurosci 1996; 16: 2027–2033.
Malberg JE, Eisch AJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS . Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 2000; 20: 9104–9110.
Doetsch F, Petreanu L, Caille I, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A . EGF converts transit-amplifying neurogenic precursors in the adult brain into multipotent stem cells. Neuron 2002; 36: 1021–1034.
Reif A, Schmitt A, Fritzen S, Chourbaji S, Bartsch C, Urani A et al. Differential effect of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (NOS-III) on the regulation of adult neurogenesis and behaviour. Eur J Neurosci 2004; 20: 885–895.
Pham K, McEwen BS, Ledoux JE, Nader K . Fear learning transiently impairs hippocampal cell proliferation. Neuroscience 2005; 130: 17–24.
Morreale de Escobar G, Pastor R, Obregon MJ, Escobar del Rey F . Effects of maternal hypothyroidism on the weight and thyroid hormone content of rat embryonic tissues, before and after onset of fetal thyroid function. Endocrinology 1985; 117: 1890–1900.
Rao MS, Shetty AK . Efficacy of doublecortin as a marker to analyse the absolute number and dendritic growth of newly generated neurons in the adult dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci 2004; 19: 234–246.
Couillard-Despres S, Winner B, Schaubeck S, Aigner R, Vroemen M, Weidner N et al. Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 2005; 21: 1–14.
Williams RW, Rakic P . Three-dimensional counting: an accurate and direct method to estimate numbers of cells in sectioned material. J Comp Neurol 1988; 278: 344–352.
Paxinos G, Watson C . The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. London: Academic Press Inc, 1986.
Sousa N, Madeira MD, Paula-Barbosa MM . Effects of corticosterone treatment and rehabilitation on the hippocampal formation of neonatal and adult rats. An unbiased stereological study. Brain Res 1998; 794: 199–210.
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M . Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 1977; 266: 730–732.
Ennaceur A, Delacour J . A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: Behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 1988; 31: 47–59.
Kee N, Sivalingam S, Boonstra R, Wojtowicz JM . The utility of Ki-67 and BrdU as proliferative markers of adult neurogenesis. J Neurosci Methods 2002; 115: 97–105.
Ribak CE, Korn MJ, Shan Z, Obenaus A . Dendritic growth cones and recurrent basal dendrites are typical features of newly generated dentate granule cells in the adult hippocampus. Brain Res 2004; 1000: 195–199.
Jiang W, Zhang Y, Xiao L, Van Cleemput J, Ji SP, Bai G et al. Cannabinoids promote embryonic and adult hippocampus neurogenesis and produce anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 3104–3116.
Myhrer T . The role of medial and lateral hippocampal perforant path lesions and object distinctiveness in rats’ reaction to novelty. Physiol Behav 1988; 42: 371–377.
Vnek N, Rothblat LA . The hippocampus and long-term object memory in the rat. J Neurosci 1996; 16: 2780–2787.
Cameron HA, McKay RD . Adult neurogenesis produces a large pool of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol 2001; 435: 406–417.
Uchida K, Yonezawa M, Nakamura S, Kobayashi T, Machida T . Impaired neurogenesis in the growth-retarded mouse is reversed by T3 treatment. NeuroReport 2005; 16: 103–106.
Nixon K, Crews FT . Temporally specific burst in cell proliferation increases hippocampal neurogenesis in protracted abstinence from alcohol. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 9714–9722.
Doetsch F, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A . Regeneration of a germinal layer in the adult mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 11619–11624.
Steiner B, Kronenberg G, Jessberger S, Brandt MD, Reuter K, Kempermann G . Differential regulation of gliogenesis in the context of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Glia 2004; 46: 41–52.
Nunez J, Couchie D, Aniello F, Bridoux AM . Regulation by thyroid hormone of microtubule assembly and neuronal differentiation. Neurochem Res 1991; 16: 975–982.
Ruiz-Marcos A, Sanchez-Toscano F, Escobar del Rey F, Morreale de Escobar G . Reversible morphological alterations of cortical neurons in juvenile and adult hypothyroidism in the rat. Brain Res 1980; 185: 91–102.
Cameron HA, Gould E . Adult neurogenesis is regulated by adrenal steroids in the dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 1994; 61: 203–209.
Karishma KK, Herbert J . Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) stimulates neurogenesis in the hippocampus of the rat, promotes survival of newly formed neurons and prevents corticosterone-induced suppression. Eur J Neurosci 2002; 16: 445–453.
Kamilaris TC, DeBold CR, Johnson EO, Mamalaki E, Listwak SJ, Calogero AE et al. Effects of short and long duration hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism on the plasma adrenocorticotropin and corticosterone responses to ovine corticotropin-releasing hormone in rats. Endocrinology 1991; 128: 2567–2576.
Baez M, Volosin M . Corticosterone influences forced swim-induced immobility. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1994; 49: 729–736.
Porsolt R, Lenegre A, McArthur R . Pharmacological models of depression. In: Olivier B, Mos J, Slangen JL (eds). Animal Models in Psychopharmacology. Birkhauser: Basel, 1991, pp 137–159.
Redei EE, Ahmadiyeh N, Baum AE, Sasso DA, Slone JL, Solberg LC et al. Novel animal models of affective disorders. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry 2001; 6: 43–67.
Kulikov A, Torresani J, Jeanningros R . Experimental hypothyroidism increases immobility in rats in the forced swim paradigm. Neurosci Lett 1997; 234: 111–114.
Redei EE, Solberg LC, Kluczynski JM, Pare WP . Paradoxical hormonal and behavioral responses to hypothyroid and hyperthyroid states in the Wistar–Kyoto rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001; 24: 632–639.
Wilcoxon JS, Kuo AG, Disterhoft JF, Redei EE . Behavioral deficits associated with fetal alcohol exposure are reversed by prenatal thyroid hormone treatment: a role for maternal thyroid hormone deficiency in FAE. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 961–971.
Oomen HA, Schipperijn AJ, Drexhage HA . The prevalence of affective disorder and in particular of a rapid cycling of bipolar disorder in patients with abnormal thyroid function tests. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1996; 45: 215–223.
Bauer M, London ED, Rasgon N, Berman SM, Frye MA, Altshuler LL et al. Supraphysiological doses of levothyroxine alter regional cerebral metabolism and improve mood in bipolar depression. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 456–469.
Baumgartner A, Bauer M, Hellweg R . Treatment of intractable non-rapid cycling bipolar affective disorder with high-dose thyroxine: an open clinical trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 1994; 10: 183–189.
Bruel-Jungerman E, Laroche S, Rampon C . New neurons in the dentate gyrus are involved in the expression of enhanced long-term memory following environmental enrichment. Eur J Neurosci 2005; 21: 513–521.
Acknowledgements
We thank Marina Sanz Sancristóbal, Mario Soriano, and Ana Isabel Herrero for their excellent technical help, Carmina Criado for providing facilities to perform the behavioral studies, Laura Barrios for her assistance with the statistical analyses and Javier Perez for the art work. We also thank Gabriela Morreale de Escobar and Francisco Escobar del Rey for helpful discussions and advise in the experimental animal design. This work was supported by Grants BFI2001-2412 and BFU2004-05944 (AG-F), BFI2002-00489 (JB), BFI2003-07524 (CV) from the Ministry of Science and Technology and FIS, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Red de Centros RCMN (C03/08). AM-P and IF-L are the recipients of a fellowship and AG-F and CV of a contract from the Ramón y Cajal Program, all of the Ministry of Science and Technology, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary information accompanies the paper on Molecular Psychiatry website (http://www.nature.com/mp)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montero-Pedrazuela, A., Venero, C., Lavado-Autric, R. et al. Modulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis by thyroid hormones: implications in depressive-like behavior. Mol Psychiatry 11, 361–371 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001802
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001802
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Thyroxine restores hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptogenesis in a male rat model of carbimazole-induced hypothyroidism: a histological study
Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences (2023)
-
Primary Hypothyroidism and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Tale of Two
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Thyroid hormone levels in Alzheimer disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Endocrine (2022)
-
The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease
Molecular Psychiatry (2019)
-
Adult-onset hypothyroidism increases ethanol consumption
Psychopharmacology (2019)