Abstract
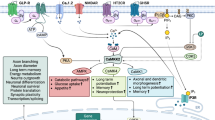
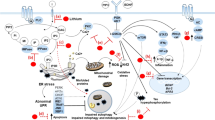
The complexity of the unique biology of bipolar disorder—which includes the predisposition to episodic, and often progressive, mood disturbance—and the dynamic nature of compensatory processes in the brain, coupled with limitations in experimental design, have hindered our ability to identify the underlying pathophysiology of this fascinating neuropsychiatric disorder. Although we have yet to identify the specific abnormal genes in mood disorders, recent studies have implicated critical signal transduction pathways as being integral to the pathophysiology and treatment of bipolar disorder. In particular, a converging body of preclinical data has shown that chronic lithium and valproate, at therapeutically relevant concentrations, regulate the protein kinase C signaling cascade. This has led to the investigation of the antimanic efficacy of tamoxifen (at doses sufficient to inhibit protein kinase C), with very encouraging preliminary results. A growing body of data also suggests that impairments of neuroplasticity and cellular resilience may also underlie the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. It is thus noteworthy that mood stabilizers, such as lithium and valproate, indirectly regulate a number of factors involved in cell survival pathways—including cAMP response element binding protein, brain derived neurotrophic factor, bcl-2 and mitogen-activated protein kinases—and may thus bring about some of their delayed long-term beneficial effects via under-appreciated neurotrophic effects. The development of novel treatments, which more directly target molecules involved in critical central nervous system cell survival and cell death pathways, has the potential to enhance neuroplasticity and cellular resilience, thereby modulating the long-term course and trajectory of these devastating illnesses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lenox RH . Role of receptor coupling to phosphoinositide metabolism in the therapeutic action of lithium Adv Exp Med Biol 1987 221: 515–530
Manji HK, Drevets WC, Charney DS . The cellular neurobiology of depression Nature Med 2001 7: 541–547
Drevets WC . Neuroimaging studies of mood disorders Biol Psychiatry 2000 48: 813–829
Garlow SJ, Musselman DL, Nemeroff CB . The neurochemistry of mood disorders clinical studies In: Charney DS, Nester EJ, Bunney BS (eds) Neurobiology of Mental Illness Oxford University Press: New York 1999 pp 348–364
Wang JF, Young LT, Li PP et al. Signal transduction abnormalities in bipolar disorder In: Joffe RT, Young LT (eds) Bipolar Disorder: Biological Models and Their Clinical Application Marcel Dekker: New York 1996 pp 41–79
Bowden CL . Toward an integrated biological model of bipolar disorder In: Young LT, Joffe RT (eds) Bipolar Disorder: Biological Models and Their Clinical Application Marcel Dekker: New York 1997 pp 235–254
Bhalla US, Iyengar R . Emergent properties of networks of biological signaling pathways Science 1999 283: 381–387
Jope RS, Williams MB . Lithium and brain signal transduction systems Biochem Pharmacol 1994 77: 429–441
Moore GJ, Bebchuk JM, Parrish JK et al. Temporal dissociation between lithium-induced CNS myo-inositol changes and clinical response in manic-depressive illness Am J Psychiatry 1999 156: 1902–1908
Jope RS . Anti-bipolar therapy: mechanism of action of lithium Mol Psychiatry 1999 4: 117–128
Manji HK, Lenox RH . Protein kinase C signaling in the brain: molecular transduction of mood stabilization in the treatment of bipolar disorder Biol Psychiatry 1999 46: 1328–1351
Hahn CG, Friedman E . Abnormalities in protein kinase C signaling and the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder Bipolar Disord 1999 1: 81–86
Manji HK, Moore GJ, Rajkowska G, Chen G . Neuroplasticity and cellular resilience in mood disorders. Millennium article Mol Psychiatry 2000 5: 578–593
Stabel S, Parker PJ . Protein kinase C Pharmacol Ther 1991 51: 71–95
Newton AC . Protein kinase C: structure, function and regulation J Biol Chem 1995 270: 28495–28498
Nishizuka Y . Protein kinase C and lipid signaling for sustained cellular responses FASEB J 1995 9: 484–496
Manji HK, Etcheberrigaray R, Chen G, Olds JL . Lithium decreases membrane-associated protein kinase C in hippocampus: selectivity for the ∞ isozyme J Neurochem 1993 61: 2303–2310
Chen G, Huang LD, Manji HK . Mood stabilizers regulate cytoprotective and mRNA binding proteins in the brain: long term effects on cell survival and transcript stability Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2001 4: 47–64
Lenox RH, Watson DG, Ellis J . Chronic lithium administration alters a prominent PKC substrate in rat hippocampus Brain Res 1992 570: 333–340
Chen G, Manji HK, Hawver DB, Wright CB, Potter WZ . Chronic sodium valproate selectively decreases protein kinase C alpha and epsilon in vitro J Neurochem 1994 63: 2361–2365
Conn PJ, Sweatt JD . Protein kinase C in the nervous system In: Kuo JF (ed) Protein Kinase C Oxford University Press: New York 1994 pp 199–235
Couldwell WT, Weiss MH, DeGiorgio CM et al. Clinical and radiographic response in a minority of patients with recurrent malignant gliomas treated with high dose tamoxifen Neurosurgery 1993 32: 485–489
Bebchuk JM, Arfken CL, Dolan-Manji S et al. A preliminary investigation of a protein kinase C inhibitor (tamoxifen) in the treatment of acute mania Arch Gen Psychiatry 2000 57: 95–97
Hyman SE, Nestler EJ . Initiation and adaptation: a paradigm for understanding psychotropic drug action Am J Psychiatry 1996 153: 151–162
Kandel ER . A new intellectual framework for psychiatry Am J Psychiatry 1998 155: 457–469
Ikonomov O, Manji HK . Molecular mechanisms underlying mood-stabilization in manic-depressive illness: the phenotype challenge Am J Psychiatry 1999 156: 1506–1514
Flint J, Corley R . Do animal models have a place in the genetic analysis of quantitative human behavioral traits? J Mol Med 1996 74: 515–521
Manji HK, Lenox RH . Signaling: cellular insights into the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder Biol Psychiatry 2000 48: 518–530
Chen G, Zeng WZ, Jiang L et al. The mood stabilizing agents lithium and valproate robustly increase the expression of the neuroprotective protein bcl-2 in the CNS J Neurochem 1999 72: 879–882
Manji HK, Moore GJ, Chen G . Lithium at 50: have the neuroprotective effects of this unique medication been overlooked? Biol Psychiatry 1999 46: 929–940
Rajkowska G, Halaris A, Selemon LD . Reductions in neuronal and glial density characterize the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in bipolar disorder Biol Psychiatry 2001 49: 741–752
Chen G, Rajkowska G, Du F, Seraji-Bozorgzad N, Manji HK . Enhancement of hippocampal neurogenesis by lithium J Neurochem 2000 75: 1729–1734
Chen RW, Chuang DM . Long term lithium treatment suppresses p53 and Bax expression but increases bcl-2 expression J Biol Chem 1999 274: 6039–6042
Lu R, Song L, Jope RS . Lithium attenuates p53 levels in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells Neuroreport 1999 10: 1123–1125
Nonaka S, Chuang DM . Neuroprotective effects of chronic lithium on focal cerebral ischemia in rats Neuroreport 1998 9: 2081–2084
Mamounas LA, Blue ME, Siuciak JA, Anthony AC . BDNF promotes the survival and sprouting of serotonergic axons in the rat brain J Neurosci 1995 15: 7929–7939
Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC . Programmed cell death in animal development Cell 1997 88: 347–354
Pettman B, Henderson CE . Neuronal cell death Neuron 1998 20: 633–647
Thoenen H . Neurotrophins and neuronal plasticity Science 1995 270: 593–598
Segal RA, Greenberg ME . Intracellular signaling pathways activated by neurotrophic factors Ann Rev Neurosci 1996 19: 463–489
Tao X, Finkbeiner S, Arnold DB, Shaywitz AJ, Greenberg ME . Ca2+ influx regulates BDNF transcription by a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism Neuron 1998 20: 709–726
Riccio A, Ahn S, Davenport CM, Blendy JA, Ginty DD . Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons Science 1999 286: 2358–2361
Bonni A, Brunet A, West AE, Datta SR, Takasu MA, Greenberg ME . Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms Science 1999 286: 1358–1362
Gutkind JS . The pathways connecting G protein-coupled receptors to the nucleus through divergent mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades J Biol Chem 1998 273: 1839–1842
English JD, Sweatt JD . A requirement for the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in hippocampal long term potentiation J Biol Chem 1997 272: 19103–19106
Martin KC, Michael D, Rose JC et al. MAP kinase translocates into the nucleus of the presynaptic cell and is required for long-term life facilitation in Aplysia Neuron 1997 18: 899–912
Roberson ED, English JD, Adams JP, Selcher JC, Kondratick C, Sweatt JD . The mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade couples PKA and PKC to cAMP response element binding protein phosphorylation in area CA1 of hippocampus J Neurosci 1999 19: 4337–4348
Nestler EJ . Antidepressant treatments in the 21st century Biol Psychiatry 1998 44: 526–533
Yuan PX, Chen G, Manji HK . Lithium activates the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases (JNKs) in vitro and in the CNS in vivo J Neurochem 1999 73: 2299–2309
Yuan PX, Huong LD, Jiang YM, Gutkind JS, Manji HK, Chen G . The mood-stabilizer valproic acid activates mitogen-activated protein kinases and promotes neurite growth J Biol Chem 2001 276: 31674–31683
Finkbeiner S . CREB couples neurotrophin signals to survival messages Neuron 2000 25: 11–14
Manji HK, Duman RS . Impairments of neuroplasticity and cellular resilience in severe mood disorders: implications for the development of novel therapeutics Psychopharmacol Bull 2001 35: 5–49
McEwen BS . Stress and hippocampal plasticity Ann Rev Neurosci 1999 22: 105–122
Duman RS, Malberg J, Nakagawa S, D'Sa C . Neuronal plasticity and survival in mood disorders Biol Psychiatry 2000 48: 32–39
Drevets WC, Price JL, Simpson JR Jr et al. Subgenual prefrontal cortex abnormalities in mood disorders Nature 1997 386: 824–827
Tsai G, Coyle JT . N-acetylaspartate in neuropsychiatric disorders Prog Neurobiol 1995 46: 531–540
Moore GJ, Bebchuk JM, Hasanat K et al. Lithium increases N-acetyl-aspartate in the human brain: in vivo evidence in support of bcl-2’s neurotrophic effects? Biol Psychiatry 2000 48: 1–8
Moore GJ, Bebchuk JM, Wilds IB, Chen G, Manji HK . Lithium-induced increase in human brain gray matter The Lancet 2000 356: 1241–1242
Goodwin FK, Jamison KR . Manic-Depressive Illness Oxford University Press: New York 1990
Sheline Y, Sang M, Mintun M, Gado M . Depression duration but not age predicts hippocampal volume loss in medical healthy women with recurrent major depression J Neurosci 1999 19: 5034
Strakowski SM, Wilson DR, Tohen M et al. Structural brain abnormalities in first-episode mania Biol Psychiatry 1993 33: 602–609
Hirayasu Y, Shenton ME, Salisbury DF et al. Subgenual cingulate cortex volume in first-episode psychosis Am J Psychiatry 1999 156: 1091–1093
Li PP, Andreopoulos S, Warsh JJ . Signal transduction abnormalities in bipolar affective disorder In: Reith MEA (ed) Cerebral Signal Transduction Humana Press: New Jersey 2000 pp 283–312
Guo Z, Zhou D, Schultz PG . Designing small-molecule switches for protein–protein interactions Science 2000 288: 2042–2045
Acknowledgements
The author's research was supported by the NIMH, the Theodore and Vada Stanley Foundation and NARSAD. Ms Kerri R Gibala provided outstanding editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manji, H., Chen, G. PKC, MAP kinases and the bcl-2 family of proteins as long-term targets for mood stabilizers. Mol Psychiatry 7 (Suppl 1), S46–S56 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001018
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001018
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mood and behavior regulation: interaction of lithium and dopaminergic system
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2023)
-
The Impact of Lithium on Brain Function in Bipolar Disorder: An Updated Review of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies
CNS Drugs (2021)
-
NMDA Antagonists and Their Role in the Management of Bipolar Disorder: a Review
Current Behavioral Neuroscience Reports (2020)
-
Validation of the animal model of bipolar disorder induced by Ouabain: face, construct and predictive perspectives
Translational Psychiatry (2019)
-
Effects of psychotropic drugs on inflammation: consequence or mediator of therapeutic effects in psychiatric treatment?
Psychopharmacology (2016)