Abstract
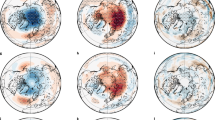
THE chemical processes involved in the depletion of polar stratospheric ozone are now fairly well understood1,2. But the effect of small-scale stirring and mixing of the chemical species involved can be misrepresented in three-dimensional chemical-transport models because of their coarse resolution. Because of the non-linearities in the chemical rate laws, especially those involving chlorine in the main catalytic cycle, these effects can be important—particularly in the Arctic, where the polar vortex is less uniform and less isolated from surrounding air than in the Antarctic. Here we use a very-high-resolution model with simplified ozone-depletion chemistry to show that the depletion is sensitive to small-scale inhomogeneities in the distribution of reactant species. Under the conditions of the winter of 1994–95 the effect is large enough to account for the observed discrepancies of about 40% between modelled and observed ozone depletion in the Arctic environment3–5.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webster, C. et al. Science 261, 1130–1133 (1993).
Lefèvre, F. et al. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 8183–8195 (1994).
Goutail, F. et al. in Air Pollution Res. Rep. No. 56 (eds Pyle, J. A., Harris, N. R. P. & Amanatadis, G. T.) 574–579 (European Communities, Brussels, 1996).
Goutail, F. et al. J. Atmos. Chem. (submitted).
Chipperfield, M. et al. J. Atmos. Chem. (submitted).
Holton, J. R. et al. Rev. Geophys. 33, 403–436 (1995).
Edouard, S., Legras, B. & Zeitlin, V. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 16771–16779 (1996).
Thuburn, J. & Tan, D. J. Geophys. Res. (submitted).
Haynes, P. H. & Anglade, J. J. Atmos. Sci. (in the press).
Selmin, V. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 102, 107–138 (1993).
van Leer, B. J. Comput. Phys. 23, 276–299 (1977).
Salawitch, R., Wofsy, S. & Gottlieb, E. P. Science 261, 1146–1149 (1993).
Molina, M. J. & Molina, L. T. J. Phys. Chem. 91, 433–436 (1987).
Molina, M. J., Tso, T., Molina, L. T. & Wang, F. Science 238, 1253–1257 (1987).
DeMore, W. B. NASA Tech. Rep. 92–20 (Jet Propulsion Lab., Pasadena, 1992).
Brunet, G., Vautard, R., Legras, B. & Edouard, S. Mon. Weath. Rev. 123, 1037–1058 (1995).
Haynes, P. H. & Ward, W. E. J. Atmos. Sci. 50, 3431–3453 (1993).
Manney, G. et al. Geophys. Res. Lett. 23, 85–88 (1996).
Donovan, D. et al. Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 3489–3492 (1996).
Chipperfield, M., Cariolle, D. & Simon, P. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 1467–1470 (1994).
Bojkov, R. et al. Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 2729–2732 (1995).
Pommereau, J. P. & Goutail, F. Geophys. Res. Lett. 15, 891–893 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edouard, S., Legras, B., Lefèvre, F. et al. The effect of small-scale inhomogeneities on ozone depletion in the Arctic. Nature 384, 444–447 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/384444a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/384444a0
This article is cited by
-
Universal alignment in turbulent pair dispersion
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Probability distribution function of a forced passive tracer in the lower stratosphere
Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2007)
-
Scalar turbulence
Nature (2000)
-
Ubiquity of quasi-horizontal layers in the troposphere
Nature (1999)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.