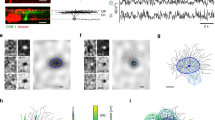
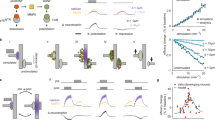
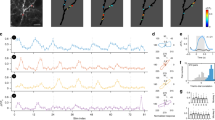
Abstract
ACTIVE membrane mechanisms have been found in the dendrites of many nerve cells1–7. Their contribution to dendritic signal processing, however, remains unclear8 because few experimental preparations allow for detailed characterization of dendritic physiology under normal conditions. To investigate the functional implications of active dendritic processes in an in vivo preparation, we compared the response properties of different types of non-spiking, motion-sensitive interneurons of the fly visual system, only one of which is equipped with a fast sodium inward current in its axon as well as in its dendrite. We report here that cells with fast activating sodium currents can respond to temporal changes in their synaptic input signals up to much higher frequencies than can those which lack such currents. Thus fast sodium currents lead to a frequency-dependent amplification of synaptic signals, enhancing cellular responses specifically to transient inputs which otherwise would be attenuated because of the passive properties of the dendritic tree.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spencer, W. A. & Kandel, E. R. J. Neurophysiol. 24, 272–285 (1961).
Stuart, G. J. & Sakmann, B. Nature 367, 69–72 (1994).
Spruston, N., Schiller, Y., Stuart, G. & Sakmann, B. Science 268, 297–300 (1995).
Magee, J. C. & Johnston, D. Science 268, 301–304 (1995).
Llinas, R. R. Science 242, 1654–1664 (1988).
Laurent, G. J. Physiol., Lond. 470, 45–54 (1993).
Yuste, R., Gutnick, M. J., Saar, D., Delaney, K. R. & Tank, D. W. Neuron 13, 23–43 (1994).
Bemander, O., Koch, C. & Douglas, R. J. J. Neurophysiol. 72, 2743–2753 (1994).
Hausen, K. in Photoreception and Vision in Invertebrates (ed. Ali, M. A.) 523–559 (Plenum, New York, 1984).
Egelhaaf, M. & Borst, A. J. Neurosci. 13, 4563–4574 (1993).
Strausfeld, N. J. in Photoreception and Vision in Invertebrates (ed. Ali, M. A.) 483–522 (Plenum, New York, 1984).
Borst, A. & Egelhaaf, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 4139–4143 (1992).
Haag, J., Egelhaaf, M. & Borst, A. Neurosci. Lett. 140, 173–176 (1992).
Hengstenberg, R. Nature 270, 338–340 (1977).
Hausen, K. Z. Naturforsch. 31c, 629–633 (1976).
Eckert, H. & Dvorak, D. R. J. Insect Physiol. 29, 547–560 (1983).
Egelhaaf, M., Borst, A., Warzecha, A. K., Flecks, S. & Wildemann, A. J. Neurophysiol. 69, 340–351 (1993).
Hausen, K. Biol. Cybern. 45, 143–156 (1982).
Hausen, K. Biol. Cybern. 46, 67–79 (1982).
Haag, J. thesis, Univ. Tuebingen (1994).
Borst, A., Egelhaaf, M. & Haag, J. J. comput. Neurosci. 2, 5–18 (1995).
Reichardt, W. J. comp. Physiol. A161, 533–547 (1987).
Borst, A. & Egelhaaf, M. Trends Neurosci. 12, 297–306 (1989).
Borst, A. & Egelhaaf, M. in Visual Motion and its Role in the Stabilization of Gaze (eds Miles, F. A. & Wallman, J.) 3–27 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1993).
Gauck, V., Egelhaaf, M. & Borst, A. in Göttingen Neurobiology Report 1994 (eds Elsner, N. & Breer, H.) 445 (Thieme, Stuttgart, 1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haag, J., Borst, A. Amplification of high-frequency synaptic inputs by active dendritic membrane processes. Nature 379, 639–641 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/379639a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/379639a0
This article is cited by
-
Non-uniform weighting of local motion inputs underlies dendritic computation in the fly visual system
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Subcellular mapping of dendritic activity in optic flow processing neurons
Journal of Comparative Physiology A (2014)
-
Different receptive fields in axons and dendrites underlie robust coding in motion-sensitive neurons
Nature Neuroscience (2009)
-
Encoding and processing biologically relevant temporal information in electrosensory systems
Journal of Comparative Physiology A (2006)
-
Dye-coupling visualizes networks of large-field motion-sensitive neurons in the fly
Journal of Comparative Physiology A (2005)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.