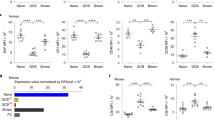
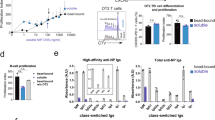
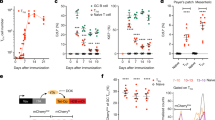
Abstract
GERMINAL centres are dynamic microenvironments of B-lympho-cyte differentiation, which develop in secondary lymphoid tissues during immune responses1-3. Within germinal centres, activated B lymphocytes proliferate and point mutations are rapidly introduced into the genes encoding their immunoglobulin receptors4-10. As a result, new specificities of B cells are created, including those with a heightened capacity to bind the immunizing antigen4-11. Immunoglobulin gene mutation can also lead to reactivity to self antigens12-14. It has been suggested that any newly formed self-reactive B cells are eliminated within the germinal centre in order to avoid autoimmunity15,16. Here we present evidence that antigen-specific, high-affinity, germinal-centre B cells are rapidly killed by apoptosis in situ when they encounter soluble antigen. The effect seems to act directly on the B cells, rather than through helper T cells. Furthermore, the apoptosis is unique to germinal-centre cells, and is only incompletely impeded by constitutive expression of the proto-oncogene bcl-2. This phenomenon may reflect clonal deletion of self-reactive B cells within germinal centres.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacLennan, I. C. M. A. Rev. Immun. 12, 117–139 (1994).
MacLennan, I. C. M., Liu, Y. J., Oldfield, S., Zhang, J. & Lane, P. J. L. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immun. 159, 138–148 (1990).
Jacob, J., Kassir, R. & Kelsoe, G. J. exp. Med. 172, 1165–1175 (1991).
Berek, C., Berger, A. & Apel, M. Cell. 67, 1121–1129 (1991).
Jacob, J., Kelsoe, G., Rajewsky, K. & Weiss, U. Nature. 354, 389–392 (1991).
Lalor, P. A., Nossal, G. J. V., Sanderson, R. D. & McHeyzer-Williams, M. G. Eur. J. Immun. 22, 3001–3011 (1992).
McHeyzer-Williams, M. G., McLean, M. J., Lalor, P. A. & Nossal, G. J. V. J. exp. Med. 178, 295–307 (1993).
Kuppers, R., Zhao, M., Hansmann, M. L. & Rajewsky, K. EMBO J. 12, 4955–4967 (1993).
Allen, D. et al. Immun. Rev. 96, 5–22 (1987).
Allen, D., Simon, T., Sablitzky, F., Rajewsky, K. & Cumano, A. EMBO. J. 7, 1995–2001 (1988).
Berek, C. & Milstein, C. Immun. Rev. 96, 23–41 (1987).
Shlomchik, M. J., Marshak-Rothstein, A., Wolfowicz, C. B., Rothstein, T. L. & Weigert, M. G. Nature. 328, 805–811 (1987).
Shlomchik, M. et al. J. exp. Med. 171, 265–297 (1990).
Diamond, B. et al. A. Rev. Immun. 10, 737–757 (1992).
Linton, P.-J., Rudie, A. & Klinman, N. R. J. Immun. 146, 4099–4104 (1991).
Nossal, G. J. V., Karvelas, M. & Pulendran, B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 3088–3092 (1993).
Jack, R. S., Imanishi-Kari & Rajewsky, K. Eur. J. Immun. 7, 559–565 (1977).
Reth, M. G., Hammerling, G. J. & Rajewsky, K. Eur. J. Immun. 8, 393–400 (1978).
Herzenberg, L. A., Black, S. J., Tokuhisha, T. & Herzenberg, L. A. J. exp. Med. 151, 1071–1087 (1980).
Gavrieli, Y., Sherman, Y. & Ben-Sasson, S. A. J. Cell. Biol. 119, 493–501 (1992).
Theofilopoulos, A. N. & Dixon, F. J. Adv. Immun. 28, 89–220 (1978).
Vaux, D. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 786–789 (1993).
Nakayama, K.-i. et al. Science. 261, 1548–1588 (1993).
Veis, D. J., Sorenson, C. M., Shutter, J. R. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Cell. 75, 229–240 (1993).
Hartley, S. B. et al. Cell. 72, 325–335 (1993).
Nisitani, S., Tsubata, T., Murakami, M., Okamoto, M. & Honjo, T. J. exp. Med. 178, 1247–1254 (1993).
Hockenbery, D. M., Zutter, M., Hickey, W., Nahm, M. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 6961–6965 (1991).
Liu, Y. J. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 21, 1905–1910 (1991).
Smith, K. G. C., Weiss, U., Rajewsky, K., Nossal, G. J. V. & Tarlinton, D. M. Immunity. 1, 803–813 (1994).
Strasser, A. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 8661–8665 (1991).
Shokat, K. M. & Goodnow, C. C. Nature 375, 334–338 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pulendran, B., Kannourakis, G., Nouri, S. et al. Soluble antigen can cause enhanced apoptosis of germinal-centre B cells. Nature 375, 331–334 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/375331a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/375331a0
This article is cited by
-
FcγRIIb differentially regulates pre-immune and germinal center B cell tolerance in mouse and human
Nature Communications (2019)
-
B cell signaling in context
Nature Immunology (2019)
-
CXCR5+PD-1+ follicular helper CD8 T cells control B cell tolerance
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Poly- and autoreactivity of HIV-1 bNAbs: implications for vaccine design
Retrovirology (2018)
-
Germinal centers and autoimmune disease in humans and mice
Immunology & Cell Biology (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.