Abstract
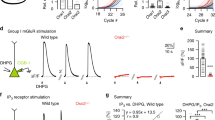
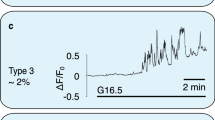
lNOSiTOL-l,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3)-induced Ca2+ release is a key mechanism for intracellular Ca2+ mobilization1. The rate of Ca2+ release declines progressively with time until a higher concen-tration of InsP3 is added, which is referred to as the incremental detection mechanism2. Two hypotheses have been postulated to explain these complex kinetics: (1) Ca2+ stores consist of multiple compartments (quanta) with different sensitivities to InsP3 (refs 3-7), and (2) the rate of Ca2+ release is modulated by the Ca2+ concentration in the lumen of Ca2+ stores8–12. We studied this phenomenon by real-time measurement of the luminal Ca2+ con-centration of Ca2+ stores using a Ca2+-sensitive fluorescent dye, but our results were not explained by either of these hypotheses. Here we report that the complex kinetics of Ca2+ release results from the heterogeneous density of equally InsP3-sensitive channels on the Ca2+ stores. This heterogeneity creates Ca2+ stores with apparently different sensitivities to InsP3, which may have different functions in Ca2+ mobilization.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge, M. J. Nature 361, 315–325 (1993).
Meyer, T. & Stryer, L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 3841–3845 (1990).
Muallem, S., Pandol, S. J. & Beeker, T. G. J. biol. Chem. 264, 205–212 (1989).
Parker, I. & Ivorra, I. Science 250, 977–979 (1990).
Oldershaw, K. A., Nunn, D. L. & Taylor, C. W. Biochem. J. 278, 705–708 (1991).
Ferris, C. D., Cameron, A. M., Huganir, R. L. & Snyder, S. H. Nature 356, 350–352 (1992).
Bootman, M. D., Berridge, M. J. & Taylor, C. W. J. Physiol., Lond. 450, 163–178 (1992).
Irvine, R. F. FEBS Lett. 263, 5–9 (1990).
Missiaen, L., Taylor, C. W. & Berridge, M. J. Nature 352, 241–244 (1991).
Missiaen, L., De-Smedt, H., Droogmans, G. & Casteels, R. Nature 357, 599–602 (1992).
Loomis-Husselbee, J. W. & Dawson, A. P. Biochem. J. 289, 861–866 (1993).
Parys, J. B., Missiaen, L., De Smedt, H. & Casteels, R. J. biol. Chem. 268, 25206–25212 (1993).
Raju, B., Murphy, E., Levy, L. A., Hall, R. D. & London, R. E. Am. J. Physiol. 256, C54O–C548 (1989).
Uyama, Y., Imaizumi, Y. & Watanabe, M. Br. J. Pharmac. 106, 208–214 (1992).
Kobayashi, S., Somlyo, A. V. & Somlyo, A. P. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 153, 625–631 (1988).
Iino, M. J. gen. Physiol. 95, 1103–1122 (1990).
Bezprozvanny, I., Watras, J. & Ehrlich, B. E. Nature 351, 751–754 (1991).
Finch, E. A., Turner, T. J. & Goldin, S. M. Science 252, 443–446 (1991).
Iino, M. & Endo, M. Nature 360, 76–78 (1992).
Hirose, K., Iino, M. & Endo, M. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 194, 726–732 (1993).
Swillens, S. Molec. Pharmac. 41, 110–114 (1992).
Reonard-Rooney, D. C., Hajnóczky, G., Seitz, M. B., Schneider, T. G. & Thomas, A. P. J. biol. Chem. 268, 23601–23610 (1993).
Somlyo, A. V. in Handbook of Physiology Section 2: Vol. II (eds Bohr, D. F., Somlyo, A. P. & Sparks, H. V.) 33–67 (American Physiological Society, Bethesda, 1980).
Kasai, H. & Petersen, O. H. Trends Neurosci. 17, 95–101 (1994).
Short, A. D., Klein, M. G., Schneider, M. F. & Gill, D. L. J. biol. Chem. 268, 25887–25893 (1993).
Hofer, A. M. & Machen, T. E. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 2598–2602 (1993).
Iino, M. J. gen. Physiol. 94, 363–383 (1989).
Ahnert-Hilger, G. & Gratzl, M. Trends pharmacol. Sci. 9, 195–197 (1988).
Ghosh, T. K., Mullaney, J. M., Tarazi, F. I. & Gill, D. L. Nature 340, 236–239 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirose, K., lino, M. Heterogeneity of channel density in inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ stores. Nature 372, 791–794 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/372791a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/372791a0
This article is cited by
-
Calcium‐pH crosstalks in rat mast cells: cytosolic alkalinization, but not intracellular calcium release, is a sufficient signal for degranulation
British Journal of Pharmacology (2000)
-
Regulatory and spatial aspects of inositol trisphosphate-mediated calcium signals
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (1999)
-
Mechanisms responsible for quantal Ca2+ release from inositol trisphosphate-sensitive calcium stores
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (1996)
-
Opening up Ca2+ stores with lnsP3
Nature (1995)
-
Luminal calcium regulation of calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Bioscience Reports (1995)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.