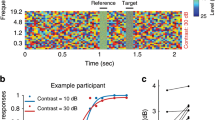
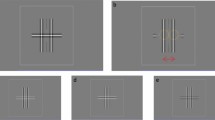
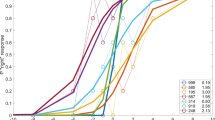
Abstract
NEURONS in the cat primary visual cortex are selective for particular contour orientations1 but their responsiveness can vary under certain conditions. After prolonged stimulation (adaptation), the contrast sensitivity of cortical cells is reduced2–5 and the 'gain' (the strength of response as a function of contrast) falls5,6. The response to an optimal contour is also reduced when a different stimulus is superimposed on the receptive field in the same eye7–9. Here we report that the sudden appearance of an inappropriate stimulus in one eye can interocularly suppress the activity of cortical neurons if they are already responding to an optimally oriented stimulus in the other eye. In strabismic cats, whose cortical neurons lack binocular facilitation, even contours of similar orientation shown to the two eyes trigger such suppression. This interocular control of cortical responsiveness could serve to veto signals from one eye under conditions that would otherwise cause double vision and perceptual confusion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hubel, D. H. & Wiesel, T. N. J. Physiol. 160, 106–154 (1962).
Maffei, L., Fiorentini, A. & Bisti, S. Science 182, 1036–1038 (1973).
Vautin, R. G. & Berkley, M. A. J. Neurophysiol. 40, 1051–1065 (1977).
Movshon, J. A. & Lennie, P. Nature 278, 850–852 (1979).
Albrecht, D. G., Farrar, S. B. & Hamilton, D. B. J. Physiol. 347, 713–739 (1984).
Ohzawa, I., Sclar, G. & Freeman, R. D. J. Neurophysiol. 54, 651–667 (1985).
Bonds, A. B. Vis. Neurosci. 2, 41–55 (1989).
Morrone, M. C., Burr, D. C. & Maffei, L. Proc. R. Soc., Lond. B216, 335–354 (1982).
DeAngelis, G. C., Robson, J. G., Ohzawa, I. & Freeman, R. D. J. Neurophysiol. 68, 144–163 (1992).
Barlow, H. B., Blakemore, C. & Pettigrew, J. D. J. Physiol. 193, 327–342 (1967).
Poggio, G. F. & Fischer, B. J. Neurophysiol. 40, 1392–1405 (1977).
Freeman, R. D. & Ohzawa, I. Vis. Res. 30, 1661–1676 (1990).
Freeman, R. D., Ohzawa, I. & Robson, J. G. J. Physiol. 396, 69P (1987).
Blakemore, C. Fiorentini, F. & Maffei, L. J. Physiol. 226, 725–749 (1972).
Morrone, M. C., Burr, D. C. & Speed, H. D. Expl Brain Res. 67, 635–644 (1987).
Holopigian, K., Blake, R. & Greenwald, M. J. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 29, 444–451 (1988).
Hubel, D. H. & Wiesel, T. N. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 1041–1059 (1965).
Xue, J. D., Freeman, R. D., Carney, T. & Shadlen, M. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 28 (suppl.), 102 (1987).
Matsuoka, K. Biol. Cybern. 49, 201–208 (1984).
Lehky, S. R. Perception 17, 215–228 (1988).
Blake, R. Psychol. Rev. 96, 145–167 (1989).
Sengpiel, F., Harrad, R. A. & Blakemore, C. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 18, 295 (1992).
Varela, F. J. & Singer, W. Expl Brain Res. 66, 10–20 (1987).
Tong, L., Guido, W., Tumosa, N., Spear, P. D. & Heidenreich, S. Vis. Neurosci. 8, 557–566 (1992).
Ts'o, D., Gilbert, C. D. & Wiesel, T. N. J. Neurosci. 6, 1160–1170 (1986).
Schwarz, C. & Bolz, J. J. Neurosci. 11, 2995–3007 (1991).
Somogyi, P., Kisvárday, Z. F., Martin, K. A. C. & Whitteridge, D. Neuroscience 10, 261–294 (1983).
Kisvárday, Z. F., Kim, D.-S., Eysel, U. T. & Bonhoeffer, T. Eur. J. Neurosci. 6 (suppl.), 14 (1993).
Douglas, R. J., Martin, K. A. C. & Whitteridge, D. Neural Comp. 1, 480–488 (1989).
Blakemore, C. & Price, D. J. J. Physiol. 384, 263–292 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sengpiel, F., Blakemore, C. Interocular control of neuronal responsiveness in cat visual cortex. Nature 368, 847–850 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/368847a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/368847a0
This article is cited by
-
Research on stereoscopic visual masking in binocular combination and unconscious rivalry
Multimedia Tools and Applications (2023)
-
Primary visual cortex and visual awareness
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2003)
-
Neuronal activity in human primary visual cortex correlates with perception during binocular rivalry
Nature Neuroscience (2000)
-
The neural basis of suppression and amblyopia in strabismus
Eye (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.