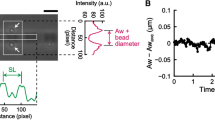
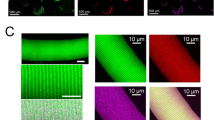
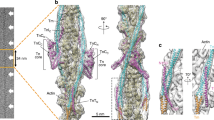
Abstract
THE development of mechanical force in skeletal muscle fibres is brought about by rapid increases in the intracellular calcium concentration (Ca2+transients) which can be detected by optical methods1–7. Local stimulation experiments8 and ultrastructural evidence9,10suggest that, at a microscopic level, these Ca2+ transients are generated by the release of Ca2+ ions from the terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to the depolarization of the transverse tubules (t-tubules)11–14. Nevertheless, to date, there is no functional information on the exact location at which Ca2+ release takes place. The present experiments were designed to obtain direct evidence about dynamic changes in localization and microscopic distribution of Ca2+ in a single sarcomere using two independent novel methodologies: confocal spot detection of Ca2+ transients15,16 and Ca2+ imaging with pulsed laser excitation17,18.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebashi, S. & Endo, M. Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol. 18, 123–183 (1968).
Sandow, A. A. Rev. Physiol. 32, 87–138 (1970).
Miledi, R., Parker, S. & Schalow, G. Prog. R. Soc. B198, 201–211 (1977).
Palade, P. & Vergara, J. J. gen. Physiol. 79, 679–707 (1982).
Baylor, S. M., Chandler, W. K. & Marshall, M. J. Physiol., Lond. 331, 179–210 (1982).
Vergara, J., Di Franco, M., Compagnon, D. & Suarez-lsla, B. Biophys. J. 59, 12–24 (1991).
Vergara, J. & Di Franco, M. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 311, 227–236 (1992).
Huxley, A. F. & Taylor, R. E. J. Physiol., Lond. 144, 426–441 (1958).
Winegrad, S. J. gen. Physiol. 55, 77–88 (1970).
Somlyo, A. V. et al. J. Cell Biol. 90, 577–594 (1981).
Endo, M. Physiol. Rev. 57, 71–108 (1977).
Schneider, M. F. & Chandler, W. K. Nature 242, 244–246 (1973).
Rios, E. & Pizarro, G. Physiol. Rev. 71, 849–908 (1991).
Fleisher, S. & Inui, M. A. Rev. Biophys. biophys. Chem 18, 333–364 (1989).
Escobar, A. & Vergara, J. Biophys. J. 64, A241 (1993).
Parker, I. & Ivorra, I. J. Physiol., Lond. 461, 133–165 (1992).
Hibino, M., Sigemori, M., Itoh, H., Nagayama, K. & Kinosita, K. Jr, Biophys. J. 59, 209–220 (1991).
Monck, J. R., Escobar, A., Robinson, I. M., Vergara, J. & Fernandez, J. M. Biophys. J. 66, A351 (1994).
Peachey, L. D. J. Cell Biol. 25, 209–231 (1965).
Vergara, J. & Escobar, A. Biophys. J. 64, A37 (1993).
Minta, A. et al. J. biol. Chem. 264, 8171–8178 (1989).
Wilson, T. & Carlini, A. R. Opt. Lett. 12, 227–229 (1987).
Dulhunty, A., Junankar, P. & Stanhope, C. Proc. R. Soc. B247, 69–75 (1992).
Takamatsu, T. & Wier, W. G. Cell Calcium 11, 111–120 (1990).
Niggli, E. & Lederer, W. J. Cell Calcium 11, 121–1130 (1990).
Parker, I. & Yao, Y. Proc. R. Soc. B246, 269–274 (1991).
Girard, S. & Clapham, D. Science 260, 229–232 (1993).
Grinvald, A., Frostig, R., Lieck, E. & Hildesheim, R. Physiol. Rev. 68, 1285–1358 (1988).
Monck, J., Oberhauser, A., Keating, T. & Fernandez, J. J. Cell Biol. 116, 745–759 (1992).
Sheppard, J. R. J. Microsc. 149, 73–75 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Escobar, A., Monck, J., Fernandez, J. et al. Localization of the site of Ca2 + release at the level of a single sarcomere in skeletal muscle fibres. Nature 367, 739–741 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/367739a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/367739a0
This article is cited by
-
Attenuated Ca2+ release in a mouse model of limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2A
Skeletal Muscle (2016)
-
Bioelectrochemical control mechanism with variable-frequency regulation for skeletal muscle contraction—Biomechanics of skeletal muscle based on the working mechanism of myosin motors (II)
Science China Technological Sciences (2012)
-
Major translocation of calcium upon epidermal barrier insult: imaging and quantification via FLIM/Fourier vector analysis
Archives of Dermatological Research (2011)
-
Ca2+ /S100 regulation of giant protein kinases
Nature (1996)
-
Two mechanisms of quantized calcium release in skeletal muscle
Nature (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.