Abstract
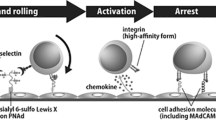
TISSUE-SPECIFIC homing of lymphocytes is regulated by interac-tions with the endothelium of specialized venules, such as the high endothelial venules (HEY) in lymph nodes and mucosal Ivmphoid tissues1–3. The mucosal vascular addressin, a 58–66K glycoprotein adhesion receptor for lymphocytes, is selectively expressed on HEV of mucosal lymphoid organ and on lamina propria venules and helps direct lymphocyte traffic to these mucosal tissues4,5. We now report the isolation of a complementary DNA that, on transfection into COS cells, encodes immunoreactive addressin that specifically binds the mucosal HEV-binding T-cell lymphoma TK1. The predic-ted amino-acid sequence defines the mucosal addressin as a novel immunoglobulin family member, MAdCAM-1, with two amino-terminal domains that display strong homology to previously described vascular adhesion receptors for leukocytes, ICAM-1 (ref. 6) and VCAM-1 (ref. 7). The membrane proximal domain is homologous to the third domain (Cα2) of another mucosa-associ-ated immunoglobulin family member, IgA1 (refs 8,9). In addition to the immunoglobulin domains, there is a erine/threonine-rich region which may serve as a backbone to present carbohydrate ligands to lymphocytes. MAdCAM-1 is thus a complex multi-domain receptor displaying several structural motifs that may participate in lymphocyte homing interactions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butcher, E. C., Scollay, R. G. & Weissman, I. L. Eur. J. Immun. 10, 551–561 (1980).
Butcher, E. C. Curr. Topics microbiol. Immun. 133, 2961–2965 (1986).
Picker, L. J. & Butcher, E. C. Ann. Rev. Immun. 10, 561–591 (1992).
Streeter, P. R., Berg, E. L., Rouse, B. N., Bargatze, R. F. & Butcher E. C. Nature 331, 41–46 (1988).
Nakache, M., Berg, E. L., Streeter, P. R. & Butcher, E. C. Nature 337, 179–181 (1989).
Kita, Y. et al. Biochim. biophys. Acta 1131, 108–110 (1992).
Osborn, L. et al. Cell 59, 1203–1211 (1989).
Kawamura, S., Omoto, K. & Ueda, S. Nucleic Acids Res. 17, 6732 (1989).
Flanagan, J. G., Lefranc, M. P. & Rabbitts, T. H. Cell 36, 681–688 (1984).
Montesano, R. et al. Cell 62, 435–445 (1990).
von Heijne, G. Nucleic Acids Res. 14, 4683–4690 (1986).
Berg, E. L., Picker, L. J., Robinson, M. K., Streeter, P. R. & Butcher, E. C. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation, Vol. 2, 111–129 (Academic, San Diego, 1991).
Seed, B. & Aruffo, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 3365–3369 (1987).
Simonet-Martin, M. T., Schaaf-Lafontaine, N. & Firket, H. C.r. Soc. Biol. 180, 229–233 (1986).
Williams, A. F. & Barclay, A. N. A. Rev. Immun. 6, 381–405 (1988).
Hunkapillar, T. & Hood, L. Adv. Immun. 44, 1–63 (1989).
Lipman, D. J. & Pearson, W. R. Science 227, 1435–1441 (1985).
Staunton, D. E., Dustin, M. L., Erickson, H. P. & Springer, T. A. Cell 61, 243–254 (1990).
Osborn, L. Vassallo, C. & Benjamen, C. D. J. exp. Med. 176, 99–107 (1992).
Holtzman, B., Mclntyre, B. W. & Weissman, I. L. Cell 56, 37–46 (1989).
Hession, C. et al. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 183, 163–169 (1992).
Frutiger, S., Hughes, G. J., Hanley, W. C., Kingzette, M. & Jaton, J. J. biol. Chem. 261, 6673–6681 (1986).
Jentoft, N. Trends Biochem. Sci. 15, 291–294 (1990).
Lasky, L. A. et al. Cell 69, 927–938 (1992).
Berg, E. L., Robinson, M. K., Warnock, R, A. & Butcher, E. C. J. Cell Biol. 114, 343–349 (1991).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1990).
Gallatin, W. M., Weissman, I. L. & Butcher, E. C. Nature 303, 30–34 (1983).
Jalkanen, S. T., Bargatze, R. F., de los Toyos, J. & Butcher E. C. J. Cell Biol 105, 983–990 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Briskin, M., McEvoy, L. & Butcher, E. MAdCAM-1 has homology to immunoglobulin and mucin-like adhesion receptors and to IgA1. Nature 363, 461–464 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/363461a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/363461a0
This article is cited by
-
Bile acids modulate colonic MAdCAM-1 expression in a murine model of combined cholestasis and colitis
Mucosal Immunology (2021)
-
Integrin-based therapeutics: biological basis, clinical use and new drugs
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2016)
-
β7-Integrin exacerbates experimental DSS-induced colitis in mice by directing inflammatory monocytes into the colon
Mucosal Immunology (2016)
-
Mucosal Addressin Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 of Rhesus Macaques: Molecular Cloning, Expression, and Alteration After Viral Infection
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2014)
-
Development of adenoviral vector-based mucosal vaccine against influenza
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.