Abstract
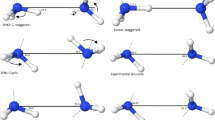
AMINES have long been characterized as amphoteric (acting as both donor and acceptor) in terms of their hydrogen-bond interactions in the condensed phase. With the possible exception of (NH3)2, however, no gas-phase complexes exhibiting hydrogen-bond donation by ammonia, the ‘simplest amine’, have been observed1,2. Here we present high-resolution optical and microwave spectra of the benzene–ammonia dimer in the gas phase, which show that the ammonia molecule resides above the benzene plane and undergoes free or nearly free internal rotation. In the vibrationally averaged structure, the C3 symmetry axis of NH3 is tilted by about 58° relative to the benzene C6 axis, such that the ammonia protons interact with the benzene π-cloud. Our ab initio calcula-tions predict a ‘monodentate’ minimum-energy structure, with very low barriers to rotation of ammonia. The larger separation of the two molecular components, and the smaller dissociation energy, relative to the benzene–water dimer3 reflect the weak hydrogen-bond donor capability of ammonia, but the observed geometry greatly resembles the amino–aromatic interaction found naturally in proteins4.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson, D. D. Jr, Fraser, G. T. & Klemperer, W. Science 238, 1670–1674 (1987).
Loeser, J. G. et al. J. chem. Phys. 97, 4727–4749 (1992).
Suzuki, S. et al. Science 257, 942–945 (1992).
Burley, S. K. & Petsko, G. A. FEBS Lett. 203, 139–143 (1986).
Pimental, G. C. & McClellan, A. L. The Hydrogen Bond, 202–203 (Freeman, San Francisco, 1960).
Dougherty, D. & Stauffer, D. A. Science 250, 1558–1560 (1990).
Waksman, G. et al. Nature 358, 646–653 (1992).
Perutz, M. F. in The Chemical Bond (ed. Zewail, A.) 17–30 (Academic, New York, 1992).
Wanna, J., Menapace, J. A. & Bernstein, E. R. J. chem. Phys. 85, 1795–1805 (1986).
Gotch, A. J. & Zwier, T. S. J. chem. Phys. 96, 3388–3401 (1992).
Read, W. G., Campbell, E. J. & Henderson, G., J. chem. Phys. 78, 3501–3508.
Baiocchi, F. A., Williams, J. H. & Klemperer, W. J. phys. Chem. 87, 2079–2084 (1983).
Cohen, R. C. & Saykally, R. J. J. phys. Chem. 96, 1024–1040 (1992).
Fritsch, M. J. et al. Gaussian 92 (Gaussian, Pittsburgh, PA, 1992).
Cheney, B. V., Schulz, M. W., Cheney, J. & Richards, W. G. J. Am. chem. Soc. 110, 4195–4198 (1988).
Bredas, J. L. & Street, G. B. J. chem. Phys. 90, 7291–7299 (1989).
Bumgarner, R. E. & Blake, G. A. Chem. Phys. Lett. 161, 308–314 (1989).
Suenram, R. D. et al. J. molec. Spectrosc. 137, 127–137 (1989).
Fraser, G. T., Lovas, F. J., Suenram, R. D., Nelson, D. D. & Klemperer, W. J. chem. Phys. 84, 5983–5988 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodham, D., Suzuki, S., Suenram, R. et al. Hydrogen bonding in the benzene–ammonia dimer. Nature 362, 735–737 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/362735a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/362735a0
This article is cited by
-
Strong structuring arising from weak cooperative O-H···π and C-H···O hydrogen bonding in benzene-methanol solution
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Rapid insight into C60 influence on biological functions of proteins
Structural Chemistry (2017)
-
A molecular dynamics study of the evolution from the formation of the \({\text {C}}_{6}{\text {F}}_{6}\) C 6 F 6 –( \({\text {H}}_{2}{\text {O}})_{n}\) H 2 O ) n small aggregates to the \({\text {C}}_{6}{\text {F}}_{6}\) C 6 F 6 solvation
Theoretical Chemistry Accounts (2015)
-
Direct detection of CH/π interactions in proteins
Nature Chemistry (2010)
-
Probing the architecture of the Mycobacterium marinum arylamine N-acetyltransferase active site
Protein & Cell (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.