Abstract
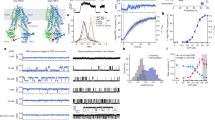
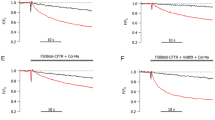
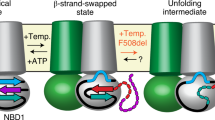
THE cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is a phosphorylation-regulated Cl- channel located in the apical membrane of epithelia1–10. Although cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by mutations in a single gene encoding CFTR11,12, the disease has a variable clinical phenotype13,14. The most common mutation associated with cystic fibrosis, deletion of a phenylalanine at position 508 (frequency, 67%), is associated with severe disease15–17. But some missense mutations, for example ones in which arginine is replaced by histidine at residue at 117 (R117H; 0.8%), tryptophan at 334 (0.4%), or proline at 347 (0.5%), are associated with milder disease15,17,18. These missense mutations affect basic residues located at the external end of the second (M2) and in the sixth (M6) putative membrane-spanning sequences. Here we report that, when expressed in heterologous epithelial cells, all three mutants were correctly processed and generated cyclic AMP-regulated apical Cl- currents. Although the macroscopic current properties were normal, the amount of current was reduced. Patch-clamp analysis revealed that all three mutants had reduced single-channel conductances. In addition, R117H showed altered sensitivity to external pH and had altered single-channel kinetics. These results explain the quantitative decrease in macroscopic Cl- current, and suggest that R117, R334 and R347 contribute to the pore of the CFTR Cl- channel. Our results also suggest why R117H, R334W and R347P produce less severe clinical disease and have implications for our understanding of cystic fibrosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rich, D. P. et al. Nature 347, 358–363 (1990).
Drumm, M. L. et al. Cell 62, 1227–1233 (1990).
Anderson, M. P. et al. Science 253, 202–205 (1991).
Bear, C. E. et al. Cell 68, 809–818 (1992).
Marino, C. R., Matovcik, L. M., Gorelick, F. S. & Cohn, J. A. J. clin. Invest. 88, 712–716 (1991).
Denning, G. M., Ostedgaard, L. S. & Welsh, M. J. J. Cell Biol. 118, 551–559 (1992).
Berger, H. A. et al. J. clin. Invest. 88, 1422–1431 (1991).
Tabcharani, J. A., Chang, X-B., Riordan, J. R. & Hanrahan, J. W. Nature 352, 628–631 (1991).
Cheng, S. H. et al. Cell 66, 1027–1036 (1991).
Anderson, M. P. et al. Cell 67, 775–784 (1991).
Riordan, J. R. et al. Science 245, 1066–1073 (1989).
Kerem, B. et al. Science 245, 1073–1080 (1989).
Boat, T. F., Welsh, M. J. & Beaudet, A. L. in The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease (eds Scriver, C. R., Beaudet, A. L., Sly, W. S. & Valle, D.) Vol. 6, 2649–2680 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1989).
Tsui, L.-C. & Buchwald, M., in Advances in Human Genetics (eds Harris, H. & Hirschhorn, K.) Vol. 20, 153–266 (Plenum, New York, 1991).
Tsui, L.-C. Trends Genet. 8, 392–398 (1992).
Kerem, E. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 323, 1517–1522 (1990).
Kristidis, P. et al. Am. J. hum. Genet. 50, 1178–1184 (1992).
Dean, M. et al. Cell 61, 863–870 (1990).
Cheng, S. H. et al. Cell 63, 827–834 (1990).
Gregory, R. J. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 11, 3886–3893 (1991).
Denning, G. M. et al. Nature 358, 761–764 (1992).
Nitsch, L., & Wollman, S. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 472–476 (1980)
Elroy-Stein, O., Fuerst, T. R. & Moss, B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 6126–6130 (1989).
Gregory, R. J. et al. Nature 347, 382–386 (1990).
Anderson, M. P. & Welsh, M. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 6003–6007 (1991).
McFadden, E. R. Jr in Pulmonary Diseases and Disorders (ed. Fishman, A. P.) Vol. 2, 1311–1323 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988).
Hamill, O. P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B. & Sigworth, F. J. Pfluegers Arch. 391, 85–100 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheppard, D., Rich, D., Ostedgaard, L. et al. Mutations in CFTR associated with mild-disease-form CI- channels with altered pore properties. Nature 362, 160–164 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/362160a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/362160a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular dynamics study of Cl− permeation through cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Rate of Lung Function Decline in People with Cystic Fibrosis Having a Residual Function Gene Mutation
Pulmonary Therapy (2022)
-
Novel frameshift variant of the CFTR gene: S511Lfs*2 from phenotype to molecular predictions
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)
-
Bicarbonate permeation through anion channels: its role in health and disease
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2020)
-
Use of ivacaftor in late diagnosed cystic fibrosis monozygotic twins heterozygous for F508del and R117H-7T – a case report
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.