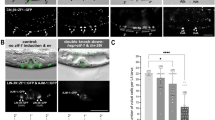
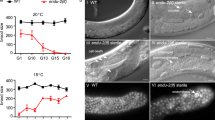
Abstract
THE induction of the hermaphrodite vulva1 and the migration of the sex myoblasts2,3 in the nematode Caenorhabdltis elegans are both controlled by intercellular signalling. The gonadal anchor cell induces formation of the vulva from nearby hypodermal cells4, and a set of somatic gonadal cells attract the migrating sex myoblasts to their final positions2. Many genes required for vulval induction have been identified1, including the let-23 receptor tyrosine kinase gene5–7 and the let-60 ras gene8–10. We report here the identification and characterization of a new gene, sem-5 (sem, sex muscle abnormal), that acts both in vulval induction and in sex myoblast migration. On the basis of its DNA sequence, sem-5 encodes a novel 228-amino-acid protein which consists almost entirely of one SH2 (SH, src homology region) and two SH3 domains. SH2 and SH3 domains are present in many signalling proteins regulated by receptor and non-receptor tyrosine kinases11. Mutations that impair sem-5 activity alter residues that are highly conserved among different SH2 and SH3 domains. Our results indicate that the sem-5 gene encodes a novel protein that functions in at least two distinct cell-signalling processes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horvitz, H. R. & Sternberg, P. W. Nature 351, 535–541 (1991).
Thomas, J. H., Stern, M. J. & Horvitz, H. R. Cell 62, 1041–1052 (1990).
Stern, M. J. & Horvitz, H. R. Development 113, 797–803 (1991).
Kimble, J. Devl Biol. 87, 286–300 (1981).
Ferguson, E. L., Sternberg, P. W. & Horvitz, H. R. Nature 326, 259–267 (1987).
Aroian, R. V., Koga, M., Mendel, J. E., Ohshima, Y. & Sternberg, P. W. Nature 348, 693–699 (1990).
Aroian, R. V. & Sternberg, P. W. Genetics 128, 251–267 (1991).
Beitel, G. J., Clark, S. G. & Horvitz, H. R. Nature 348, 503–509 (1990).
Han, M., Aroian, R. V. & Sternberg, P. W. Genetics 126, 899–913 (1990).
Han, M. & Sternberg, P. W. Cell 63, 921–931 (1990).
Koch, C. A., Anderson, D., Moran, M. F., Ellis, C. & Pawson, T. Science 252, 668–674 (1991).
Hedgecock, E. M., Culotti, J. G. & Hall, D. H. Neuron 4, 61–85 (1990).
Coulson, A., Sulston, J., Brenner, S. & Karn, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 7821–7825 (1986).
Coulson, A., Waterston, R., Kiff, J., Sulston, J. & Kohara, Y. Nature 335, 184–186 (1988).
Mello, C. C., Kramer, J. M., Stinchcomb, D. & Ambros, V. EMBO J. 10, 3959–3970 (1991).
Krause, M. & Hirsh, D. Cell 49, 753–761 (1987).
Altschul, S. F. & Lipman, D. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 5509–5513 (1990).
Sadowski, I., Stone, J. C. & Pawson, T. Molec. cell. Biol. 6, 4396–4408 (1986).
Stahl, M. L., Ferenz, C. R., Kelleher, K. L., Kriz, R. W. & Knopf, J. L. Nature 332, 269–272 (1988).
Suh, P. G., Ryu, S. H., Moon, K. H., Suh, H. W. & Rhee, S. G. Cell 54, 161–169 (1988).
Vogel, U. S. et al. Nature 335, 90–93 (1988).
Mayer, B. J., Hamaguchi, M. & Hanafusa, H. Nature 332, 272–275 (1988).
Lehmann, J. M., Riethmuller, G. & Johnson, J. P. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 1048 (1990).
Fields, C. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 1509–1512 (1990).
Mount, S. M. Nucleic Acids Res. 10, 459–472 (1982).
Shtivelman, E., Lifshitz, B., Gale, R. P., Roe, B. A. & Canaani, E. Cell 47, 277–284 (1986).
Mayer, B., Jackson, P., Van Etten, R. & Baltimore, D. Molec. cell. Biol. 12, 609–618 (1992)
Moran, M. F. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 8622–8626 (1990).
Matsuda, M., Mayer, B. J. & Hanafusa, H. Molec. cell. Biol. 11, 1607–1613 (1991).
Rodaway, A. R., Sternberg, M. J. & Bentley, D. L. Nature 342, 624 (1989).
Matsuda, M., Mayer, B. J., Fukui, Y. & Hanafusa, H. Science 248, 1537–1539 (1990).
Brenner, S. Genetics 77, 71–94 (1974).
Ferguson, E. L. & Horvitz, H. R. Genetics 110, 17–72 (1985).
Sulston, J. E. & Horvitz, H. R. Devl Biol. 56, 110–156 (1977).
Barstead, R. J. & Waterston, R. H. J. biol. Chem. 264, 10177–10185 (1989).
McCabe, P. C. in PCR Protocols (eds Innis, M. A., Gelfand, D. H., Sninsky, J. J. & White, T. J.) 76–83 (Academic, San Diego, 1990).
Jung, G., Korn, E. D. & Hammer, J. A. III Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 6720–6724 (1987).
Katzav, S., Martin, Z. D. & Barbacid, M. EMBO J. 8, 2283–2290 (1989).
Drubin, D. G., Mulholland, J., Zhu, Z. M. & Botstein, D. Nature 343, 288–290 (1990).
Takeya, T. & Hanafusa, H. Cell 32, 881–890 (1983).
Wasenius, V. M. et al. J. Cell Biol. 108, 79–93 (1989).
Huang, C. C., Hammond, C. & Bishop, J. M. J. molec Biol. 181, 175–186 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clark, S., Stern, M. & Horvritz, H. C. elegans cell-signalling gene sem-5 encodes a protein with SH2 and SH3 domains. Nature 356, 340–344 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/356340a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/356340a0
This article is cited by
-
Rs7219 Regulates the Expression of GRB2 by Affecting miR-1288-Mediated Inhibition and Contributes to the Risk of Schizophrenia in the Chinese Han Population
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2019)
-
A role for Ras in inhibiting circular foraging behavior as revealed by a new method for time and cell-specific RNAi
BMC Biology (2015)
-
A model of the regulatory network involved in the control of the cell cycle and cell differentiation in the Caenorhabditis elegans vulva
BMC Bioinformatics (2015)
-
The discovery of modular binding domains: building blocks of cell signalling
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2015)
-
Fibroblast growth factor signaling in mammalian tooth development
Odontology (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.