Abstract
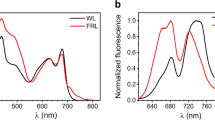
LIGHT energy for photosynthesis is collected by the antenna system, creating an excited state which migrates energetically 'downhill'. To achieve efficient migration of energy the antenna is populated with a series of pigments absorbing at progressively redshifted wavelengths. This variety in absorbing species in vivo has been created in a biosynthetically economical fashion by modulating the absorbance behaviour of one kind of (bacterio)chlorophyll molecule. This modulation is poorly understood but has been ascribed to pigment–pigment and pigment–protein interactions. We have examined the relationship between aromatic residues in antenna polypeptides and pigment absorption, by studying the effects of site-directed mutagenesis on a bacterial antenna complex. A clear correlation was observed between the absorbance of bacteriochlorophyll a and the presence of two tyrosine residues, αTyr44 and αTyr45, in the a subunit of the peripheral light-harvesting complex of Rhodobacter sphaeroides, a purple photosynthetic bacterium that provides a well characterized system for site-specific mutagenesis1–3. By constructing single (αTyr44,αTyr45-→;PheTyr) and then double (αTyr44, αTyr45→PheLeu) site-specific mutants, the absorbance of bacteriochlorophyll was blueshifted by 11 and 24 nm at 77 K, respectively. The results suggest that there is a close approach of tyrosine residues to bacteriochlorophyll, and that this proximity may promote redshifts in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sundström, V. & van Grondelle, R. J. opt. Soc. Am. 7, 1595–1603 (1990).
Feher, G., Allen, J. P., Okamura, M. Y. & Rees, D. C. Nature 339, 11–116 (1989).
Hunter, C. N., van Grondelle, R. & J. D. Olsen Trends biochem. Sci. 14, 72–76 (1989).
Kramer, H. J. M., van Grondelle, R. Hunter, C. N., Westerhius, W. H. J. & Amesz, J. Biochim. biophys. Acta. 765, 156–165 (1984).
Cogdell, R. G. et al. in Molecular Biology of Membrane-bound Complexes in Phototrophic Bacteria (eds Drews, G. & Dawes, E. A.) 211–218 (Plenum, New York, 1990).
van Mourik, F. et al. in Molecular Biology of Membrane-bound complexes in Phototrophic Bacteria (eds Drews, G. & Dawes, E. A.) 345–356 (Plenum, New York, 1990).
Brunisholz, R. A. & Zuber, R. In Photosynthetic Light-harvesting Systems. Organisation and Function (eds Scheer, H. & Schneider, S.) 103–114 (De Gruyter, New York, 1988).
Pearlstein, R. M. in Photosynthetic Light-harvesting Systems. Organisation and Function (eds Scheer, H. & Schneider, S.) 555–566 (De Gruyter, New York, 1988).
Gudowska-Novak, E., Newton, M. D. & Fajer, J. J. phys. Chem. 94, 5795–5801 (1990).
Van Grondelle, R., Kramer, H. J. M. & Rijgersberg, C. P. Biochim. biophys. Acta 682, 208–215 (1982).
Simon, R., Priefer, U. & Puhler, A. Biotechnology 1, 748–791 (1983).
Hunter, C. N. & Turner, G. J. gen. Microbiol. 134, (1988).
Burgess, J. G., Ashby, M. K. & Hunter, C. N. J. gen. Microbiol. 135, 1809–1816 (1989).
Jones, M. R. et al. Molec. Microbiol. (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fowler, G., Visschers, R., Grief, G. et al. Genetically modified photosynthetic antenna complexes with blueshifted absorbance bands. Nature 355, 848–850 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/355848a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/355848a0
This article is cited by
-
Light polarization dependency existing in the biological photosystem and possible implications for artificial antenna systems
Photosynthesis Research (2020)
-
Characterisation of a pucBA deletion mutant from Rhodopseudomonas palustris lacking all but the pucBAd genes
Photosynthesis Research (2018)
-
The role of charge-transfer states in the spectral tuning of antenna complexes of purple bacteria
Photosynthesis Research (2018)
-
Generality of relationships between leaf pigment contents and spectral vegetation indices in Mallorca (Spain)
Regional Environmental Change (2017)
-
Natural strategies for photosynthetic light harvesting
Nature Chemical Biology (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.