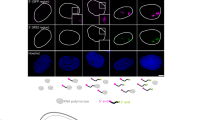
Abstract
RNA polymerase II transcripts, heterogeneous nuclear RNAs (hnRNAs), associate in the nucleus with specific proteins that bind premessenger RNA (hnRNP proteins)1,2 and with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs)3#150;5. These hnRNA-hnRNP-snRNP complexes assemble on nascent transcripts and hnRNA is processed to mRNA in them6–8. HnRNP proteins have been localized to the nucleoplasm9–13 and their functions were presumed to be limited to nuclear events in mRNA biogenesis. It was proposed that an exchange of hnRNP for mRNA-binding proteins accompanies transport of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm1,14. We show here that several of the abundant hnRNP proteins, including Al, shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. HnRNP proteins may thus also have cytoplasmic functions. Furthermore, when in the cytoplasm, Al is bound to mRNA and RNA polymerase II transcription is necessary before it can return to the nucleus. We propose that the cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein complex of mRNA with hnRNP proteins is the substrate of nuclear–cytoplasmic transport of mRNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dreyfuss, G. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 2, 459–498 (1986).
Dreyfuss, G., Swanson, M. S. & Piñol-Roma, S. Trends Biochem. Sci. 13, 86–91 (1988).
Steitz, J. A. et al. in Functions of the Abundant snRNPs. Structure and Function of Major and Minor Smalt Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein Particles (ed. Birnstiel, M. L.) (Sprínger, Berlin, 1988)
Lührmann, R., Kastner, B. & Bach, M. Biochym. biophys. Acta 1087, 265–292 (1990).
Gall, J. G. Science 252, 1499–1500 (1991).
Osheim, Y. N., Miller, O. L. & Beyer, A. L. Cell 43, 143–151 (1985).
Fakan, S., Leser, G. & Martin, T. E. J. Cell Biol. 103, 1153–1157 (1986).
Wu, Z., Murphy, C., Callan, H. G. & Gall, J. G. J. Cell Biol. 113, 465–483 (1991).
Martin, T. E. & Okamura, C. S. in The Cell Nucleus (ed. Busch. H.) Vol. 9 119–144 (Academic: New York, 1981).
Leser, G. P., Escara-Wilke, J. & Martin, T. E. J. biol. Chem. 259, 1827–1833 (1984).
Dreyfuss, G., Choi, Y. D. & Adam, S. A. Molec cell. Biol. 4, 1104–1114 (1984).
Choi, Y. D. & Dreyfuss, G. J. Cell Biol. 99, 1997–2004 (1984).
Piñol-Roma, S., Swanson, M. S., Gall, J. G. & Dreyfuss, G. J. Cell Biol. 109, 2575–2587 (1989).
Dreyfuss, G., Adam, S. A. & Choi, Y. D. Molec. cell. Biol. 4, 415–423 (1984).
Choi, Y. D. & Dreyfuss, G. Proc. natn. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 81, 7471–7475 (1984).
Piñrol-Roma, S., Choi, Y. D., Matunis, M. J. & Dreyfuss, G. Genes Dev. 2, 215–227 (1988).
Pĩnol-Roma, S., & Dreyfuss, G. Science 253, 312–314 (1991).
Hurwitz, J., Furth, J. J., Malamy, M. & Alexander, M. Proc. natn. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 48, 1222–1230 (1962).
Perry, R. P. & Kelley, D. E. J. Cell Physiol. 76, 127–140 (1970)
Tamm, I. & Seghal, P. B. Adv. Virus Res. 22, 187–258 (1978).
Egyhazi, E., Pigon, A. & Rydlander, L. Eur. J. Biochem. 122, 445–451 (1982).
Borer, R. A., Lehner, C. F., Eppenberger, H. M. & Nigg, E. A. Cell 56, 379–390 (1989).
Adam, S. A., Choi, Y. D. & Dreyfuss, G. J. Virol. 57, 614–622 (1986).
Beyer, A. L. & Osheim, Y. N. Genes Dev. 2, 754–765 (1988).
Chang, D. D. & Sharp, P. A. Cell 59, 789–795 (1989).
Legrain, P. & Rosbash, M. Cell 57, 573–583 (1989).
Hamm, J. & Mattaj, I. W. Cell 63, 109–118 (1990).
Guddat, U., Bakken, A. H. & Pieler, T. Cell 60, 619–628 (1990).
Stevens, B. J. & Swift, H. J. Cell Biol. 31, 55–78 (1966).
Skoglund, U., Anderson, K., Björkroth, B., Lamb, M. M. & Daneholt, B. Cell 34, 847–855 (1983).
Mehlin, H., Skoglund, U. & Daneholt, B. Expl. Cell Res. 193, 72–77 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piñol-Roma, S., Dreyfuss, G. Shuttling of pre-mRNA binding proteins between nucleus and cytoplasm. Nature 355, 730–732 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/355730a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/355730a0
This article is cited by
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B: an emerging group of cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
Rethinking nomenclature for interspecies cell fusions
Nature Reviews Genetics (2022)
-
Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins: Implications in Neurological Diseases
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
An epilepsy-associated mutation in the nuclear import receptor KPNA7 reduces nuclear localization signal binding
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Active nuclear import and passive nuclear export are the primary determinants of TDP-43 localization
Scientific Reports (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.