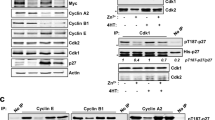
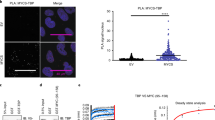
Abstract
PROTO-ONCOGENE fos encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein of 380 amino acids that can modulate the transcription of other genes either by transactivation or by transrepression1-7. The v-Fos protein (381 amino acids) shares the first 332 amino acids with the c-Fos protein (with five single amino-acid changes), but differs at the C terminus8. We have previously reported that the c-Fos protein undergoes more extensive post-translational modification than v-Fos (refs 9, 10). The major modification of the c-Fos protein involves serine phosphoesterification of sites in the extreme C terminus10. We therefore argued that modification of the C-terminal region of the c-Fos protein may be involved in its ability to transrepress transcription without compromising its ability to transactivate other genes. Here we show that mutant c-Fos protein which is hypophosphorv lated at its C terminus is unable to repress transcription of the c-fos promoter following induction with serum or tetraphorbol acetate. The C-terminal phosphorylation-deficient mutant is, however, fully competent to activate transcription of promoters containing a phorbol response element. The requirement for phosphorylation can be offset by the introduction of a net negative charge in the C terminus of the Fos protein.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curran, T. & Franza Jr, B. R. Cell 55, 395–397 (1988).
Jones, N. Cell 61, 9–11 (1990).
Chiu, R. et al. Cell 54, 541–552 (1988).
Sassone-Corsi, P., Lamph, W. W., Kamps, M. & Verma, I. M. Cell 54, 553–560 (1988).
Lucibello, F. C. et al. Oncogene 3, 43–51 (1988).
Sassone-Corsi, P., Sisson, J. C. & Verma, I. M. Nature 334, 314–319 (1988).
Lucibello, F. C., Lowag, C., Neuberg, M. & Muller, R. Cell 59, 999–1007 (1988).
Van Beveren, C. et al. Cell 32, 1241–1255 (1983).
Curran, T., Miller, A. D., Zokos, L. & Verma, I. M. Cell 36, 259–268 (1984).
Barber, J. R. & Verma, I. M. Molec. cell. Biol. 7, 2201–2211 (1987).
Kemp E., Graves, D. J., Benjamini, E. & Krebs, E. G. J. biol. Chem. 262, 4888–4894 (1977).
De Togni, P. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 8, 2251–2256 (1988).
Wilson, T. & Treisman, R. EMBO J. 7, 4193–4202 (1988).
Gorman, C. M., Moffat, L. F. & Howard, B. H. Molec. cell. Biol. 2, 1044–1051 (1982).
Kunkel, T. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 488–492 (1985).
McClary, J. A., Witney, F. & Geisselsoder, J. Biotechniques 7, 282–284 (1989).
Deschamps, J., Meijlink, F. & Verma, I. M. Science 230, 1174–1177 (1985).
Curran, T. & Verma, I. M. Virology 135, 218–228 (1984).
Lamph, W. W., Wamsley, P., Sassone-Corsi, P. & Verma, I. M. Nature 334, 629–631 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ofir, R., Dwarki, V., Rashid, D. et al. Phosphorylation of the C terminus of Fos protein is required for transcriptional transrepression of the c-fos promoter. Nature 348, 80–82 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/348080a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/348080a0
This article is cited by
-
Functions of Fos phosphorylation in bone homeostasis, cytokine response and tumourigenesis
Oncogene (2011)
-
Phosphorylation-Induced Structural Changes in the C-Terminus of c-Fos Detected by CD and NMR
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2011)
-
Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions Induced by Phosphorylation Influence the Local Conformation of Phosphopeptides
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2010)
-
MAP kinases and the control of nuclear events
Oncogene (2007)
-
Interaction with GATA transcription factors provides a mechanism for cell-specific effects of c-Fos
Oncogene (2003)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.