Abstract
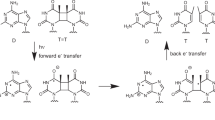
HOMOPYRIMIDINE oligonucleotides bind to homopurine–homopyrimidine sequences of duplex DNA forming a local triple helix1–8. This binding can be demonstrated either directly by a footprinting technique3, gel assays4, or indirectly by inducing irreversible reactions in the target sequence, such as photocrosslinking1,5 or cleavage2,6–8. Binding occurs in the major groove with the homopyrimidine oligonucleotide orientated parallel to the homopurine strand. Thymine and protonated cytosine in the oligonucleotide form Hoogsteen-type hydrogen bonds with A·T and G·C Watson–Crick base pairs, respectively. Here we report that an 11-residue homopyrimidine oligonucleotide covalently attached to an ellipticine derivative by its 3' phosphate photo-induces cleavage of the two strands of a target homopurine–homopyrimidine sequence. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a sequence-specific artificial photoendonuclease. In addition we show that a strong binding site for a free ellipticine derivative is induced at the junction between the triplex and duplex structures on the 5' side of the bound oligonucleotide. On irradi-ation, cleavage is observed on both strands of DNA. This opens new possibilities for inducing irreversible reactions on DNA at specific sites by the synergistic action of a triple helix-forming oligonucleotide and an intercalating agent.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Doan, T. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 15, 7749–7760 (1987).
Moser, H. E. & Dervan, P. B. Science 238, 645–650 (1987).
François, J. C., Saison-Behmoaras, T. & Hélène, C. Nucleic Acids Res. 16, 11431–11440 (1988).
Lyamychev, V. I., Mirkin, S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii, D. & Cantor C. R. Nucleic Acids Res. 16, 2165–2178 (1988).
Praseuth, D. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 1349–1353 (1988).
Povsic, T. J. & Dervan, P. B. J. Am. chem. Soc. 111, 3059–3061 (1988).
François, J. C., Saison-Behmoaras, T., Chassignol, M., Thuong, N. T. & Hélène, C. J. biol. Chem. 264, 5891–5898 (1989).
François, J. C. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 9702–9706 (1989).
Lee, B. K., Murakami, A., Blake, K. R., Lin, S. B. & Miller, P. S. Biochemistry 27, 3197–3203 (1988).
Praseuth, D. et al. Biochemistry 27, 3031–3038 (1988).
Schwaller, M. A., Aubard, J., Auclair, C., Paoletti, C. & Dodin, G. Eur. J. Biochem. 181, 129–134 (1989).
Sun, J. S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 9198–9202 (1989).
Sigman, D. S. Accts chem. Res. 19, 180–186 (1986).
Ducrocq, C. et al. J. med. Chem. 23, 1212–1216 (1980).
Asseline, U. & Thuong, N. T. Tetrahedron Lett. 30, 2521–2524 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perrouault, L., Asseline, U., Rivalle, C. et al. Sequence-specific artificial photo-induced endonucleases based on triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Nature 344, 358–360 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/344358a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/344358a0
This article is cited by
-
Mapping the diffusion pattern of 1O2 along DNA duplex by guanine photooxidation with an appended biphenyl photosensitizer
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Synthesis, Biological Activity and Photophysical Studies of Ellipticine and its Derivatives: State of the Art
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds (2022)
-
Computational analysis of triplex formation of oligonucleotides: protonated and 5-methylated py-pu-py motif
Science in China Series B: Chemistry (1997)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.