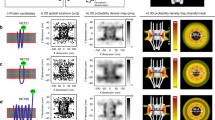
Abstract
CELL nuclei are capable of partitioning a wide variety of molecules from the cytosol, including macromolecules such as proteins1–11 and RNA12–14, and smaller peptides9,14–16, amino acids17, sugars18,19 and Na+and K+ ions20,21, all of which can be accumulated in or excluded from the nuclear domain. There are two mechanisms behind this compartmentalization: selective retention of freely diffusible molecules, and selective entry through the nuclear envelope. It is generally accepted that the nuclear envelope restricts only the larger molecules22–24. Here we apply the patch-clamp technique to isolated murine pronuclei25 and show that the nuclear envelope contains K+-selective channels which have multiple conductance states, the maximal conductance being 200 pS. These channels, which contribute to the nuclear membrane potential26, may be important in balancing the charge carried by the movement of macromolecules in and out of the nucleus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonner, W. M. J. Cell Biol. 64, 421–430 (1975).
Bonner, W. M. J. Cell Biol. 64, 431–437 (1975).
Feldherr, C. M. & Pomerantz, J. J. Cell Biol. 78, 168–175 (1978).
De Robertis, E., Longthorne, R. F. & Gurdon, J. B. Nature 272, 254–256 (1978).
Dabauvalle, M. C. & Franke, W. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 5302–5306 (1982).
Feldherr, C. M., Cohen, R. J. & Ogburn, J. A. J. Cell Biol. 96, 1486–1490 (1983).
Feldherr, C. M., Kallenbach, E. & Schultz, N. J. Cell Biol. 99, 2216–2222 (1984).
Lanford, R. E. & Butel, J. S. Cell 37, 801–813 (1984).
Lanford, R. E., Kanda, P. & Kennedy, R. C. Cell 46, 575–582 (1986).
Newmeyer, D. D., Finlay, D. R. & Forbes, D. J. J. Cell Biol. 103, 2091–2102 (1986).
Newmeyer, D. D., Lucocq, J. M., Burglin, T. R. & DeRobertis, E. D. EMBO J. 5, 501–510 (1986).
Steven, B. J. & Swift, H. J. Cell Biol. 31, 55–77 (1966).
Zasloff, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 6436–6440 (1983).
Dworetzky, S. I. & Feldherr, C. M. J. Cell Biol. 106, 575–584 (1988).
Feldherr, C. M. J. Cell Biol. 20, 188–192 (1964).
Horowitz, S. B. & Moore, L. C. J. Cell Biol. 6, 405–415 (1974).
Frank, M. & Horowitz, S. B. J. Cell Sci. 19, 127–139 (1975).
Paine, P. L., Moore, L. C. & Horowitz, S. B. Nature 254, 109–114 (1975).
Horowitz, S. B. J. Cell Biol. 54, 609–625 (1972).
Century, T. J., Fenichel, I. R. & Horowitz, S. B. J. Cell Sci. 7, 5–13 (1970).
Century, T. J. & Horowitz, S. B. J. Cell Sci. 16, 465–471 (1974).
Dingwall, C. & Laskey, R. A. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 2, 367–390 (1986).
Newport, J. W. & Forbes, D. J. A. Rev. Biochem. 56, 535–565 (1987).
Gerace, L. & Burke, B. A. Rev. Cell. Biol. 4, 335–374 (1988).
McGrath, J. & Solter, D. Science 220, 1300–1302 (1983).
Loewenstein, W. R. & Kanno, Y. J. gen. Physiol. 46, 1123–1140 (1963).
Kanno, Y. & Loewenstein, W. R. Expl Cell Res. 31, 149–166 (1963).
Coronado, R., Rosenberg, R. L. & Miller, C. J. gen. Physiol. 76, 425–446 (1980).
Coronado, R. & Miller, C. J. gen. Physiol. 79, 529–547 (1982).
Unwin, P. N. T. & Milligan, R. A. J. Cell Biol. 93, 63–75 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazzanti, M., DeFelice, L., Cohen, J. et al. Ion channels in the nuclear envelope. Nature 343, 764–767 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/343764a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/343764a0
This article is cited by
-
Effect of Tubocurarine on Large-Conductance Cationic Channels in the Inner Nuclear Membrane of Purkinje Neurons of the Rat Cerebellum
Neurophysiology (2016)
-
Importance of Cationic Channels for Functioning of the Nuclear Envelope of Neurons as a Calcium Store
Neurophysiology (2011)
-
The large-conductance ion channels in the nuclear envelope of central neurons
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2010)
-
Large-conductance cationic channels in the nuclear envelope of Purkinje neurons from the rat cerebellum
Neurophysiology (2007)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.