Abstract
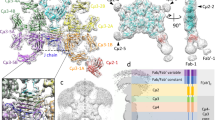
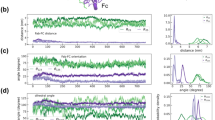
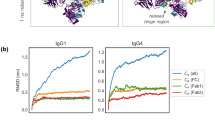
Studies by electron microscopy, fluorescence polarization, hydrodynamics and X-ray crystallography have demonstrated the ability of different parts of immunoglobulin molecules to move relative to each other. This movement facilitates the multiple interactions that antibodies make with polyvalent antigens and effector proteins. Comparisons of the atomic structures of immunoglobulins of the same sequence in different crystal environments, and of those with different sequences, have shown that the movements involve local changes in the conformation of the peptides linking different domains. These changes occur in (1) the hinge regions that link the Fab fragment to the Fc, and (2) the switch regions that link the VL–VH dimer to the CL–CH1 dimer1–15. We show here that in immunoglobulins of known structure, the movement of the VL–VH dimer relative to the CL–CH1 dimer also involves the interactions of three VH and two CH1 residues that form the molecular equivalent of a ball-and-socket joint. The almost absolute conservation in the sequences of immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors of the residues that form these interactions suggests that this is a general feature of functional importance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poljak, R. J., Amzel, L. M., Chen, B. L., Phizackerley, R. P. & Saul, F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 3440–3444 (1974).
Colman, P. M., Deisenhofer, J., Huber, R. & Palm, W. J. molec. Biol. 100, 257–282 (1976).
Silverton, E. W., Navia, M. A. & Davis, D. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5140–5149 (1977).
Abola, E. E., Ely, K. R. & Edmundson, A. B. Biochemistry 19, 432–439 (1980).
Saul, F. A., Amzel, L. M. & Poljak, R. J. J. biol. Chem. 253, 585–597 (1978).
Satow, Y., Cohen, G. H., Padlan, E. A. & Davies, D. R. J. molec. Biol. 190, 593–604 (1986).
Marquart, M., Deisenhofer, J. & Huber, R. J. molec. Biol. 141, 369–391 (1980).
Sun, S. E. et al. Proteins 1, 74–80 (1986).
Sheriff, S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 8075–8079 (1987).
Amit, A. G., Mariuzza, R. A., Phillips, S. E. V. & Poljak, R. J. Science 233, 747–753 (1986).
Colman, P. M. et al. Nature 326, 358–362 (1987).
Cygler, M., Boodhoo, A., Lee, J. S. & Anderson, W. F. J. biol. Chem. 262, 643–648 (1987).
Prased, L., Vandonselaar, M., Lee, J. S. & Delbaere, L. T. J. J. biol. Chem. 263, 2571–2574 (1987).
Vitali, J., Young, W. W., Schatz, V. B., Sobottka, S. E. & Kretsinger, R. H. J. molec. Biol. 198, 351–355 (1987).
Davies, D. R. & Metzger, H. A. Rev. Immun. 1, 87–117 (1983).
Bernstein, F. C. et al. J. molec. Biol. 112, 535–542 (1977).
Rabat, E. A., Wu, T. T., Reid-Miller, M., Perry, H. M. & Gottesman, K. S. Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest 4th edn (Public Health Service, NIH, Washington DC, 1987).
Chien, Y. et al. Nature 312, 31–35 (1984).
Hedrick, S. M., Nielsen, E. A., Kavaler, J., Cohen, D. I. & Davies, M. M. Nature 308, 153–158 (1984).
Saito, H. et al. Nature 312, 36–40 (1984).
Yanagi, Y. et al. Nature 308, 145–149 (1984).
Saito, H. et al. Nature 309, 757–762 (1984).
Chothia, C., Lesk, A. M., Dodson, G. G. & Hodgkin, D. C. Nature 302, 500–505 (1983).
Lesk, A. M. & Chothia, C. J. molec. Biol. 174, 175–191 (1984).
Elber, R. & Karplus, M. Science 235, 318–321 (1987).
Perutz, M. F. Nature 228, 726–739 (1970).
Baldwin, J. & Chothia, C. J. molec. Biol. 129, 175–200 (1979).
Bennett, W. S. & Huber, R. Crit. Revs Biochem. 15, 291–384 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lesk, A., Chothia, C. Elbow motion in the immunoglobulins involves a molecular ball-and-socket joint. Nature 335, 188–190 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/335188a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/335188a0
This article is cited by
-
Selection of immunoglobulin elbow region mutations impacts interdomain conformational flexibility in HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibodies
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Sequencing of modern Lepus VDJ genes shows that the usage of VHn genes has been retained in both Oryctolagus and Lepus that diverged 12 million years ago
Immunogenetics (2013)
-
Properties, production, and applications of camelid single-domain antibody fragments
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2007)
-
The crystal structure of a llama heavy chain variable domain
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (1996)
-
Fv fragment-mediated crystallization of the membrane protein bacterial cytochrome c oxidase
Nature Structural Biology (1995)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.