Abstract
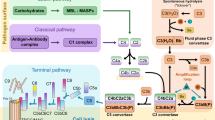
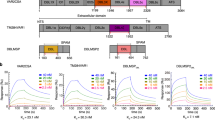
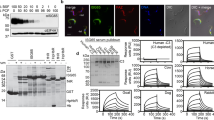
Properdin is a plasma glycoprotein which stabilizes the C3bnBb¯ enzyme complex of the alternative pathway of the complement system1,2. Unlike the classical pathway, which is initiated by interaction of C1q with the Fc regions of IgG or IgM antibodies in immune complexes, the alternative pathway can be directly activated via binding of C3b to surfaces of foreign organisms3,4. The stabilized C3bnBbP¯ complex activates components C3 and C5 resulting in opsonization of foreign material (via C3b) and assembly of the membrane attack complex (via C5b) on target cells. Therefore properdin greatly enhances complement-mediated clearance and inactivation mechanisms in both natural and acquired resistance to infection1,4. This paper shows that the primary amino acid sequence of properdin is composed mainly of six repeating motifs, each of ∼60 amino acids, and that similar sequences are found in thrombospondin5, the circumsporozoite protein of malaria parasites6–8 and regions of the membrane-attack components of complement9. These similarities may provide insight into the mechanisms by which parasites avoid host defences mediated by complement.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pillemer, L. et al. Science 120, 279–285 (1954).
Fearon, D. T. & Austen, K. F. J. exp. Med. 142, 856–863 (1975).
Reid, K. B. M. & Porter, R. R. A. Rev. Biochem. 50, 433–464 (1981).
Whaley, K. Complement in Health and Disease (MTP Lancaster, 1987).
Lawler, J. & Hynes, R. O. J. cell. Biol. 103, 1635–1648 (1986).
Ozaki, L. S., Dvec, P., Nussenzweig, R. S., Nussenzweig, V. & Godson, G. N. Cell 34, 815–822 (1983).
Dame, J. B. et al. Science 225, 593–599 (1984).
Arnot, D. E. et al. Science 230, 815–818 (1985).
DiScipio, R. G., Chakravarti, D. N., Müller-Eberhard, H. J. & Fey, G. J. biol. Chem. 263, 549–560 (1988).
Reid, K. B. M. & Gagnon, J. Molec. Immun. 18, 949–959 (1981).
Nakamo, Y., Matsuda, T., Sakamoto, T. & Motowa, T. J. immunol. Meth. 90, 77–83 (1986).
DiScipio, R. G. Molec. Immun. 19, 631–635 (1982).
Smith, C. A., Pangburn, M. K., Vogel, C. & Müller-Eberhard, H. J. J. biol. Chem. 259, 4582–4588 (1984).
Good, M. F. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 1199–1203 (1988).
Sjoholm, A. G., Braconier, J. H. & Sonderstrom, C. Clin. expl. Immun. 50, 291–297 (1982).
Spath, P. J., Misiano, G. & Schaad, U.B. Complement 2, 74 (1985).
Densen, P., Weiler, J. M., Griffis, J. McL. & Hoffmann, L. G. New Engl. J. Med. 316, 922–926 (1987).
Gelfand, E. W. et al. Am. J. Med. 82, 671–675 (1987).
Bohnsack, J. F. & Brown, E. J. Am. Rev. Med. 37, 49–59 (1986).
Robson, K. J. H. et al. Nature 335, 79–82 (1988).
Anson, D. S. et al. EMBO J. 3, 1053–1060 (1984).
Maxam, A. M. & Gilbert, W. Meth. Enzym. 65, 499–569 (1980).
Sanger, F., Coulson, A. R., Barell, B. G., Smith, A. J. H. & Roe, B. A. J. molec. Biol. 143, 161–178 (1980).
Dayhoff, M. O., Barker, W. C. & Hunt, L. T. Meth. Enzym. 91, 524–545 (1983).
Chrigwin, J. M., Przybyla, A. E., MacDonald, R. J. & Rutter, W. J. Biochemistry 18, 5294–5299 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goundis, D., Reid, K. Properdin, the terminal complement components, thrombospondin and the circumsporozoite protein of malaria parasites contain similar sequence motifs. Nature 335, 82–85 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/335082a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/335082a0
This article is cited by
-
The biological function of antibodies induced by the RTS,S/AS01 malaria vaccine candidate is determined by their fine specificity
Malaria Journal (2016)
-
The genome of the simian and human malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi
Nature (2008)
-
A gene family of putative immune recognition molecules in the hydroid Hydractinia
Immunogenetics (2007)
-
Genes coding for tryptophan-rich proteins are transcribed throughout the asexual cycle of Plasmodium falciparum
Parasitology Research (2005)
-
Sequence similarities of protein kinase peptide substrates and inhibitors: Comparison of their primary structures with immunoglobulin repeats
Folia Microbiologica (2002)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.