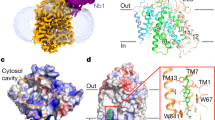
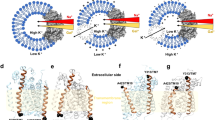
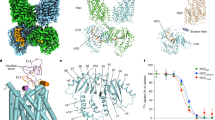
Abstract
Organic substrates (sugars, amino acids, carboxylic acids and neutrotransmitters) are actively transported into eukaryotic cells by Na+ co-transport. Some of the transport proteins have been identified—for example, intestinal brush border Na+/glucose and Na+/proline transporters1,2 and the brain Na+/Cl–/GABA transporter3—and progress has been made in locating their active sites and probing their conformational states1,2,4–7. The archetypical Na+-driven transporter is the intestinal brush border Na+/glucose co-transporter (see ref. 8), and a defect in the co-transporter is the origin of the congenital glucose–galactose malabsorption syndrome9. Here we describe cloning of this co-transporter by a method new to membrane proteins. We have sequenced the cloned DNA and have found no homology between the Na+/glucose co-transporter and either the mammalian facilitated glucose carrier or the bacterial sugar transport proteins. This suggests that the mammalian Na+-driven transporter has no evolutionary relationship to the other sugar transporters.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. Peerce, B. E. & Wright, E. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 8, 2223-2226 (1984). 2. Wright, E. M. & Peerce, B. E. / biol Chem. 259, 14993-14996 (1984). 3. Radian, R., Bendahan, A. & Kanner, B. I. /. biol. Chem. 261, 15437-15441 (1986). 4. Peerce, B, E. & Wright, E. M. J. biol. Chem. 259, 14105-14112 (1984). 5. Peerce, B. E. & Wright, E. M. 7. biol Chem. 260, 6026-6031 (1985). 6. Peerce, B. E. & Wright, E. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 8092-8096 (1986). 7. Peerce, B. E. & Wright, E. M. Biochemistry 26, 4272-4276 (1987). 8. Semenza, G., Kessler, M., Hosang, M., Weber, J. & Schmidt, U. Biochim. biophys. Acta 779,343-379 (1984). 9. Rosenberg, L. E. in Membranes and Disease (eds Biles, L., Hoffman, J. F. & Leaf, A.) 253-261 (Raven, New York, 1975). 10. Noma, Y. et al. Nature 319, 640-646 (1986). 11. Hediger, M. A., Ikeda, T., Coady, M., Gundersen, C. B. & Wright, E. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 2634-2637 (1987). 12. Flier, J. S., Mueckler, M., McCall, A. L. & Lodish, H. F. J. din. Invest. 79, 657-661 (1987). 13. Kozak, M. Nucleic Acid Res. 12, 857-872 (1984). 14. Eisenberg, D., Schwarz, E., Komaromy, M. & Wall, R. /. molec. Biol. 179, 125-142 (1984). 15. Gamier, J., Osguthorpe, D. J. & Robson, B. J. molec. Biol. 120, 97-120 (1978). 16. Quiocho, F. A. A. Rev. Biochem. 55, 287-315 (1986). 17. Quiocho, F. A. & Vyas, N. K. Nature 310, 381-386 (1984). 18. Mueckler, M. et al. Science, 229, 941-945 (1985). 19. Birnbaum, M. J., Haspel, H. C. & Rosen, O. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 5784-5788 (1986). 20. Buchel, D. E., Gronenborn, B. & Muller-Hill, B. Nature 283, 541-545 (1980). 21. Maiden, M. C. J., Davis, E. O., Baldwin, S. A., Moore, D. C. M. & Henderson, P. J. F. Nature 325, 641-643 (1987). 22. Sasatsu, M., Misra, T. K., Chu, L., Laddaga, R. & Silver, S. 3. Bact. 164, 983-993 (1985). 23. Yazyu, H. et al. 7. biol. Chem. 259, 4320-4326 (1984). 24. Staden, R. Nucleic Acid Res. 10, 2951-2961 (1982). 25. Kasahara, M., Inui, K., Takano, M. & Hori, R. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 132,490-496 (1985). 26. Tanabe, T. et al. Nature 328, 313-318 (1987). 27. Noda, M. et al. Nature 312, 121-127 (1984). 28. Shull, G. E., Schwartz, A. & Lingrel, J. B. Nature 316, 691-695 (1985). 29. Hager, K. M. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 7693-7697 (1986). 30. Gubler, U. & Hoffman, B. Gene 25, 263-269 (1983). 31. Hediger, M. A. Analyt. Biochem. 159, 280-286 (1986). 32. Krieg, P. A. & Melton, D. A. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 7057-7070 (1984). 33. Holmes, D. S. & Quigley, M. Analyt. Biochem. 114, 193-197 (1981). 34. Church, G. M. & Gilbert, W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 1991-1995 (1984). 35. Sanger, F., Coulson, A. R., Barrell, B. G., Smith, A. J. H. & Roe, B. A. J. molec. Biol. 143, 161-178 (1980). 36. Hediger, M. A., Johnson, D. F., Nierlich, D, P. & Zabin, I. Proc.natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 6414-6418 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hediger, M., Coady, M., Ikeda, T. et al. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. Nature 330, 379–381 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/330379a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/330379a0
This article is cited by
-
Regulatory mechanisms of glucose absorption in the mouse proximal small intestine during fasting and feeding
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
What can we learn about acid-base transporters in cancer from studying somatic mutations in their genes?
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2023)
-
Transporter-protein structures show how salt gets a sweet ride into cells
Nature (2022)
-
30 years of progress from positional cloning to precision genome editing
Nature Genetics (2022)
-
Molecular characterization and nutritional regulation of sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 1 (Sglt1) in blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala)
Scientific Reports (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.