Abstract
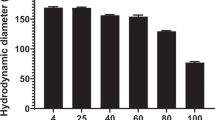
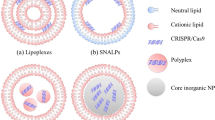
the structure of ‘stabilized plasmid-lipid particles’ (splp) and their properties as systemic gene therapy vectors has been investigated. we show that splp can be visualized employing cryo-electron microscopy to be homogeneous particles of diameter 72 ± 5 nm consisting of a lipid bilayer surrounding a core of plasmid dna. it is also shown that splp exhibit long circulation lifetimes (circulation half-life >6 h) following intravenous (i.v.) injection in a murine tumor model resulting in accumulation of up to 3% of the total injected dose and concomitant reporter gene expression at a distal (hind flank) tumor site. In contrast, i.v. injection of naked plasmid DNA or plasmid DNA–cationic liposome complexes did not result in significant plasmid delivery to the tumor site or gene expression at that site. Furthermore, it is shown that high doses of SPLP corresponding to 175 μg plasmid per mouse are nontoxic as assayed by monitoring serum enzyme levels, whereas i.v. injection of complexes give rise to significant toxicity at dose levels above 20 μg plasmid per mouse. It is concluded that SPLP exhibit properties consistent with potential utility as a nontoxic systemic gene therapy vector.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huard J et al. The route of administration is a major determinant of the transduction efficiency of rat tissues by adenoviral recombinants Gene Therapy 1995 2: 107–115
Worgall S, Wolff G, Falck PE, Crystal RG . Innate immune mechanisms dominate elimination of adenoviral vectors following in vivo administration Hum Gene Ther 1997 8: 37–44
Zhu N, Liggitt D, Liu Y, Debs R . Systemic gene expression after intravenous DNA delivery into adult mice Science 1993 261: 209–211
Thierry AR et al. Systemic gene therapy: biodistribution and long-term expression of a transgene in mice Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 9742–9746
Li S, Huang L . In vivo gene transfer via intravenous administration of cationic lipid-protamine-DNA (LPD) complexes Gene Therapy 1997 4: 891–900
Liu Y et al. Factors influencing the efficiency of cationic liposome-mediated intravenous gene delivery Nat Biotechnol 1997 15: 167–173
Templeton NS et al. Improved DNA: liposome complexes for increased systemic delivery and gene expression Nat Biotechnol 1997 15: 647–652
Huang L, Li S . Liposomal gene delivery: a complex package Nat Biotechnol 1997 15: 620–621
Proffitt RT et al. Liposomal blockade of the reticuloendothelial system: improved tumor imaging with small unilamellar vesicles Science 1983 220: 502–505
Gabizon A, Papahadjopoulos D . Liposome formulations with prolonged circulation time in blood and enhanced uptake by tumors Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988 85: 6949–6953
Chonn A, Cullis PR . Recent advances in liposomal drug-delivery systems Curr Opin Biotechnol 1995 6: 698–708
Wheeler JJ et al. Stabilized plasmid-lipid particles: construction and characterization Gene Therapy 1999 6: 271–281
Mimms LT et al. Phospholipid vesicle formation and transmembrane protein incorporation using octyl glucoside Biochemistry 1981 20: 833–840
Mayer LD et al. Comparison of free and liposome encapsulated doxorubicin tumor drug uptake and antitumor efficacy in the SC115 murine mammary tumor Cancer Lett 1990 53: 183–190
Roerdink F et al. The involvement of parenchymal, Kuppfer and endothelial cells in the hepatic uptake of intravenously injected liposomes. Effects of lanthanum and gadolinium salts Biochim Biophys Acta 1981 677: 79–89
Mortimer I et al. Cationic lipid-mediated transfection of cells in culture requires mitotic activity Gene Therapy 1999 6: 403–411
Lewis RJ, Huang JH, Pecora R . Rotational and translational motion of supercoiled plasmids in solution Macromolecules 1985 18: 944–948
Gnant MFX et al. Sensitization of tumor necrosis factor α-resistant human melanoma by tumor-specific in vivo transfer of the gene encoding endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide II using recombinant vaccinia virus Cancer Res 1999 59: 4668–4674
Gnant MFX et al. Tumor-specific gene delivery using recombinant vaccinia virus in a rabbit model of liver metastases J Natl Cancer Inst 1999 91: 1744–1750
Heise CC et al. Intravenous administration of ONYX-015, a selectively replicating adenovirus, induces antitumoral efficacy Cancer Res 1999 59: 2623–2628
Ogris M et al. PEGylated DNA/transferring–PEI complexes: reduced interaction with blood components, extended circulation in blood and potential for systemic gene delivery Gene Therapy 1999 6: 595–605
Xu M et al. Gene therapy with p53 inhibits human breast tumors in vivo through a bystander mechanism without evidence of toxicity Hum Gene Ther 1997 8: 177–185
Xu L et al. Transferrin-liposome-mediated systemic p53 gene therapy in combination with radiation results in regression of human head and neck cancer xenografts Hum Gene Ther 1999 10: 2941–2952
Thurston G et al. Cationic liposomes target angiogenic endothelial cells in tumors and chronic inflammation in mice J Clin Invest 1998 101: 1401–1413
Lasic DD et al. Sterically stabilized liposomes: a hypothesis on the molecular origin of the extended circulation times Biochim Biophys Acta 1991 1070: 187–192
Mok KWC, Lam AMI, Cullis PR . Stabilized plasmid-lipid particles: factors influencing plasmid entrapment and transfection properties Biochim Biophys Acta 1999 1419: 137–150
Webb M et al. Comparison of hydrophobic anchors conjugated to poly(ethylene)glycol: effects on the pharmacokinetics on the liposomal vincristine Biochim Biophys Acta 1998 1372: 272–282
Hope MJ et al. Generation of multilamellar and unilamellar phopholipid vesicles Chem Phys Lipids 1986 40: 89–107
Bally MB, Mayer LD, Hope MJ, Nayar R . Pharmacodynamics of liposomal drug carriers: methodological considerations Liposome Technol 1993 18: 27–41
Acknowledgements
We thank T Nolan, N Turcotte and J Johnson for excellent technical assistance, Dr P Joshi for assistance in preparing the manuscript and Dr S Ansell and Dr Z Wang for supplying the DODAC and PEG-CerC20 respectively. Plasmid DNA was prepared by C Giesbrecht and J Thompson.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tam, P., Monck, M., Lee, D. et al. Stabilized plasmid-lipid particles for systemic gene therapy. Gene Ther 7, 1867–1874 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301308
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301308
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Structure and Function of Cationic and Ionizable Lipids for Nucleic Acid Delivery
Pharmaceutical Research (2023)
-
Therapeutic efficacy in a hemophilia B model using a biosynthetic mRNA liver depot system
Gene Therapy (2016)
-
Novel nano polymeric system containing biosynthesized core shell silver/silica nanoparticles for functionalization of cellulosic based material
Microsystem Technologies (2016)
-
Strengthening the Skin with Topical Delivery of Keratinocyte Growth Factor-1 Using a Novel DNA Plasmid
Molecular Therapy (2014)
-
Enhancing physical stability of positively charged catanionic vesicles in the presence of calcium chloride via cholesterol-induced fluidic bilayer characteristic
Colloid and Polymer Science (2014)