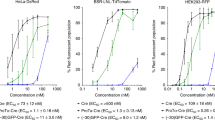
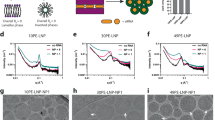
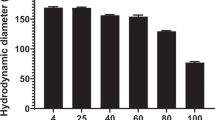
Abstract
Cationic lipids can deliver genes efficiently in vitro, but are generally inhibited by the presence of serum, and their efficiency in vivo is much lower than in vitro. An attractive strategy is to induce strong DNA compaction by its association with proteins, before addition of lipids. However the use of whole proteins might present both production and immunological limitations. We have devised a system in which DNA is associated with short peptides derived from human histone or protamine, before the addition of a cationic lipid or polymer. Peptides strongly associating with DNA confer to such peptide–DNA–lipid particles an enhanced in vitro transfection efficiency over that observed with classical DNA/lipid lipoplexes, and particularly confer the capacity to transfect in the presence of serum. This acquisition of serum resistance is cell type-independent, and observed with all four lipopolyamines tested and polyethylenimine. Precompacting DNA with a histone H1-derived peptide enhances cationic lipid RPR 115335-mediated gene transfer in an in vivo model of Lewis lung carcinoma. Apart from their use in peptide–DNA–lipid association, such peptides could be useful as part of chimeric gene delivery vectors presenting a DNA-binding moiety that can be easily associated with other functional domains.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nabel EG et al. Recombinant gene expression in vivo within endothelial cells of the arterial wall Science 1989 244: 1342–1344
Nabel GJ et al. Direct gene transfer with DNA–liposome complexes in melanoma: expression, biologic activity and lack of toxicity in humans Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993 90: 11307–11311
Schwartz B et al. Lipospermine-based gene transfer into the newborn mouse brain is optimized by a low lipospermine/DNA charge ratio Hum Gene Ther 1995 6: 1515–1524
Thierry AR et al. Systemic gene therapy: biodistribution and long-term expression of a transgene in mice Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 9742–9746
Lee ER et al. Detailed analysis of structures and formulations of cationic lipids for efficient gene transfer to the lung Hum Gene Ther 1996 7: 1701–1717
Wheeler C et al. A novel cationic lipid greatly enhances plasmid DNA delivery and expression in mouse lung Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 11454–11459
Egilmez N, Iwanuma Y, Bankert R . Evaluation and optimization of different cationic liposome formulations for in vivo gene transfer Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996 221: 169–173
Stephan D et al. A new cationic liposome DNA complex enhances the efficiency of arterial gene transfer in vivo Hum Gene Ther 1996 7: 1803–1812
Hofland H et al. In vivo gene transfer by intravenous administration of stable cationic lipid DNA complex Pharm Res 1997 14: 742–749
Oudrhiri N et al. Gene transfer by guanidinium-cholesterol cationic lipids into airway epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 1651–1656
Lewis JG et al. A serum-resistant cytofectin for cellular delivery of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides and plasmid DNA Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 3176–3181
Brunette E, Stribling R, Debs R . Lipofection does not require the removal of serum Nucleic Acids Res 1991 20: 1151
Vitiello L et al. Condensation of plasmid DNA with polylysine improves liposome-mediated gene transfer into established and primary muscle cells Gene Therapy 1996 3: 396–404
Zlatanova J, Yaneva J . Histone H1-DNA interactions and their relation to chromatin structure and function DNA Cell Biol 1991 10: 239–248
Garcia-Ramirez M, Subirana JA . Condensation of DNA by basic proteins does not depend on protein composition Biopolymers 1994 34: 285–292
Kaneda Y, Iwai K, Uchita T . Increased expression of DNA cointroduced with nuclear protein in adult rat liver Science 1989 243: 375–378
Breeuwer M, Goldfarb D . Facilitated nuclear transport of histone H1 and other small nucleophilic proteins Cell 1990 60: 999–1008.
Cotten M et al. Transferrin-polycation-mediated introduction of DNA into human leukemic cells: stimulation by agents that affect the survival of transfected DNA or modulate transferrin receptor levels Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990 87: 4033–4037
Wagner E et al. Transferrin–polycation conjugate as carrier for DNA uptake into cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990 87: 3410–3414
Zenke M et al. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin–polycation conjugates: an efficient way to introduce DNA into hematopoietic cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990 87: 3655–3659
Zhou X, Klibanov AL, Huang L . Lipophilic polylysine mediated efficient DNA transfection in mammalian cells Biochim Biophys Acta 1991 1065: 8–14
Wagner E et al. Influenza virus hemagglutinin HA-2 N-terminal fusogenic peptides augment gene transfer by transferrin-polylysine-DNA complexes: toward a synthetic virus-like gene transfer vehicle Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 7934–7938
Plank C et al. Gene transfer using asialoglycoprotein receptor-mediated endocytosis of DNA complexed with an artificial tetra-antennary galactose ligand Bioconj Chem 1992 3: 533–539
Erbacher P et al. Gene transfer by DNA/glycosylated polylysine complexes into human blood monocyte-derived macrophages Hum Gene Ther 1996 7: 721–729
Batra RK et al. Receptor-mediated gene delivery employing lectin-binding specificity Gene Therapy 1994 1: 255–260
Chen J et al. A novel gene delivery system using EGF receptor-mediated endocytosis FEBS Lett 1994 338: 167–169
Chen J, Stickles RJ, Daichendt KA . Galactosylated histone-mediated gene transfer and expression Hum Gene Ther 1994 5: 429–435
Hart SL et al. Gene delivery and expression mediated by an integrin-binding peptide Gene Therapy 1995 2: 552–554
Chen S-Y et al. Design of a genetic immunotoxin to eliminate toxin immunogenicity Gene Therapy 1995 2: 116–126
Coll J-L et al. In vitro targeting and specific transfection of human neuroblastoma cells by chCE7 antibody-mediated gene transfer Gene Therapy 1997 4: 156–161
Wu GY et al. Receptor-mediated gene delivery in vivo: partial correction of albuminemia in Nagase rats J Biol Chem 1991 266: 14338–14442
Stankovics JC et al. Overexpression of human methylmalonyl CoA mutase in mice after in vivo gene transfer with asialoglycoprotein/polylysine/DNA complexes Hum Gene Ther 1994 5: 1095–1104
Behr JP . Gene transfer with synthetic cationic amphiphiles: prospects for gene therapy Bioconj Chem 1994 5: 382–389
Zhou X, Huang L . DNA transfection mediated by cationic liposomes containing lipopolylysine: characterization and mechanism of action Biochim Biophys Acta 1994 1189: 195–203
Boussif O et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethyleneimine Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 7297–7301
Farhood H, Serbina N, Huang L . The role of phosphatidylethanolamine in cationic liposome-mediated gene transfer Biochim Biophys Acta 1995 1235: 289–295
Kamata H et al. Amphiphilic peptides enhance the efficiency of liposome-mediated transfection Nucleic Acids Res 1994 22: 536–537
Trubetskoy VS et al. Cationic liposomes enhance targeted delivery and expression of exogenous DNA mediated by N-terminal modified poly(L-lysine)-antibody conjugate in mouse lung endothelial cells Biochim Biophys Acta 1992 1131: 311–313
Gershon H et al. Mode of formation and structural features of DNA-cationic liposome complexes used for transfection Biochemistry 1993 32: 7143–7151
Mack KD, Walzem R, Zeldis JB . Cationic lipid enhances in vitro receptor-mediated transfection Am J Med Sci 1994 307: 138–143
Fritz JD et al. Gene transfer into mammalian cells using histone-condensed plasmid DNA Hum Gene Ther 1996 7: 1395–1404
Gao X, Huang L . Potentiation of cationic liposome-mediated gene delivery by polyanions Biochemistry 1996 35: 1027–1036
Mack KD et al. Polylysine enhances cationic liposome-mediated transfection of the hepatoblastoma cell line Hep G2 Biotechnol Appl Biochem 1996 23: 217–220
Li S, Huang L . In vivo gene transfer via intravenous administration of cationic lipid-protamine-DNA (LPD) complexes Gene Therapy 1997 4: 891–900
Gottschalk S et al. A novel DNA-peptide complex for efficient gene transfer and expression in mammalian cells Gene Therapy 1996 3: 448–457
Plank C et al. Activation of the complement system by synthetic DNA complexes: a potential barrier for intravenous gene delivery Hum Gene Ther 1996 7: 1437–1446
Erard M, Lakhdar-Ghazal F, Amalric F . Repeat motifs which contain β-turns and modulate DNA condensation Eur J Biochem 1990 191: 19–26
Byk G et al. Novel nonviral vectors for gene delivery: synthesis and applications Lett Peptide Sci 1997 4: 263–267
Byk G et al. Synthesis, activity, and structure–activity relationship studies of novel cationic lipids for DNA transfer J Med Chem 1998 41: 229–235
Delouis C et al. Xenotropic and amphotropic pseudotyped recombinant retrovirus to transfer genes into cells from various species Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1990 169: 8–14
Barthel F et al. Gene transfer optimisation with lipospermine-coated DNA DNA Cell Biol 1993 12: 553–560
Takeuchi K et al. Effect of zeta potential of cationic liposomes containing cholesterol derivatives on gene transfection FEBS Lett 1996 397: 207–209
Escriou V et al. Cationic lipid-mediated gene transfer: effect of serum on cellular uptake and intracellular fate of lipopolyamine/DNA complexes Biochim Biophys Acta 1998 1368: 276–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwartz, B., Ivanov, MA., Pitard, B. et al. Synthetic DNA-compacting peptides derived from human sequence enhance cationic lipid-mediated gene transfer in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther 6, 282–292 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300795
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300795
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genetic pharmacology: progresses in siRNA delivery and therapeutic applications
Gene Therapy (2017)
-
Aerosol-delivered programmed cell death 4 enhanced apoptosis, controlled cell cycle and suppressed AP-1 activity in the lungs of AP-1 luciferase reporter mice
Gene Therapy (2007)
-
Progress in non-viral gene delivery systems fabricated via supramolecular assembly
Chinese Science Bulletin (2005)
-
Increased receptor-mediated gene delivery to the liver by protamine-enhanced-asialofetuin-lipoplexes
Gene Therapy (2003)
-
Medicinal chemistry of plasmid DNA with peptide nucleic acids: A new strategy for gene therapy
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2003)