Abstract
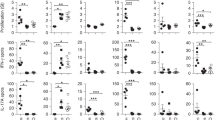
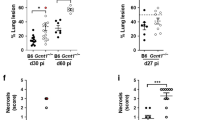
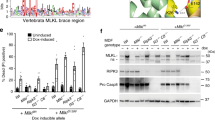
The bacteriocidal capacity of phagocytic cells is impaired in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (X-CGD), a disorder characterized by the absence of functional plasma-membrane-associated NADPH oxidase1. The components of this oxidase system, their correspondence with specific genetic loci, and the primary protein defect in X-CGD remain incompletely defined. We recently reported cloning of the putative X-CGD gene on the basis of DNA linkage2,3. To identify the predicted protein in vivo, antibodies were raised to a synthetic peptide derived from the complementary DNA sequence and to a fusion protein produced in Escherichia coli. In Western blots antisera detect a neutrophil protein of relative molecular mass in 90,000 (90K) that is absent in X-CGD patients. Antisera also react with the larger component of cytochrome b recently purified from neutrophil plasma membranes as a complex of glycosylated 90K and non-glycosylated 22K polypeptides4. Based on our identification of the X-CGD protein in vivo, we propose that one of its critical roles is to interact with the 22K species to form a functional cytochrome b complex.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. Tauber, A. I., Bornegaard, N., Simons, E. & Wright, J. Medicine 62, 286–369 (1983).
2. Baehner, R. L. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 3398–3401 (1986).
3. Royer–Pokora, et al Nature 322, 32–38 (1986).
4. Parkos, C. A., Alien, R. A., Cochrane, C. G. & Jesaitis, A. J. 7. din. Invest, (in the press).
5. Kozak, M. Cell 47, 481–483 (1986).
6. Creighton, T. E. Nature 324, 21 (1986).
7. Kreig, P. A. & Melton, D. A. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 7057–7070 (1984).
8. Segal, A. W. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 308, 245–251 (1983).
9. Bohler, M. et al J. din. Immun. 6, 136–145 (1986).
10. Harper, A. M., Dunne, M. J. & Segal, A. W. Biochem. J. 219, 519–527 (1984).
11. Pember, S. O., Heyl, B. L., Kinkade, J. M. Jr & Lambeth, J. P. J. biol Chem. 259,10590–10595 (1984).
12. Serra, M. C. et al Biochim. biophys. Acta 788, 138–146 (1984).
13. Lutter, R. et al. J. biol. Chem. 260, 2237–2244 (1985).
14. Harper, A. M., Chaplin, M. F. & Segal, A. W. Biochem. J. 227, 783–788 (1985).
15. Ashworth, A., Shephard, E. A. & Phillips, I. R. Nature 322, 599 (1986).
16. Young, R. A. & Davis, R. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 1194–1198 (1983).
17. Ruther, U. & Muller–Hill, N. Embo J. 2, 1791–1794 (1983).
18. Laemmli, U. K. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
19. Towbin, H., Staehlin, T. & Gordon, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 4350–4354 (1979).
20. Boyum, A. Scand. J. din. Lab. Invest. 21 (Suppl. 97), 77–89 (1968).
21. Bradford, M. Analyt. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976).
22. Segal, A. W. Nature 326, 88–91 (1987).
23. Teahan, C., Rowe, P., Parker, P., Totty, N. & Segal, A. W. Nature 327, 720–721 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinauer, M., Orkin, S., Brown, R. et al. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex . Nature 327, 717–720 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/327717a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/327717a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular Challenges in the Diagnosis of X-Linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease: CNVs, Intronic Variants, Skewed X-Chromosome Inactivation, and Gonosomal Mosaicism
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2023)
-
A puromycin-dependent activity-based sensing probe for histochemical staining of hydrogen peroxide in cells and animal tissues
Nature Protocols (2022)
-
Recent topics and advanced therapies in chronic granulomatous disease
Human Cell (2022)
-
NADPH oxidases and oxidase crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases: novel therapeutic targets
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2020)
-
Control and dysregulation of redox signalling in the gastrointestinal tract
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.