Abstract
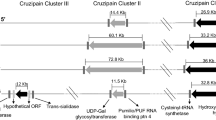
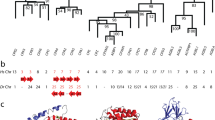
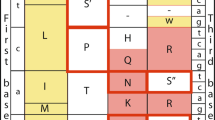
The serine protease inhibitors (serpins) are a family of proteins that function to control the action of serine proteases in many diverse physiological processes. The functional region or reactive centre of these inhibitors is near the C-terminal end and is an exposed site that acts as a bait for the appropriate serine protease to recognize and covalently bind. The specificity of the inhibitor is determined, at least in part, by a single amino acid that resides in this region at the P1 position1. We show here that following a gene duplication event the reactive centres of three related rodent protease inhibitors have diverged from each other at unprecedented rates. This has resulted in proteins with different predicted specificities and we postulate that these changes were fixed by positive darwinian selection and that the most likely selective forces are extrinsic proteases, namely those used by parasites to facilitate their spread throughout the host.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Travis, J. & Salvesen, G. S. A. Rev. Biochem. 52, 655–709 (1983).
Hill, R. E., Shaw, P. H., Boyd, P. A., Baumann, H. & Hastie, N. D. Nature 311, 175–177 (1984).
Takahori, H. & Sinohara, H. J. biol. Chem. 257, 2435–2446 (1982).
Takahori, H. & Sinohara, H. J. Biochem., Tokyo 93, 1411–1419 (1983).
Beatty, K., Bieth, J. & Travis, J. J. biol. Chem. 255, 3931–3934 (1980).
Travis, J., Bowen, J. & Baugh, R. Biochemistry 17, 5651–5656 (1978).
Laine, A., Davril, M. & Hayem, A. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 105, 186–193 (1982).
Hill, R. E., Shaw, P. H., Barth, R. K. & Hastie, N. D. Molec. cell. Biol. 5, 2114–2122 (1985).
Baumann, H., Hill, R. E., Saunder, D. N. & Jahreis, G. P. J. Cell Biol. 102, 370–383 (1986).
Li, W.-H., Wu, C.-I. & Luo, C.-C. Molec. Biol. Evol. 2, 150–174 (1985).
Goodman, M. in Molecular Evolution (ed. Ayala, F. J.) 141–159 (Sinauer, Sunderland Massachusetts, 1976).
Goodman, M. Nature 295, 630 (1981).
Kimura, M. J. Molec. Evol. 17, 110–113 (1981).
Li, W.-H., Wu, C.-C. & Wu C.-I. in Molecular Evolutionary Genetics (ed. R. J. MacIntyre) 1–94 (Plenum, New York, 1985).
Li, W.-H. Evolution of Genes and Proteins (eds Nei, M. & Koehn, R. K.) 14–37 (Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts 1983).
Morii, M. & Travis, J. J. biol. Chem. 258, 12749–12752 (1983).
Carrell, R. & Travis, J. Trends Biochem. Sci. 10, 20–24 (1985).
Rosenberg, S., Barr, P. J., Najarian, R. C. & Hallewell, R. A. Nature 312, 77–80 (1984).
Courtney, M. et al. Nature 313, 149–151 (1984).
Bode, W. et al. EMBO J. 5, 2453–2458 (1986).
McKerrow, J. H., Pino-Heiss, S., Lindquist, R. & Werb, Z. J. biol. Chem. 260, 3703–3707 (1985).
Werb, Z., Banda, M. J., McKerrow, J. H. & Sandhaus, R. A. J. invest. Derm. 79, 154–159 (1982).
Perler, F. et al. Cell 20, 555–565 (1980).
Barth, R. K., Gross, K. W., Gremke, L. C. & Hastie, N. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 500–504 (1982).
Meehan, R. R., Barlow, D. P., Hill, R. E., Hogan, B. L. M. & Hastie, N. D. EMBO J. 3, 1881–1885 (1984).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, R., Hastie, N. Accelerated evolution in the reactive centre regions of serine protease inhibitors. Nature 326, 96–99 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/326096a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/326096a0
This article is cited by
-
Avian corticosteroid-binding globulin: biological function and regulatory mechanisms in physiological stress responses
Frontiers in Zoology (2021)
-
Evolutionary Aspects of the Structural Convergence and Functional Diversification of Kunitz-Domain Inhibitors
Journal of Molecular Evolution (2020)
-
Characterisation of major histocompatibility complex class IIa haplotypes in an island sheep population
Immunogenetics (2019)
-
Positive selection and climatic effects on MHC class II gene diversity in hares (Lepus capensis) from a steep ecological gradient
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Positive selection in cathelicidin host defense peptides: adaptation to exogenous pathogens or endogenous receptors?
Heredity (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.