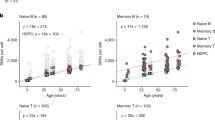
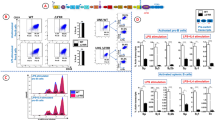
Abstract
The development from stem cells to pre-B cells, B lymphocytes and, finally, plasma cells and memory cells proceeds through various stages which have been defined by the genomic context in which immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy (H) and light (L) chain gene segments are found, as well as by their state of expression1–7. They have also been identified by surface marker analysis5,8,9 and susceptibility to various stimuli regulating growth and differentiation10. We have searched for genes that are expressed at given stages in the B-lymphocyte development pathway and which might function to control this development at various stages. A complementary DNA sequence called pZ183 was found in a library constructed from messenger RNA of the murine pre-B lymphoma cell line 70Z/3 which is selectively expressed in pre-B cells11. Here we report the nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone (pZ183-l) containing 0.7 kilobases (kb) of the pZ183 gene. Part of this sequence shows strong homology to constant (C) and joining (J) region sequences of λ1 L chains. Our findings define a new immunoglobulin L-chain-related locus, which we call λ5, that is selectively transcribed in pre-B lymphocytes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tonegawa, S. Nature 302, 575–581 (1983).
Maki, R., Kearney, J., Paige, C. & Tonegawa, S. Science 209, 1366–1369 (1982).
Alt, F. W., Rosenberg, N., Lewis, S., Thomas, E. & Baltimore, D. Cell 27, 381–390 (1981).
Perry, R. P., Kelley, D. E., Coleclough, C. & Kearney, J. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 247–251 (1981).
Coffman, R. L. & Weissman, I. L. Molec. cell. Immun. 1, 33–38 (1983).
Paige, C. J., Kincade, P. W. & Ralph, P. J. Immun. 121, 641–647 (1978).
Reth, M. G., Ammirati, P., Jackson, S. & Alt, F. W. Nature 317, 353–355 (1985).
McKearn, J. P., Baum, C. & Davie, J. M. J. Immun. 132, 332–339 (1984).
Kincade, P. W., Lee, G., Watanabe, T., Sun, L. & Scheid, M. P. J. Immun. 126, 2262–2266 (1981).
Melchers, F., Andersson, J. & Phillips, R. A. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 41, 147–158 (1977).
Sakaguchi, N., Berger, C. N. & Melchers, F. EMBO J. 5, 2139–2147 (1986).
Hozumi, N. & Tonegawa, S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 3628–3632 (1976).
Sakano, H., Maki, R., Kurosawa, Y., Roder, W. & Tonegawa, S. Nature 286, 676–683 (1980).
Sugiyama, H. et al. Nature 303, 812–815 (1983).
Alt, F. W. et al. EMBO J. 3, 1209–1219 (1984).
Lewis, S., Rosenberg, N., Alt, F. & Baltimore, D. Cell 30, 807–816 (1983).
Burrows, O. D., Beck-Engeser, G. B. & Wabl, M. R. Nature 306, 243–246 (1983).
Hieter, P. A., Korsmeyer, S. J., Waldmann, T. A. & Leder, P. Nature 290, 368–372 (1981).
GenBank, Genetic Sequence Data Bank Release 35.0 (1985).
Scott, C. L., Mushinski, J. F., Huppi, C., Weigert, M. & Potter, M. Nature 300, 757–760 (1982).
Kabat, E. A., Wu, T. T., Bilofsky, H., Reid-Miller, M. & Perry, H. . in Sequences of Proteins of Immunoiogical Interest (NIH, Bethesda, 1983).
Hedrock, S. M., Nielsen, E. A., Kavaler, J., Cohen, D. I. & Davis, M. M. Nature 308, 253–258 (1984).
Weiss, S., Meyer, J. & Wabl, M. R. Eur. J. Immun. 15, 765–768 (1985).
Saito, H. et al. Nature 309, 757–762 (1984).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. & Sambrook, J. . in Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual, 230–242 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1982).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Bothwell, A. L. M. et al. Nature 298, 380–383 (1982).
Saito, H. et al. Nature 312, 36–40 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakaguchi, N., Melchers, F. λ5, a new light-chain-related locus selectively expressed in pre-B lymphocytes. Nature 324, 579–582 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/324579a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/324579a0
This article is cited by
-
CD34+ myeloma cells with self-renewal activities are therapy-resistant and persist as MRD in cell cycle quiescence
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Autoimmunity checkpoints as therapeutic targets in B cell malignancies
Nature Reviews Cancer (2018)
-
Interference with pre-B-cell receptor signaling offers a therapeutic option for TCF3-rearranged childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Blood Cancer Journal (2014)
-
BACH2 mediates negative selection and p53-dependent tumor suppression at the pre-B cell receptor checkpoint
Nature Medicine (2013)
-
Proceedings of the Conference “Lymphocyte Development, Tolerance and Autoimmunity: Solved and Open Questions”, Held at the Ludwik Hirszfeld Institute of Immunology and Experimental Therapy, Polish Academy of Sciences, on May 12, 2011 (Wrocław, Poland)
Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.