Abstract
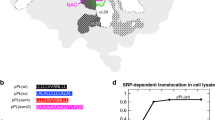
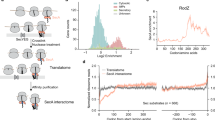
Hydrophobic signal sequences direct the translocation of nascent secretory proteins and many membrane proteins across the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum1,2. Initiation of this process involves the signal recognition particle (SRP)3,4, which consists of six polypeptide chains and a 7S RNA4 and interacts with ribosomes carrying nascent secretory polypeptide chains. In the case of aminoterminal, cleavable signal sequences, in the absence of microsomal membranes it exerts a site-specific translational arrest in vitro3,5,6. The size of the arrested fragment (60–70 amino-acid residues) suggests that elongation stops when the signal sequence has emerged fully from the ribosome. However, a direct interaction between the signal sequence and SRP has not previously been demonstrated and has even been questioned recently7. We now show for the first time a direct interaction between the signal sequence of a secretory protein and a component of SRP, the 54K polypeptide (relative molecular mass (Mr) 54,000). This was achieved by means of a new method of affinity labelling which involves the translational incorporation of an amino acid, carrying a photoreactive group, into nascent polypeptides.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blobel, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 1496–1500 (1980).
Rapoport, T. A. & Wiedmann, M. Curr. Topics Membrane Transport 24, 1–63 (1985).
Walter, P. & Blobel, G. J. Cell Biol. 91, 557–561 (1981).
Walter, P. & Blobel, G. Nature 299, 691–698 (1982).
Walter, P., Ibrahimi, I. & Blobel, G. J. Cell Biol. 91, 545–550 (1981).
Meyer, D. I., Krause, E. & Dobberstein, B. Nature 297, 647–650 (1982).
von Heijne, G. FEBS Lett. 190, 1–5 (1985).
Johnson, A.E., Woodward, W.R., Herbert, E. & Menninger, J.R. Biochemistry 15, 569–575 (1976).
Sasavage, N. L., Nilson, J. H., Horowitz, S. & Rottman, F. M. J. biol Chem. 257, 678–681 (1982).
Walter, P. & Blobel, G. J. Cell Biol. 97, 1693–1699 (1983).
Hobden, A. H. & Cundliffe, E. Biochem. J. 170, 57–61 (1978).
Gilmore, R. & Blobel, G. Cell (in the press).
Blobel, G. & Dobberstein, B. J. Cell Biol. 67, 852–862 (1975).
Prehn, S., Tsamaloukas, A. & Rapoport, T. A. Eur. J. Biochem. 107, 185–195 (1980).
Finkelstein, A. V., Bendzko, P. & Rapoport, T. A. FEBS Lett. 161, 176–179 (1983).
von Heijne, G. & Blomberg, C. Eur. J. Biochem. 97, 175–181 (1979).
Engelman, D. M. & Steitz, T. A. Cell 23, 411–422 (1981).
Wickner, W. A. Rev. Biochem. 48, 23–45 (1979).
Bommer, U. A., Henske, A. & Bielka, H. Acta biol. med. germ. 37, 1363–1376 (1978).
Galardy, R. E., Craig, L. C., Jamieson, J. D. & Printz, M. P. J. biol. Chem. 249, 3510–3518 (1974).
Wiedmann, M., Huth, A. & Rapoport, T. A. Nature 309, 637–639 (1984).
Walter, P. & Blobel, G. Meth. Enzym. 96, 682–691 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurzchalia, T., Wiedmann, M., Girshovich, A. et al. The signal sequence of nascent preprolactin interacts with the 54K polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Nature 320, 634–636 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/320634a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/320634a0
This article is cited by
-
Crosslinking and Reconstitution Approaches to Study Protein Transport
The Protein Journal (2019)
-
Mammalian SRP receptor switches the Sec61 translocase from Sec62 to SRP-dependent translocation
Nature Communications (2015)
-
Plasmodium falciparum signal recognition particle components and anti-parasitic effect of ivermectin in blocking nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of SRP
Cell Death & Disease (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.