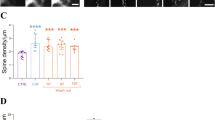
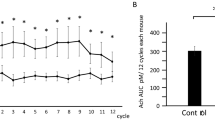
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive degenerative disease of the nervous system characterized neuropathologically by the presence of senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in amygdala, hippocampus and neocortex1–4. Dysfunction and death of basal forebrain cholinergic neurones projecting to forebrain targets5,6 are associated with marked decreases in cholinergic markers, including the activity of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)2,3,7–9. Although cortical levels of somatostatin10–12 and somatostatin receptors13 are reduced in Alzheimer’s, no consistent changes have been reported in other neuropeptide systems12,14–17. We have now examined in control and Alzheimer’s brain tissues pre- and postsynaptic markers of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF), a hypothalamic peptide regulating pituitary-adrenocortical secretion18,19 which also seems to act as a neu retransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS) (reviewed in refs 20, 21). We have found that in Alzheimer’s, the concentrations of CRF-like immunoreactivity (CRF-IR) are reduced and that there are reciprocal increases in CRF receptor binding in affected cortical areas. These changes are significantly correlated with decrements in ChAT activity. Our results strongly support a neurotransmitter role for CRF in brain and demonstrate, for the first time, a modulation of CNS CRF receptors associated with altered CRF content. These observations further suggest a possible role for CRF in the pathophysiology of the dementia. Future therapies directed at increasing CRF levels in brain may prove useful for treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terry, R. D. & Davies, P. A. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 77–95 (1980).
Price, D. L., Whitehouse, P. J. & Struble, R. G. A. Rev. Med. 36, 349–356 (1985).
Bowen, D. M., Smith, C. B., White, P. & Davison, A. N. Brain 99, 459–496 (1976).
Terry, R. D. & Katzman, R. Ann. Neurol. 14, 497–506 (1983).
Whitehouse, P. J. et al. Science 215, 1237–1239 (1982).
Cuello, A. C. & Sofroniew, M. V. Trends Neurosci. 7, 74–78 (1984).
Davies, P. & Maloney, A. J. R. Lancet ii, 1403 (1976).
Perry, E. K., Perry, R. H., Blessed, G. & Tomlinson, B. E. Lancet i, 89 (1977).
Rossor, M. N., Iversen, L. L., Reynolds, G. P., Mountjoy, C. Q. & Roth, M. Br. med. J. 288, 961 (1984).
Davies, P., Katzman, R. & Terry, R. D. Nature 288, 279–280 (1980).
Rossor, M., Emson, P. C., Mountjoy, C. G., Roth, S. M. & Iversen, L. L. Neurosci Lett. 20, 373–377 (1980).
Ferrier, I. N. et al. J. neurol. Sci. 62, 159–170 (1983).
Beal, M. F. et al. Science 229, 289–291 (1985).
Rossor, M. N. et al. Life Sci. 29, 405–410 (1981).
Rossor, M. N. et al. Brain Res. 201, 249–253 (1980).
Yates, C. M. et al. Brain Res. 258, 45–52 (1983).
Biggins, J. A. et al. J. neurol. Sci. 58, 117–122 (1983).
Vale, W., Spiess, J., Rivier, C. & Rivier, J. Science 213, 1394–1397 (1981).
Rivier, C., Rivier, J. & Vale, W. W. Science 218, 377–379 (1982).
Vale, W. et al. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 39, 245–270 (1983).
De Souza, E. B. Compreh. Ther. 11, 3–5 (1985).
Vale, W. et al. Meth. Enzym. 103, 565–577 (1983).
Bull, G. & Oderfeld-Nowak, B. J. Neurochem. 18, 935–94 (1971).
De Souza, E. B., Perrin, M. H., Rivier, J. E., Vale, W. W. & Kuhar, M. J. Brain Res. 296, 202–207 (1984).
De Souza, E. B. et al. Neuroendocrinology 40, 419–422 (1985).
De Souza, E. B. et al. Science 224, 1449–1451 (1984).
De Souza, E. B. et al. J. Neurosci. 5, 3189–3202 (1985).
Wynn, P. C., Aguilera, G., Morell, J. & Catt, K. J. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 110, 602–608 (1983).
Wynn, P. C. et al. Peptides 5, 1077–1084 (1984).
Olschowka, J. A., O'Donohue, T. L., Mueller, G. P. & Jacobowitz, D. M. Peptides 3, 995–1015 (1982).
Swanson, L. W., Sawchenko, P. E., Rivier, J. & Vale, W.W. Neuroendocrinology 36, 165–186 (1983).
Bissette, G., Reynolds, G. P., Kilts, C. D., Widerlov, E. & Nemeroff, C. B. J. Am. med. Ass. 254, 3067–3069 (1985).
Jacobowitz, D. M., Skofitsch, G., Sills, M. A. & Crawley, J. N. Neural and Endocrine Peptides and Receptors '85, abstr., 39 (1985).
Whitehouse, P. J. & Au, K. S. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol Biol. Psychiat. (in the press).
Lang, W. & Henke, H. Brain Res. 267, 271–280 (1983).
Mash, D. C., Flynn, D. D. & Potter, L. T. Science 228, 1115–1117 (1985).
Bird, T. D., Stranahan, S., Sumi, S. M. & Raskind, M. Ann. Neurol. 14, 284–293 (1983).
Sims, N. R. et al. J. Neurochem. 40, 503–509 (1983).
Crawley, J. N., Olschowska, J. A., Diz, D. & Jacobowitz, D. Peptides 6, 891–901 (1985).
Peterfreund, R. A. & Vale, W. W. Endocrinology 112, 1275–1278 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Souza, E., Whitehouse, P., Kuhar, M. et al. Reciprocal changes in corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-like immunoreactivity and CRF receptors in cerebral cortex of Alzheimer's disease. Nature 319, 593–595 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/319593a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/319593a0
This article is cited by
-
Corticotropin releasing factor-binding protein (CRF-BP) as a potential new therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease and stress disorders
Translational Psychiatry (2019)
-
The role of G protein-coupled receptors in the pathology of Alzheimer's disease
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2011)
-
Time- and dose-dependent effects of corticotropin releasing factor on cerebral glucose metabolism in rats
Journal of Neural Transmission (2005)
-
Effects of CRF1 receptor antagonists and benzodiazepines in the Morris water maze and delayed non-matching to position tests
Psychopharmacology (2005)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.