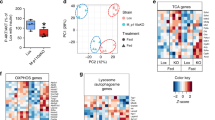
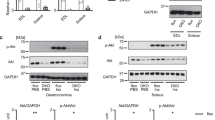
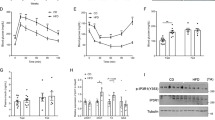
Abstract
Obese syndromes of genetic origin or experimentally induced are characterized by resistance to insulin both in vivo (association of hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinaemia) and in vitro1. Thus, skeletal muscle of obese mice, which is the most important target organ for the action of insulin, displays a reduced response to insulin2–4. This hormonal resistance cannot be explained by the moderate decrease in the number of insulin receptors found in obese animals3–5. In fact, it is generally believed that a biochemical event occurring very early after binding of insulin to its receptor, which is the first step in insulin action, is defective in obesity. One of the earliest post-binding events so far recognized, and which is thought to have a key role in cellular signalling by the insulin receptor, is the insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of its receptor6–8. In an effort to localize the defect responsible for the insulin resistance in obesity, we have studied the insulin receptor protein kinase activity and we show here that insulin receptors from skeletal muscles of insulin-resistant obese mice have an altered kinase activity for phosphorylation of both the receptor itself and of exogeneous substrates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assimacopoulos-Jeannet, F. & Jeanrenaud, B. Clin. endocr. Metab. 5, 337–365 (1976).
Cuendet, G. S., Loten, E. G., Jeanrenaud, B. & Renold, A. E. J. clin. Invest. 58, 1078–1088 (1976).
Le Marchand-Brustel, Y., Jeanrenaud, B. & Freychet, P. Am. J. Physiol. 234, E348–E358 (1978).
Le Marchand, Y., Freychet, P. & Jeanrenaud, B. Endocrinology 102, 74–85 (1978).
Le Marchand-Brustel, Y. & Freychet, P. Metabolism 27, 1982–1993 (1978).
Kasuga, M., Karlsson, F. A. & Kahn, C. R. Science 215, 185–187 (1982).
Van Obberghen, E. & Kowalski, A. FEBS Lett. 143, 179–182 (1982).
Van Obberghen, E., Rossi, B., Kowalski, A., Gazzano, H. & Ponzio, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 945–949 (1983).
Van Obberghen, E. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 1052–1056 (1981).
Van Obberghen, E. Biochem. Pharmac. 33, 889–896 (1984).
Burant, C. F., Treutelaar, M. K., Landreth, G. E. & Buse, M. G. Diabetes 33, 704–708 (1984).
Kahn, C. R. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 294, 739–745 (1976).
Braun, S., Raymond, W. E. & Racker, E. J. biol. Chem. 259, 2051–2054 (1984).
Kadowaki, T., Kasuga, M., Akanuma, Y., Ezaki, O. & Takaku, F. J. biol. Chem. 259, 14208–14216 (1984).
Grigorescu, F., Flier, J. S. & Kahn, C. R. J. biol. Chem. 259, 15003–15006 (1984).
Grunberger, G., Zick, Y. & Gorden, P. Science 223, 932–934 (1984).
Blackshear, P. J., Nemenoff, R. A. & Avruch, J. Endocrinology 114, 141–152 (1984).
Carlin, C. R., Phillips, P. D., Knowles, B. B. & Cristofalo, V. J. Nature 306, 617–620 (1983).
Soll, A. H., Kahn, C. R., Neville, D. M. Jr & Roth, J. J. clin. Invest. 56, 769–780 (1975).
Kasuga, M., Kahn, C. R., Hedo, J. A., Van Obberghen, E. & Yamada, K. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 6916–6921 (1981).
Laemmli, U. K. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Fehlmann, M. et al. J. Cell Biol. 93, 82–87 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Marchand-Brustel, Y., Grémeaux, T., Ballotti, R. et al. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase is defective in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant obese mice. Nature 315, 676–679 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/315676a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/315676a0
This article is cited by
-
Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
Novel roles for insulin receptor (IR) in adipocytes and skeletal muscle cells via new and unexpected substrates
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2013)
-
Nitric oxide agents impair insulin-mediated signal transduction in rat skeletal muscle
BMC Biochemistry (2006)
-
Decreased skeletal muscle phosphotyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) activity towards insulin receptors in insulin-resistant Zucker rats measured by delayed Europium fluorescence
Diabetologia (1996)
-
Impaired tyrosine-kinase activity of muscle insulin receptors from hypomagnesaemic rats
Diabetologia (1995)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.