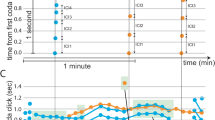
Abstract
Little is known about how vocal patterns develop in non-human primates, mainly because suitable controlled experiments are difficult to carry out on these animals1. Results of isolation experiments2–4 and observations of interspecific hybrids1,5 suggest no greater role for vocal learning than exists in many other vertebrates6–9, and less than has been found in birds10–13. We have now studied vocal patterns of hybrids between white-handed gibbons (Hylobates lar) and pileated gibbons (Hylobates pileatus) in natural mixed-species groups, in a zone of interspecies contact in central Thailand, and in some captive mixed-species groups. We find that in female hybrids, the patterns of the loud and stereotyped ‘great-calls’ show no evidence of learning from parents, and appear to be under strong genetic control. Daughters maturing in groups with genetically unlike parents develop great-calls unlike those of their mothers, even though these calls develop only while the daughters sing simultaneously with their mothers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newman, J. D. & Symmes, D. in Primate Communication (eds Snowdon, C. T., Brown, C. H. & Petersen, M. R.) 259–278 (Cambridge University Press, 1982).
Kellogg, W. N. Science 162, 423–427 (1968).
Winter, P., Handley, P., Ploog, D. & Schott, D. Behaviour 47, 230–239 (1973).
Newman, J. D. & Symmes, D. Devl Psychol. 7, 351–358 (1974).
Marler, P. & Tenaza, R. R. in How Animals Communicate (ed. Sebeok, T. A.) 965–1033 (Indiana University Press, Bloomington, 1977).
Blair, W. F. Evolution 9, 469–480 (1955).
Zweifel, R. G. Copeia 1968, 269–285 (1968).
Gerhardt, H. C. Behaviour 59, 130–151 (1974).
Littlejohn, M. J. & Watson, G. F. Evolution 30, 848–850 (1976).
Lade, B. I. & Thorpe, W. H. Nature 202, 366–368 (1964).
McGrath, T. A., Shalter, M. D., Schleidt, W. M. & Sarvella, P. Nature 237, 47–48 (1972).
Marler, P. & Mundinger, P. in Ontogeny of Vertebrate Behavior (ed. Moltz, H.) 389–450 (Academic, New York, 1971).
Kroodsma, D. E., Miller, E. H. & Ouellet, H. (eds) Acoustic Communication in Birds (Academic, New York, 1982).
Ellefson, J. O. in Gibbon and Siamang Vol. 3 (ed. Rumbaugh, D. M.) 1–136 (Karger, Basel, 1974).
Chivers, D. J. Contr. Primatol. 4, 1–335 (1974).
Marshall, J. T. & Marshall, E. R. Science 193, 235–237 (1976).
Srikosamatara, S. thesis, Mahidol Univ., Bangkok (1980).
Gittins, S. P. in The Lesser Apes: Evolutionary and Behavioural Biology (eds Preuschoft, H., Chivers, D., Brockelman, W. & Creel, N.) 354–375 (Edinburgh University Press, 1984).
Deputte, B. L. in Primate Communication (eds Snowdon, C. T., Brown, C. H. & Petersen, M. R.) 67–93 (Cambridge University Press, 1982).
Schilling, D. in The Lesser Apes: Evolutionary and Behavioural Biology (eds Preuschoft, H., Chivers, D., Brockelman, W. & Creel, N.) 390–403 (Edinburgh University Press, 1984).
Tenaza, R. R. Z. Tierpsychol. 40, 37–52 (1976).
Kappeler, M. in The Lesser Apes: Evolutionary and Behavioural Biology (eds Preuschoft, H., Chivers, D., Brockelman, W. & Creel, N.) 376–389 (Edinburgh University Press, 1984).
Raemaekers, J. J. & Raemaekers, P. M. Anim. Behav. (in the press).
Lamprecht, J. Z. Tierpsychol. 27, 186–204 (1970).
Brockelman, W. Y. in The Lesser Apes: Evolutionary and Behavioural Biology (eds Preuschoft, H., Chivers, D., Brockelman, W. & Creel, N.) 285–290 (Edinburgh University Press, 1984).
Goustard, M. in The Lesser Apes: Evolutionary and Behavioural Biology (eds Preuschoft, H., Chivers, D., Brockelman, W. & Creel, N.) 404–415 (Edinburgh University Press, 1984).
Marshall, J. T., Ross, B. A. & Chantharojvong, S. J. Mammal. 53, 479–486 (1972).
Haimoff, E. H. in The Lesser Apes: Evolutionary and Behavioural Biology (eds Preuschoft, H., Chivers, D., Brockelman, W. & Creel, N.) (Edinburgh University Press, in the press).
Brockelman, W. Y. & Gittins, S. P. in The Lesser Apes: Evolutionary and Behavioural Biology (eds Preuschoft, H., Chivers, D., Brockelman, W. & Creel, N.) 497–531 (Edinburgh University Press, 1984).
Brockelman, W. Y. Recent Adv. Primatol. 3, 315–318 (1978).
Brockelman, W. Y. & Srikosamatara, S. in The Lesser Apes: Evolutionary and Behavioural Biology (eds Preuschoft, H., Chivers, D., Brockelman, W. & Creel, N.) 298–323 (Edinburgh University Press, 1984).
Tilson, R. L. J. Bombay nat. Hist. Soc. 76, 1–16 (1979).
Tilson, R. L. Folia Primatol. 35, 259–287.
Whitten, A. J. Int: J. Primatol. 3, 33–51 (1982).
Chivers, D. J. & Raemaekers, J. J. in Malayan Forest Primates: Ten Years' Study in Tropical Rain Forest (ed. Chivers, D. J.) 209–260 (Plenum, New York, 1980).
Raemaekers, J. J., Raemaekers, P. H. & Haimoff, E. H. Behaviour (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brockelman, W., Schilling, D. Inheritance of stereotyped gibbon calls. Nature 312, 634–636 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/312634a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/312634a0
This article is cited by
-
Strange Tunes—Acoustic Variation and Character Displacement in a Tarsier Hybrid Zone
International Journal of Primatology (2023)
-
Evidence for Vocal Flexibility in Wild Siamang (Symphalangus syndactylus) Ululating Scream Phrases
International Journal of Primatology (2023)
-
Is Malaysia’s “mystery monkey” a hybrid between Nasalis larvatus and Trachypithecus cristatus? An assessment of photographs
International Journal of Primatology (2022)
-
Genetic analysis of hybridization between white-handed (Hylobates lar) and pileated (Hylobates pileatus) gibbons in a contact zone in Khao Yai National Park, Thailand
Primates (2022)
-
Long-Distance Vocal Signaling in White-Handed Gibbons (Hylobates lar)
International Journal of Primatology (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.