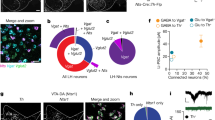
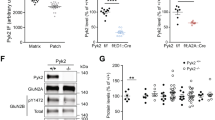
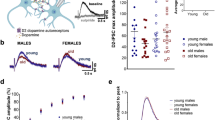
Abstract
The amino acid sequence of the opioid peptide Leu-enkephalin1–3 is found within several larger peptides4–8, which are generated from the precursors proenkephalin and prodynorphin. Proenkephalin contains four copies of the sequence of Met-enkephalin, a single copy of the sequence of Leu-enkephalin and one copy each of two extended Met-enkephalin sequences9–11. Proenkephalin contains three peptides—α-neo-endorphin, dynorphin A and dynorphin B12—the N-terminal sequences of which are identical to that of Leu-enkephalin. There is good evidence that the large amounts of Leu-enkephalin found in the adrenal medulla are generated from the precursor proenkephalin2,4,13,14, but as yet prodynorphin has not been shown to be processed to yield Leu-enkephalin. We show here that the relatively high levels of Leu-enkephalin found in the rat substantia nigra are supplied by striatonigral axons and generated from the precursor prodynorphin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hughes, J. et al. Nature 258, 577–579 (1975).
Maysinger, D. et al. Neuropeptides 2, 211–226 (1982).
North, R. A. & Egan, T. M. Br. med. Bull. 39, 71–76 (1983).
Udenfriend, S. & Kilpatrick, D. L. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 221, 309–323 (1983).
Kilpatrick, D. L., Wahlstrom, N., Lhm, H. W., Blacher, R. & Udenfriend, S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 6480–6483 (1982).
Kangawa, K., Minamino, N., Chino, N., Sakakibara, S. & Matsuo, H. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 99, 871–878 (1981).
Goldstein, A., Fischli, W., Lowney, L. I., Hunkapiller, M. & Hood, L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 7219–7223 (1981).
Minamino, N., Kangawa, K., Chino, N., Sakakibara, S. & Matsuo, H. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 99, 864–870 (1981).
Noda, M. et al. Nature 295, 202–208 (1982).
Gubler, U., Seeburg, P., Hoffman, B. J., Gage, L. P. & Udenfriend, S. Nature 295, 206–208 (1982).
Comb, M., Seeburg, P. H., Adelman, J., Eiden, L. & Herbert, E. Nature 295, 663–666 (1982).
Kakidani, H. et al. Nature 298, 245–249 (1982).
Denis, D., Day, R. & Lemaire, S. Int. J. Peptide Protein Res. 19, 18–24 (1982).
Hughes, J. Br. med. Bull. 39, 17–24 (1983).
Zamir, N., Palkovits, M. & Brownstein, M. J. Brain Res. 280, 81–93 (1983).
Zamir, N., Palkovits, M., Weber, E. & Brownstein, M. J. Brain Res. (in the press).
Cuello, A. C. & Paxinos, G. Nature 271, 178–180 (1978).
Vincent, S. R., Hölkfelt, T., Christensson, I. & Terenius, L. Neurosci. Lett. 33, 185–190 (1982).
Vincent, S. R., Hölkfelt, T., Christensson, I. & Terenius, L. Eur. J. Pharmac. 85, 251–252 (1982).
Palkovits, M., Brownstein, M. J. & Zamir, N. Neuropeptides (in the press).
Paterson, S. J., Robson, L. E. & Kosterlitz, H. W. Br. med. Bull. 39, 25–30 (1983).
Palkovits, M. Brain Res. 59, 449–450 (1973).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. & Randall, R. J. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Weber, E. & Barchas, J. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 1125–1129 (1983).
Weber, E., Geis, R., Voigt, K. M. & Barchas, J. D. Brain Res. 260, 166–171 (1983).
Weber, E., Roth, K. A., Evan, C. J., Chang, J-K. & Barchas, J. D. Life Sci. 31, 1761–1764 (1982).
Halasz, B. & Pupp, L. Endocrinology 77, 553–562 (1965).
Coons, A. H. in General Cytochemical Methods (ed. Danielli, J. F.) 399–422 (Academic, New York, (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamir, N., Palkovits, M., Weber, E. et al. A dynorphinergic pathway of Leu-enkephalin production in rat substantia nigra. Nature 307, 643–645 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/307643a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/307643a0
This article is cited by
-
Benzomorphan alkaloids: Natural peptidomimetics of opioid peptide pharmacophores
Letters in Peptide Science (1995)
-
The effect of prolonged treatment with imipramine and electroconvulsive shock on the levels of endogenous enkephalins in the nucleus accumbens and the ventral tegmentum of the rat
Journal of Neural Transmission (1995)
-
Neuropeptide levels in the basal ganglia of aged common marmosets following prolonged treatment with MPTP
Journal of Neural Transmission - Parkinson's Disease and Dementia Section (1991)
-
Two different types of dynorphin-A-immunoreactive terminals in rat substantia nigra
Cell and Tissue Research (1990)
-
Intranigral infusion of enkephalins elicits dyskinetic biting in rats
Psychopharmacology (1989)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.