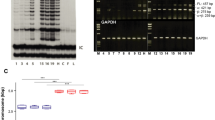
Abstract
Several groups have shown that the malignant phenotype can be transferred to NIH/3T3 fibroblasts by incorporation of DNA isolated from tumour cell lines1–5. These studies have demonstrated that the transforming activity of DNA isolated from human bladder, lung and colon carcinoma cell lines is related to an alteration of the cellular homologues of the ras genes of Harvey or Kirsten murine sarcoma viruses6–11. It is, however, unclear what relevance these observations have to the multistage nature of tumorigenesis in vivo, in which several independent events are required in both humans12,13 and experimental animals14,15. The activation of a cellular oncogene in a defined experimental system for the progressive induction of solid tumours has not yet been demonstrated. We report here that high molecular weight DNA from transplanted squamous cell carcinomas induced by sequential treatment of mouse skin with initiators and promoters of carcinogenesis causes morphological transformation of NIH/3T3 fibroblasts at high frequency. The transforming properties are due to the transfer of an activated cellular homologue of the Harvey-ras (rasH) oncogene.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shih, C., Shilo, B., Goldfarb, M. P., Dannenberg, A. & Weinberg, R. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 5714–5718 (1979).
Cooper, G. M., Okenquist, S. & Silverman, L. Nature 284, 418–421 (1980).
Shih, C., Padhy, L. C., Murray, M. J. & Weinberg, R. A. Nature 290, 261–264 (1981).
Krontiris, T. G. & Cooper, G. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 1181–1184 (1981).
Perucho, M. et al. Cell 27, 467–476 (1981).
Santos, E., Tronick, S. R., Aaronson, S. A., Pulciani, S. & Barbacid, M. Nature 298, 343–347 (1982).
Der, C. J., Krontiris, T. G. & Cooper, G. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 3637–3640 (1982).
Parada, L. F., Tabin, C. J., Shih, C. & Weinberg, R. A. Nature 297, 474–478 (1982).
Reddy, E. P., Reynolds, R. K., Santos, E. & Barbacid, M. Nature 300, 149–152 (1982).
Tabin, C. J. et al. Nature 300, 143–149 (1982).
Taparowsky, E. et al. Nature 300, 762–765 (1982).
Cairns, J. Nature 289, 353–357 (1981).
Logan, J. & Cairns, J. Nature 300, 104–105 (1982).
Hecker, E., Fusenig, N. E., Kunz, W., Marks, F. & Theilmann, H. W. (eds) Carcinogenesis Vol. 7 (RavenNew York, 1982).
Boutwell, R. K. CRC crit. Rev. Tox. 2, 419–443 (1974).
Burns, F. J., Vanderlaan, M., Snyder, E. & Albert, R. E. in Carcinogenesis Vol. 2 (eds Slaga, T. J., Sivak, A. & Boutwell, R. K.) 91–96 (Raven, New York, 1978).
Ellis, R. W. et al. J. Virol. 36, 408–420 (1980).
Pulciani, S. et al. Nature 300, 539–542 (1982).
Murray, M. J. et al. Cell 25, 355–361 (1981).
Bubenik, J. et al. Int. J. Cancer 11, 765–773 (1973).
Marshall, C. J., Franks, L. M. & Carbonnel, A. W. J. natn. Cancer Inst. 58, 1743–1747 (1977).
Yuspa, S. H. & Morgan, D. L. Nature 293, 72–74 (1981).
Shih, C., Weinberg, R. A. Cell 29, 161–169 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balmain, A., Pragnell, I. Mouse skin carcinomas induced in vivo by chemical carcinogens have a transforming Harvey-ras oncogene. Nature 303, 72–74 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/303072a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/303072a0
This article is cited by
-
Targeting PI3Kα overcomes resistance to KRasG12C inhibitors mediated by activation of EGFR and/or IGF1R
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2023)
-
Advances in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Nature Reviews Cancer (2023)
-
Peto’s paradox revisited: black box vs mechanistic approaches to understanding the roles of mutations and promoting factors in cancer
European Journal of Epidemiology (2023)
-
Synthetic lethal kinases in Ras/p53 mutant squamous cell carcinoma
Oncogene (2022)
-
The critical roles of somatic mutations and environmental tumor-promoting agents in cancer risk
Nature Genetics (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.