Abstract
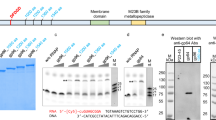
During infection of Escherichia coli, bacteriophage T7 encodes a simple RNA polymerase that consists of a single protein species of 883 amino acids1,2. This phage-specified RNA polymerase transcribes the late genes of T7 in two temporal classes (class II and class III)3. The mechanism by which late transcription is regulated is unclear. In general, class II promoters are weaker than class III promoters and in vitro the purified phage RNA polymerase discriminates between these classes of promoters as a function of ionic conditions and agents that affect the stability of the DNA helix4. Sequence analysis of 17 promoters utilized by the phage RNA polymerase reveals a highly conserved 23 base-pair (bp) consensus sequence that is different from known bacterial promoters5. To determine which structural features of the late promoters are important for the regulation of transcription, we have constructed a number of class II/III hybrid promoters and have determined their properties both in vitro and in vivo. The results reported here indicate that an A + T-rich region that overlaps the upstream end of the promoter has an important role in the control of promoter selection during T7 infection. In addition, changes in the 23-bp conserved promoter sequence may also affect promoter regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chamberlin, M., McGrath, J. & Waskell, L. Nature 228, 227–231 (1970).
Stahl, S. J. & Zinn, K. J. molec. Biol. 148, 481–485 (1981).
McAllister, W. T. & Wu, H-L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 804–808 (1978).
McAllister, W. T. & Carter, A. D. Nucleic Acids Res. 8, 4821–4837 (1980).
Rosenberg, M. & Court, D. A. Rev. Genet. 13, 319–353 (1979).
McAllister, W. T., Morris, C., Rosenberg, A. H. & Studier, F. W. J. molec. Biol. 153, 527–544 (1981).
Panayotatos, N. & Wells, R. D. Nature 280, 35–39 (1979).
Osterman, H. L. & Coleman, J. E. Biochemistry 20, 4884–4892 (1981).
Condit, R. C. J. molec. Biol. 98, 45–56 (1975).
Silberstein, S., Inouye, M. & Studier, F. W. J. molec. Biol. 96, 1–11 (1975).
Carter, A. D. & McAllister, W. T. J. molec. Biol. 153, 825–830 (1981).
Dunn, J. J. & Studier, F. W. J. molec. Biol. 148, 303–330 (1981).
Rosa, M. D. Cell 16, 815–825 (1979).
Oakley, J., Strothkamp, R., Sarris, A. & Coleman, J. Biochemistry 18, 528–537 (1979).
Maxam, A. & Gilbert, W. Meth. Enzym. 65, 499–559 (1980).
Studier, F. W. & Rosenberg, A. H. J. molec. Biol. 153, 503–525 (1981).
Colowick, S. P. & Kaplan, N. O. Meth. Enzym. 68, 1–555 (1979).
Studier, F. W. J. Bact. 124, 307–316 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jolliffe, L., Carter, A. & McAllister, W. Identification of a potential control region in bacteriophage T7 late promoters. Nature 299, 653–656 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/299653a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/299653a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.