Abstract
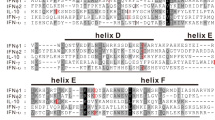
The two major classes of human type I interferons, leukocyte or α-interferon (IFN-α) and fibroblastor β-interferon (IFN-β) are antigenically distinct and encoded by separate structural genes1. Recently, genomic hybridization experiments have demonstrated the presence of ∼10 or more distinct human IFN-α (Hu IFN-α) genes which code for a family of homologous yet distinct proteins2,3, and 8 of these have been identified and sequenced3. In contrast, no evidence has been found for multiple Hu IFN-β genes3, although heterogeneity of Hu IFN-β mRNA has been observed4,5. The coding sequences of Hu IFN-α and IFN-β genes show weak but appreciable homology, indicating that they were derived from a common ancestor at a remote time6, whereas Hu IFN-α1 (a member of class D) and Hu IFN-α2 (a member of class A) diverged quite recently (∼22 Myr ago)7. We report here that all eight known IFN-α genes diverged from a common ancestor quite recently, at most ∼26 Myr ago. As mammalian divergence is known to have occurred ∼75 Myr ago8, this suggests that the IFN-α multigene family in primates is distinct in organization from that of other mammals. We provide evidence for a much lower rate of evolution for IFN-α G than for other α-interferons, and a rapid evolution of IFN-α E pseudogene similar to that of other pseudogenes9–11. A possible evolutionary origin of size heterogeneity in the 3′-noncoding region of IFN-α mRNAs is also discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavalieri, R. L., Havell, G. A., Vilcek, J. & Pestka, S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 3287–3291 (1977).
Nagata, S., Mantei, N. & Weissmann, C., Nature 287, 401–408 (1980).
Goeddel, D. V. et al. Nature 290, 20–26 (1981).
Sehgal, P. B. & Sagar, A. D. Nature 288, 95–97 (1980).
Weissenbach, J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 7152–7156 (1980).
Taniguchi, T. et al. Nature 285, 547–549 (1980).
Streuli, M., Nagata, S. & Weissmann, C. Science 209, 1343–1347 (1980).
Dayhoff, M. O. Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure Vol. 5, suppl. 3 (ed. Dayhoff, M. O.) (National Biochemical Research Foundation, Maryland, 1978).
Miyata, T. & Yasunaga, T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 450–453 (1981).
Miyata, T. & Hayashida, H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 5739–5743 (1981).
Kimura, M. J. molec. Evol. 16, 111–120 (1980).
Miyata, T. & Yasunaga, T. J. molec. Evol. 16, 23–36 (1980).
Miyata, T., Yasunaga, T. & Nishida, T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 7328–7332 (1980).
Wilson, A. C., Carlson, S. S. & White, T. J. A. Rev. Biochem. 46, 573–639 (1977).
Kimura, M. & Ohta, T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 2848–2852 (1974).
Jukes, T. H. & Cantor, C. R. Mammalian Protein Metabolism II (ed. Munro, H. N.) (Academic, New York, 1969).
Kimura, M. & Ohta, T. J. molec. Evol. 2, 87–90 (172).
Miyata, T. et al. J. molec. Evol. (submitted).
Stewart, W. E. II The Interferon System (Springer, New York, 1979).
Taira, H., Broeze, R. J., Jayram, B. M. & Lengyel, P. Science 207, 528–529 (1980).
Nishioka, Y. & Leder, P. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 2806–2809 (1980).
Vanin, E. F., Goldberg, G. I., Tucker, P. W. & Smithies, O. Nature 286, 222–226 (1980).
Jahn, C. L. et al. Cell 21, 159–168 (1980).
Lacy, E. & Maniatis, T. Cell 21, 545–553 (1980).
Proundfoot, N. J. & Maniatis, T. Cell 21, 537–544 (1980).
Bentley, D. L. & Rabbitts, T. H. Nature 288, 730–733 (1980).
Kimura, M. Nature 217, 624–626 (1968).
Kimura, M. Nature 267, 275–276 (1977).
Fritsch, E. F., Lawn, R. M. & Maniatis, T. Cell 19, 959–972 (1980).
Proundfoot, N. J. & Brownless, G. G. Nature 263, 211–214 (1976).
Setzer, D. R., McGrogan, M., Nunberg, J. H. & Schimke, R. T. Cell 22, 361–370 (1980).
Sokal, R. R. & Sneath, P. H. A. Principles of Numerical Taxonomy (Freeman, San Francisco, 1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyata, T., Hayashida, H. Recent divergence from a common ancestor of human IFN-α genes. Nature 295, 165–168 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/295165a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/295165a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular evolution of two actin genes from carrot
Plant Molecular Biology (1989)
-
Two soybean ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit genes share extensive homology even in distant flanking sequences
Plant Molecular Biology (1986)
-
Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits
Nature (1983)
-
Molecular clock of silent substitution: At least six-fold preponderance of silent changes in mitochondrial genes over those in nuclear genes
Journal of Molecular Evolution (1982)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.