Abstract
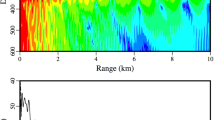
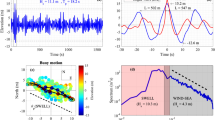
Early experimental work in the Antarctic1 using a ship-borne wave recorder has shown that pack ice can significantly attenuate incoming ocean waves, particularly those of shorter period. Wadhams2,3 has subsequently reported similar wave decay through Arctic ice in data obtained remotely by means of airborne laser profiling and inverted echo sounding from a submarine. The two predominant mechanisms by which the decay can occur—scattering by individual ice floes and energy loss by creep within each flexing floe—have been studied theoretically by Wadhams4,5, Squire6,7, and Squire and Allan8. We present here the results of further experiments to measure wave decay which took place in the Bering Sea during spring 1979 from the research ship Surveyor of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration9. During the cruise, oceanographic, meteorological and remote sensing data were also collected10,11. The results show the energy decay of waves in pack ice to be exponential with an attenuation coefficient which increases with decreasing wave period.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robin, G. de Q. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 255, 313–339 (1963).
Wadhams, P. Deep Sea Res. 25, 23–40 (1978).
Wadhams, P. J. geophys. Res. 80, 4520–4528 (1975).
Wadhams, P. J. geophys. Res. 78, 3552–3563 (1973).
Wadhams, P. thesis, Univ. Cambridge (1973).
Squire, V. A. J. Glaciol. 29, 425–431 (1978).
Squire, V. A. thesis, Univ. Cambridge (1978).
Squire, V. A. & Allan, A. J. Proc. Symp. Sea Ice Processes and Models, Seattle (in the press).
Squire, V. A. Tech. Rep. 79–2, (Scott Polar Research Institute, Cambridge, 1979).
Martin, S. Surveyor S132 Cruise Rep. (NOAA, 1979).
Martin, S. & Kauffman, P. Special Report. No. 89 (Department of Oceanography, University of Washington, Seattle, 1979).
Bendat, J. S. & Piersol, A. G. Random Data: Analysis and Measurement Procedures. (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1971).
Wadhams, P. Polar Rec. 19, 373–376 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Squire, V., Moore, S. Direct measurement of the attenuation of ocean waves by pack ice. Nature 283, 365–368 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/283365a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/283365a0
This article is cited by
-
Three-dimensional imaging of waves and floes in the marginal ice zone during a cyclone
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Analysis of Wave Distributions Using the WAVEWATCH-III Model in the Arctic Ocean
Journal of Ocean University of China (2022)
-
Thinner Sea Ice Contribution to the Remarkable Polynya Formation North of Greenland in August 2018
Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2021)
-
Propagation characteristics of damped traveling wave in a one-dimensional marginal sea ice
Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences (2015)
-
Modeling ocean wave propagation under sea ice covers
Acta Mechanica Sinica (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.