Abstract
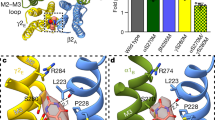
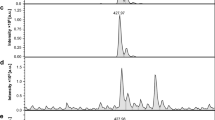
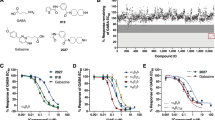
The benzodiazepines are potent anticonvulsants for a wide variety of experimental and clinical seizure disorders1,2. The demonstration of saturable, high-affinity and stereospecific binding sites for the benzodiazepines in the mammalian central nervous system suggests the presence of pharmacological receptors mediating the anticonvulsant properties of these compounds3,4. The good correlation between the anticonvulsant potencies of a series of benzodiazepines and their ability to inhibit 3H-diazepam binding in vitro further supports this hypothesis3,4, but evidence for a direct interaction between benzodiazepines and their receptors, and a subsequent inhibition of seizure activity (or elevation of seizure threshold) is lacking5. Recent reports from our laboratory6 and others7 have demonstrated the feasibility of labelling benzodiazepine receptors in vivo following parental administration of tritiated benzodiazepine. This technique permits one to study the relationship between the anticonvulsant activity of the benzodiazepines in vivo and the number of ‘drug-occupied’ receptors in vitro. We now report that there is an excellent correlation between benzodiazepine receptor occupancy by diazepam and protection against pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures. Furthermore, these results demonstrate that only a small fraction of benzodiazepine receptors need be occupied to produce a complete anticonvulsant effect.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Randall, L. O., Shallek, W., Sternbach, L. H. & Ning, R. Y. in Psychopharmacological Agents Vol. 3 (ed. Gordon, M.) 175–281 (Academic, New York, 1974).
Browne, T. R. & Penry, J. K. Epilepsia 14, 277–288 (1973).
Squires, R. F. & Braestrup, C. Nature 266, 732–734 (1977).
Mohler, H. & Okada, T. Science 198, 849–851 (1977).
Garattini, S., Mussini, E., Marcucci, F. & Guaitani, A. in The Benzodiazepines (eds Garatinni, S. et al.) 75–97 (Raven, New York, 1973).
Williamson, M. J., Paul, S. M. & Skolnick, P. Nature 275, 551–553 (1978).
Chang, R. & Snyder, S. Eur. J. Pharmac. 48, 213–218 (1978).
Skolnick, P., Goodwin, F. K. & Paul, S. M. Archs gen. Psychiat. 36, 78–80 (1979).
Braestrup, C. & Squires, R. Br. J. Psychiat. 133, 249–260 (1978).
Cuatrecases, P. A. Rev. Biochem. 43, 169–214 (1974).
Squires, R. et al. Pharmac. Biochem. Behav. 10, 825–830 (1979).
Skolnick, P. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 1515–1518 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, S., Syapin, P., Paugh, B. et al. Correlation between benzodiazepine receptor occupation and anticonvulsant effects of diazepam. Nature 281, 688–689 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/281688a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/281688a0
This article is cited by
-
Increased Kv1 Channel Expression May Contribute to Decreased sIPSC Frequency Following Chronic Inhibition of NR2B-Containing NMDAR
Neuropsychopharmacology (2012)
-
Evaluation of motor toxicity and anticonvulsant efficacy of barbiturates and benzodiazepines in a bicyclophosphate seizure model in mice
Neurotoxicity Research (2000)
-
Effect of striatum tissue transplantation on behavioral functions and state of benzodiaze-pine receptors in rats with lesioned amygdala
Neurophysiology (1994)
-
The role of the benzodiazepine receptor in mediating long-lasting anticonvulsant effects and the late-appearing reductions in motor activity and exploration
Psychopharmacology (1989)
-
Evidence of strain differences in GABA-benzodiazepine coupling
Psychopharmacology (1987)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.