Abstract
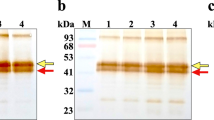
WE have found that human urinary kallikrein converts inactive plasma renin in vitro to an enzyme with renin-like activity. This observation is interesting because renal kallikrein, the presumed precursor of urinary kallikrein1, is thought to be situated in or on cells of the distal convoluted tubule, including the macula densa cells1–3, which are adjacent to the storage site of renin, the juxtaglomerular cells4. Also, human urinary kallikrein is a trypsin-like enzyme of highly restricted specificity5, and although trypsin is capable of activating inactive renin6, we have found that kallikrein is at least 10 times more active. Therefore it seems possible that urinary kallikrein is the in vivo converting enzyme of prorenin and may activate the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone hormonal system, as it participates in sodium and potassium homeostasis4 and in the blood pressure maintenance of a majority of hypertensive patients7.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nustad, K. & Vaaje, K. Br. J. Pharmac. 53, 229–234 (1975).
Scicli, A. G., Carretero, O. A., Hampton, A., Cortes, P. & Oza, N. B. Am. J. Physiol. 203, 533–536, 1976.
Ørstavik, T. B., Nustad, K., Brandtzaeg, P. & Pierce, J. V. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 24, 1037–1039 (1976).
Laragh, J. H. & Sealey, J. E. in Handbook of Physiology: Renal Physiology (eds Orloff, J. & Berliner, R. W.) 831–908 (Waverly, Maryland, 1973).
Webster, M. E. in Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology 25 (ed. Erdos, E. G.) 131–155 (Springer, Berlin, 1970).
Morris, B. J. & Lumbers, E. R. Biochim. biophys. Acta 289, 385–391 (1972).
Case, D. B., Wallace, J. M., Keim, H. J., Weber, M. A., Sealey, J. E. & Laragh, J. H. New Engl. J. Med. 296, 641–646 (1977).
Osmond, D. H., Ross, L. J. & Sciaff, K. D. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmac. 51, 705–708 (1973).
Sealey, J. E., Moon, C., Laragh, J. H. & Alderman, M. Am. J. Med. 61, 731–738 (1976).
Lumbers, E. R. Enzymologia 40, 329–336 (1971).
Atlas, S. A., Sealey, J. E. & Laragh, J. H. Circulation Res. 43 suppl. I, 128–133 (1978).
Atlas, S. A., Laragh, J. H. & Sealey, J. E. Clin. Sci. molec. Med. (in the press).
Wu, F. C. & Laskowski, M. J. Biol. Chem. 235, 1680–1685 (1960).
Harpel, P. C. & Rosenburg, R. D. in Progress in Hemostasis and Thrombosis III (ed. Spaet, T. H.) 145–189 (Grune and Stratton, New York, 1976).
Oza, N. B. & Ryan, J. W. Biochem. J. 171, 285–288 (1978).
Sealey, J. E. & Laragh, J. H. Cardiovasc. Med. 2, 1079–1092 (1977).
Sealey, J. E., White, R. P., Laragh, J. H. & Rubin, A. L. Circulation Res. 41 suppl. II, 17–20 (1977).
Ward, P. E., Gedney, C. D., Dowben, R. M. & Erdös, E. G. Biochem. J. 151, 755–758 (1975).
Carvalho, I. F. & Diniz, C. R. Biochim. biophys. Acta 128, 136–148 (1966).
Fiedler, F., Leysath, G. & Werle, E. Eur. J. Biochem. 36, 1152–1159 (1973).
Sampaio, M. U., Galembeck, F., Paiva, A. C. M. & Prado, E. S. Gen. Pharmac. 7, 167–171 (1976).
Inagami, T., Hirose, S., Murakami, K. & Matoba, T. J. biol. Chem. 252, 7733–7737 (1977).
Soffer, R. L. A. Rev. Biochem. 45, 73–94 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SEALEY, J., ATLAS, S., LARAGH, J. et al. Human urinary kallikrein converts inactive to active renin and is a possible physiological activator of renin. Nature 275, 144–145 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/275144a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/275144a0
This article is cited by
-
Renal kallikrein mRNA localization by in situ hybridization
Kidney International (1989)
-
The cellular physiology of glandular kallikrein
Kidney International (1986)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.