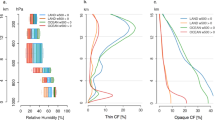
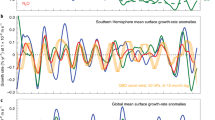
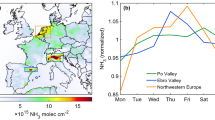
Abstract
CONTINUOUS measurements of N2O at the ground surface by Brice, et al.1 have been interpreted as “evidence for the existence of an appreciable, but unidentified, ground surface sink mechanism”. They based this conclusion on an apparent regular diurnal variation in the concentration of N2O in the air 5 m above the ground, observed during the periods 24–29 July and 4–8 August 1976. “A minimum was nearly always recorded in the early hours of the morning and a maximum was recorded in the late afternoon or evening.”1 In contrast to these results, Cicerone, et al.2 reported N2O measurements made during 25–27 May and 29 August–1 September 1977 which show exactly the opposite behaviour, suggesting instead “that the 1200–1800 h time period sees significantly (at the 1σlevel) lower N2O concentrations than does the period 0000–0600 h LT”. Contrary to both these results, we made continuous measurements of tropospheric N2O for a full year and found no significant diurnal variation in the atmospheric level of N2O. The only diurnal variation we observed was an experimental artefact created by the diurnal variation in the ambient temperature affecting the sensitivity of the instrument.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brice, K. A., Eggleton, A. E. J. & Penkett, S. A. Nature 268, 127–129 (1977).
Cicerone, R. J., Shetter, J. D., Stedman, D. H., Kelley, T. J. & Liu, S. C. J. geophys. Res. 83, 3042–3050 (1978).
Rasmussen, R. A., Krasnec, J. & Pierotti, D. Geophys. Res. Lett. 3, 615–618 (1976).
Pierotti, D. & Rasmussen, R. A. J. Geophys. Res. 82, 5823–5832 (1977).
Junge, C. E. Tellus 26, 477–488 (1974).
Blackmer, A. M. & Bremner, J. M. Geophys. Res. Lett. 3, 739–742 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PIEROTTI, D., RASMUSSEN, R. & CHATFIELD, R. Continuous measurements of nitrous oxide in the troposphere. Nature 274, 574–576 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/274574a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/274574a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.