Abstract
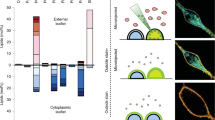
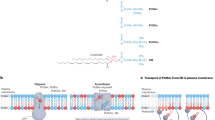
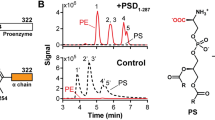
THE asymmetrical distribution of phospholipids in the membrane of the red blood cell1–3 and other membranes4,5 is well documented. How this asymmetry arises in these membranes is an obvious question which remains unanswered. One explanation is that the enzymes that catalyse the last step in the synthesis of the phospholipids are unevenly distributed on both sides of the membrane where biosynthesis occurs. The phospholipids that are produced by these enzymes would be released on to each side of the lipid bilayer and thus account for lipid asymmetry. A necessary corollary would be that this asymmetry of the phospholipids would be preserved in the movement of lipids to other membranes in the cell. Initial reports on the lack of transbilayer movement of phospholipids in artificial membranes6,7 and membranes of animal viruses8 has made an uneven distribution of phospholipid biosynthetic enzymes an attractive hypothesis. Recent reports, however, have documented the transbilayer movement of phospholipids in the red blood cell membrane9–11 and the membrane of Bacillus megaterium12. Although the mechanism for this transbilayer movement of phospholipids has yet to be elucidated, it is no longer necessary to explain lipid asymmetry by the uneven distribution of the phospholipid biosynthetic enzymes on both sides of the membrane. We summarise here our evidence that the enzymes that help to produce phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine are located exclusively on the cytoplasmic surface of the endoplasmic reticulum of rat liver and not on both sides of the membrane.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bretscher, M. S. J. molec. Biol. 71, 523–528 (1972); Science 181, 622–629 (1973).
Zwaal, R. F. A., Roelofsen, B. & Colley, C. M. Biochim. biophys. Acta 300, 159–182 (1973).
Bretscher, M. S. & Raff, M. C. Nature 258, 43–49 (1975).
Rothman, J. E. & Lenard, J. Science 195, 743–753 (1977).
Bergelson, L. D. & Barsukov, L. I. Science 197, 224–230 (1977).
Kornberg, R. D. & McConnell, H. M. Biochemistry 10, 1111–1120 (1971).
Johnson, L. W., Hughes, M. E. & Zilversmit, D. B. Biochim. biophys. Acta 375, 176–185 (1975).
Lenard, J. & Rothman, J. E. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 391–395 (1976).
Renooij, W., Van Golde, L. M. G., Zwaal, R. F. A. & Van Deenen, L. L. M. Eur. J. Biochem. 61, 53–58 (1976).
Bloj, B. & Zilversmit, D. B. Biochemistry 15, 1277–1283 (1976).
Renooij, W. & Van Golde, L. M. G. FEBS Lett 71, 321–324 (1976).
Rothman, J. E. & Kennedy, E. P. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 1821–1825 (1977).
Depierre, J. W. & Dallner, G. Biochim. biophys. Acta 415, 411–472 (1975).
Arion, W. J., Ballas, L. M., Lange, A. J. & Wallin, B. K. J. biol. Chem. 251, 4901–4907 (1976).
Arion, W. J., Lange, A. J. & Ballas, L. M. J. biol. Chem. 251, 6784–6790 (1976).
Nordlie, R. C. & Arion, W. J. Methods Enzym. 9, 619–625 (1966).
Brophy, P. J. & Gower, D. B. Biochim. biophys. Acta 360, 252–259 (1974).
Kanoh, H. & Ohno, K. Eur. J. Biochem. 66, 201–210 (1976).
Choy, P. C. & Vance, D. E. Biochim. biophys. Res. Commun. 72, 714–719 (1976).
Rehbinder, D. & Greenberg, D. M. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 108, 110–115 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VANCE, D., CHOY, P., FARREN, S. et al. Asymmetry of phospholipid biosynthesis. Nature 270, 268–269 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/270268a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/270268a0
This article is cited by
-
Synergistic mechanism between the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria and their crosstalk with other organelles
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Staurosporines decrease ORMDL proteins and enhance sphingomyelin synthesis resulting in depletion of plasmalemmal phosphatidylserine
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Transmembrane movements of lipids
Experientia (1990)
-
Solubilization and partial purification of cholinephosphotransferase in hamster tissues
Lipids (1990)
-
The assembly of lipids into lipoproteins during secretion
Experientia (1990)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.