Abstract
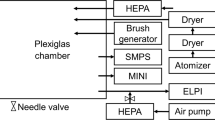
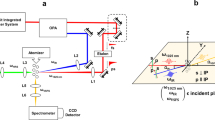
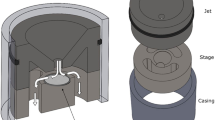
AIRBORNE particulates have a major role in the air pollution problem. They are responsible for acid rain, reduced visibility, and, in certain size ranges, are deposited in the lungs where they can cause various disorders. Considerable effort has been expended in the analysis of these particulates using techniques such as wet chemistry, X-ray fluorescence, infrared spectroscopy and ESCA. Yet there are still great uncertainties as to the chemical form and origin of many of the particulate species. We describe here preliminary studies of the feasibility of characterising particulate pollutants by means of Raman spectroscopy. We believe that this is the first attempt to apply this spectroscopic technique in this area of research. The samples studied included diesel exhaust particles, automobile exhaust particles (unleaded fuel, no catalytic converter) and several ambient air samples. The spectra from these samples were compared with those of polycrystalline graphite and activated carbon which were used as references. Our results indicate that physical structures similar to activated carbon are at least a major species and may be the dominant species in both source-enriched and ambient samples. The implications of this observation could be quite important in terms of atmospheric chemistry, health effects, weather modifications and the effects of aerosols on the albedo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goulding, F. S., Jaklevic, J. M. & Loo, B. W. Report UCID-3767, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley; Report EPA-650/2-75-048, US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, (April 1975).
Tuinstra, F. & Koenig, J. L. J. chem. Phys. 53, 1126 (1970).
Solin, S. A. & Kobliska, R. J. in Proc. 5th Int. Conf. Amorphous iquids Semiconductors, 1251 (Taylor and Francis, London, 1974).
Novakov, T., Chang, S. G. & Harker, A. B. Science 186, 259 (1974); Chang, S. G. & Novakov, T. Atmos. Environment 9, 495 (1975).
Chew, H., McNulty, P. J. & Kerker, M. Phys. Rev. A13, 396 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ROSEN, H., NOVAKOV, T. Raman scattering and the characterisation of atmospheric aerosol particles. Nature 266, 708–710 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/266708a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/266708a0
This article is cited by
-
Characterization of nanocellulose–graphene electric heating membranes prepared via ultrasonic dispersion
Journal of Materials Science (2020)
-
Oxidative Reactivity of Particulate Samples from Different Diesel Combustion Systems and Its Relation to Structural and Spectral Characteristics of Soot
Emission Control Science and Technology (2019)
-
Comparative Raman study of transparent and turbid materials: models and experiments in the remote sensing mode
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2017)
-
Experimental investigation into the oxidation reactivity and nanostructure of particulate matter from diesel engine fuelled with diesel/polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers blends
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Carbonaceous aerosols over Pune and Hyderabad (India) and influence of meteorological factors
Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.